Sorting array elements with set bits equal to K
Last Updated :
29 Jun, 2022
Given an array of integers and a number 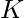 . The task is to sort only those elements of the array whose total set bits are equal to K. Sorting must be done at their relative positions only without affecting any other elements.
. The task is to sort only those elements of the array whose total set bits are equal to K. Sorting must be done at their relative positions only without affecting any other elements.
Examples:
Input : arr[] = {32, 1, 9, 4, 64, 2}, K = 1
Output : 1 2 9 4 32 64
All of the elements except 9 has exactly 1 bit set.
So, all elements except 9 are sorted without affecting
the position of 9 in the input array.
Input : arr[] = {2, 15, 12, 1, 3, 9}, K = 2
Output : 2 15 3 1 9 12
Approach:
- Initialise two empty vectors.
- Traverse the array, from left to right and check the set bits of each element.
- Here, C++ inbuilt function __builtin_popcount() to count setbits.
- In first vector, insert the index of all elements with set bits equal to K.
- In second vector, insert the elements with set bits equal to K.
- Sort the second vector.
- Now, we have the index of all elements with set bit equals to K in sorted order and also all of the elements with set bit as K in sorted order.
- So, insert the elements of the second vector into the array at the indices present in first vector one by one.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void sortWithSetbits(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
vector<int> v1, v2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (__builtin_popcount(arr[i]) == k) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(arr[i]);
}
}
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end());
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
arr[v1[i]] = v2[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 14, 255, 1, 7, 13 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int k = 3;
sortWithSetbits(arr, n, k);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Node
{
static void sortWithSetbits(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
Vector<Integer> v1 = new Vector<>(), v2 = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (Integer.bitCount(arr[i]) == k)
{
v1.add(i);
v2.add(arr[i]);
}
}
Collections.sort(v2);
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
arr[v1.get(i)] = v2.get(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {14, 255, 1, 7, 13};
int n = arr.length;
int k = 3;
sortWithSetbits(arr, n, k);
}
}
|
Python3
def sortWithSetbits(arr, n, k):
v1 = []
v2 = []
for i in range(0, n, 1):
if (bin(arr[i]).count('1') == k):
v1.append(i)
v2.append(arr[i])
v2.sort(reverse = False)
for i in range(0, len(v1), 1):
arr[v1[i]] = v2[i]
for i in range(0, n, 1):
print(arr[i], end = " ")
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [14, 255, 1, 7, 13]
n = len(arr)
k = 3
sortWithSetbits(arr, n, k)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node
{
static void sortWithSetbits(int []arr, int n, int k)
{
List<int> v1 = new List<int>();
List<int> v2 = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (bitCount(arr[i]) == k)
{
v1.Add(i);
v2.Add(arr[i]);
}
}
v2.Sort();
for (int i = 0; i < v1.Count; i++)
{
arr[v1[i]] = v2[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
static int bitCount(long x)
{
int setBits = 0;
while (x != 0)
{
x = x & (x - 1);
setBits++;
}
return setBits;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = {14, 255, 1, 7, 13};
int n = arr.Length;
int k = 3;
sortWithSetbits(arr, n, k);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function bitCount(x)
{
var setBits = 0;
while (x != 0)
{
x = x & (x - 1);
setBits++;
}
return setBits;
}
function sortWithSetbits(arr, n, k)
{
var v1 = [], v2 = [];
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (bitCount(arr[i]) == k) {
v1.push(i);
v2.push(arr[i]);
}
}
v2.sort((a,b)=> a-b);
for (var i = 0; i < v1.length; i++)
arr[v1[i]] = v2[i];
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write( arr[i] + " ");
}
var arr = [14, 255, 1, 7, 13 ];
var n = arr.length;
var k = 3;
sