Sparse Matrix and its representations | Set 1 (Using Arrays and Linked Lists)
Last Updated :
12 Sep, 2023
A matrix is a two-dimensional data object made of m rows and n columns, therefore having total m x n values. If most of the elements of the matrix have 0 value, then it is called a sparse matrix.
Why to use Sparse Matrix instead of simple matrix ?
- Storage: There are lesser non-zero elements than zeros and thus lesser memory can be used to store only those elements.
- Computing time: Computing time can be saved by logically designing a data structure traversing only non-zero elements..
Example:
0 0 3 0 4
0 0 5 7 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 2 6 0 0
Representing a sparse matrix by a 2D array leads to wastage of lots of memory as zeroes in the matrix are of no use in most of the cases. So, instead of storing zeroes with non-zero elements, we only store non-zero elements. This means storing non-zero elements with triples- (Row, Column, value).
Sparse Matrix Representations can be done in many ways following are two common representations:
- Array representation
- Linked list representation
Method 1: Using Arrays:
2D array is used to represent a sparse matrix in which there are three rows named as
- Row: Index of row, where non-zero element is located
- Column: Index of column, where non-zero element is located
- Value: Value of the non zero element located at index – (row,column)

Implementation:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int sparseMatrix[4][5] =
{
{0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 }
};
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
size++;
int compactMatrix[3][size];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
compactMatrix[0][k] = i;
compactMatrix[1][k] = j;
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<size; j++)
cout <<" "<< compactMatrix[i][j];
cout <<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
|
C
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int sparseMatrix[4][5] =
{
{0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 }
};
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
size++;
int compactMatrix[3][size];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
compactMatrix[0][k] = i;
compactMatrix[1][k] = j;
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<size; j++)
printf("%d ", compactMatrix[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int sparseMatrix[][]
= {
{0, 0, 3, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 5, 7, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 2, 6, 0, 0}
};
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
size++;
}
}
}
int compactMatrix[][] = new int[3][size];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
compactMatrix[0][k] = i;
compactMatrix[1][k] = j;
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
System.out.printf("%d ", compactMatrix[i][j]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
}
|
Python3
sparseMatrix = [[0,0,3,0,4],[0,0,5,7,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,2,6,0,0]]
size = 0
for i in range(4):
for j in range(5):
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0):
size += 1
rows, cols = (3, size)
compactMatrix = [[0 for i in range(cols)] for j in range(rows)]
k = 0
for i in range(4):
for j in range(5):
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0):
compactMatrix[0][k] = i
compactMatrix[1][k] = j
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j]
k += 1
for i in compactMatrix:
print(i)
|
C#
using System;
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] sparseMatrix
= new int[4, 5] { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 },
{ 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } };
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0)
size++;
int[, ] compactMatrix = new int[3, size];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0) {
compactMatrix[0, k] = i;
compactMatrix[1, k] = j;
compactMatrix[2, k]
= sparseMatrix[i, j];
k++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
Console.Write(" " + compactMatrix[i, j]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
|
Javascript
let sparseMatrix =
[
[0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 ],
[0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 ],
[0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 ]
];
let size = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (let j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
size++;
let compactMatrix = new Array(3);
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++)
compactMatrix[i] = new Array(size);
let k = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (let j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
compactMatrix[0][k] = i;
compactMatrix[1][k] = j;
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
for (let i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for (let j=0; j<size; j++)
process.stdout.write(" " + compactMatrix[i][j]);
console.log()
}
|
Output
0 0 1 1 3 3
2 4 2 3 1 2
3 4 5 7 2 6
Time Complexity: O(NM), where N is the number of rows in the sparse matrix, and M is the number of columns in the sparse matrix.
Auxiliary Space: O(NM), where N is the number of rows in the sparse matrix, and M is the number of columns in the sparse matrix.
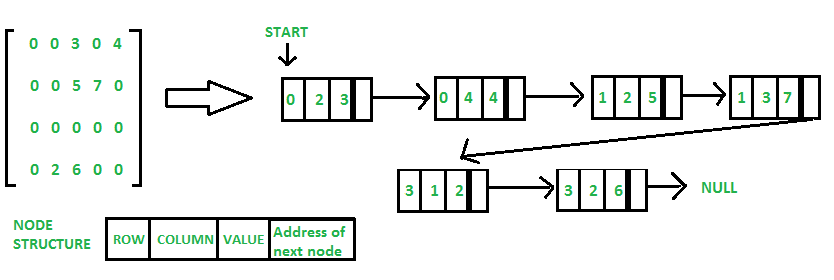
Method 2: Using Linked Lists
In linked list, each node has four fields. These four fields are defined as:
- Row: Index of row, where non-zero element is located
- Column: Index of column, where non-zero element is located
- Value: Value of the non zero element located at index – (row,column)
- Next node: Address of the next node
C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int row;
int col;
int data;
Node *next;
};
void create_new_node(Node **p, int row_index,
int col_index, int x)
{
Node *temp = *p;
Node *r;
if (temp == NULL)
{
temp = new Node();
temp->row = row_index;
temp->col = col_index;
temp->data = x;
temp->next = NULL;
*p = temp;
}
else
{
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
r = new Node();
r->row = row_index;
r->col = col_index;
r->data = x;
r->next = NULL;
temp->next = r;
}
}
void printList(Node *start)
{
Node *ptr = start;
cout << "row_position:";
while (ptr != NULL)
{
cout << ptr->row << " ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "column_position:";
ptr = start;
while (ptr != NULL)
{
cout << ptr->col << " ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Value:";
ptr = start;
while (ptr != NULL)
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int sparseMatrix[4][5] = { { 0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{ 0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 } };
Node *first = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
create_new_node(&first, i, j,
sparseMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
printList(first);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int value;
int row_position;
int column_postion;
struct Node *next;
};
void create_new_node(struct Node** start, int non_zero_element,
int row_index, int column_index )
{
struct Node *temp, *r;
temp = *start;
if (temp == NULL)
{
temp = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
temp->value = non_zero_element;
temp->row_position = row_index;
temp->column_postion = column_index;
temp->next = NULL;
*start = temp;
}
else
{
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
r = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
r->value = non_zero_element;
r->row_position = row_index;
r->column_postion = column_index;
r->next = NULL;
temp->next = r;
}
}
void PrintList(struct Node* start)
{
struct Node *temp, *r, *s;
temp = r = s = start;
printf("row_position: ");
while(temp != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", temp->row_position);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
printf("column_postion: ");
while(r != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", r->column_postion);
r = r->next;
}
printf("\n");
printf("Value: ");
while(s != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", s->value);
s = s->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int sparseMatric[4][5] =
{
{0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 }
};
struct Node* start = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatric[i][j] != 0)
create_new_node(&start, sparseMatric[i][j], i, j);
PrintList(start);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class SparseMatrix {
static Node first = null;
public static class Node {
int row;
int col;
int data;
Node next;
};
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] sparseMatrix = { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 },
{ 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) {
create_new_node(i, j,
sparseMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
printList(first);
}
private static void
create_new_node(int row_index, int col_index, int x)
{
Node temp = first;
Node r;
if (temp == null) {
temp = new Node();
temp.row = row_index;
temp.col = col_index;
temp.data = x;
temp.next = null;
first = temp;
}
else {
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
r = new Node();
r.row = row_index;
r.col = col_index;
r.data = x;
r.next = null;
temp.next = r;
}
}
public static void printList(Node start)
{
Node ptr = start;
System.out.print("row_position:");
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print(ptr.row + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.print("column_position:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print(ptr.col + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.print("Value:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print(ptr.data + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
__slots__ = "row", "col", "data", "next"
def __init__(self, row=0, col=0, data=0, next=None):
self.row = row
self.col = col
self.data = data
self.next = next
class Sparse:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.temp = None
self.size = 0
def __len__(self):
return self.size
def isempty(self):
return self.size == 0
def create_new_node(self, row, col, data):
newNode = Node(row, col, data, None)
if self.isempty():
self.head = newNode
else:
self.temp.next = newNode
self.temp = newNode
self.size += 1
def PrintList(self):
temp = r = s = self.head
print("row_position:", end=" ")
while temp != None:
print(temp.row, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
print()
print("column_postion:", end=" ")
while r != None:
print(r.col, end=" ")
r = r.next
print()
print("Value:", end=" ")
while s != None:
print(s.data, end=" ")
s = s.next
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
s = Sparse()
sparseMatric = [[0, 0, 3, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 5, 7, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 2, 6, 0, 0]]
for i in range(4):
for j in range(5):
if sparseMatric[i][j] != 0:
s.create_new_node(i, j, sparseMatric[i][j])
s.PrintList()
|
C#
using System;
class Program
{
static Node first = null;
public class Node {
public int row;
public int col;
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] sparseMatrix = { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 },
{ 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0) {
create_new_node(i, j,
sparseMatrix[i, j]);
}
}
}
printList(first);
}
private static void
create_new_node(int row_index, int col_index, int x)
{
Node temp = first;
Node r;
if (temp == null) {
temp = new Node();
temp.row = row_index;
temp.col = col_index;
temp.data = x;
temp.next = null;
first = temp;
}
else
{
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
r = new Node();
r.row = row_index;
r.col = col_index;
r.data = x;
r.next = null;
temp.next = r;
}
}
public static void printList(Node start)
{
Node ptr = start;
Console.Write("row_position:");
while (ptr != null) {
Console.Write(ptr.row + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.Write("column_position:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
Console.Write(ptr.col + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.Write("Value:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
Console.Write(ptr.data + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node
{
constructor(row, col, data)
{
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Sparse
{
constructor()
{
this.head = null
this.temp = null
this.size = 0
}
len()
{
return this.size
}
isempty()
{
return this.size == 0
}
create_new_node(row, col, data)
{
let newNode = new Node(row, col, data)
if (this.isempty())
this.head = newNode
else
(this.temp).next = newNode
this.temp = newNode
this.size += 1
}
PrintList()
{
let temp = this.head
let r = this.head
let s = this.head
process.stdout.write("row_position: ")
while (temp != null)
{
process.stdout.write(temp.row + " ")
temp = temp.next
}
console.log()
process.stdout.write("column_postion: ")
while (r != null)
{
process.stdout.write(r.col + " " )
r = r.next
}
console.log()
process.stdout.write("Value: ")
while (s != null)
{
process.stdout.write(s.data + " ")
s = s.next
}
console.log()
}
}
let s = new Sparse()
let sparseMatric = [[0, 0, 3, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 5, 7, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 2, 6, 0, 0]]
for (var i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (var j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatric[i][j] != 0)
{
s.create_new_node(i, j, sparseMatric[i][j])
s.data = sparseMatric[i][j]
}
s.PrintList()
|
Output
row_position:0 0 1 1 3 3
column_position:2 4 2 3 1 2
Value:3 4 5 7 2 6
Time Complexity: O(N*M), where N is the number of rows in the sparse matrix, and M is the number of columns in the sparse matrix.
Auxiliary Space: O(K), where K is the number of non-zero elements in the array.
Other representations:
As a Dictionary where row and column numbers are used as keys and values are matrix entries. This method saves space but sequential access of items is costly.
As a list of list. The idea is to make a list of rows and every item of list contains values. We can keep list items sorted by column numbers.
Sparse Matrix and its representations | Set 2 (Using List of Lists and Dictionary of keys)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...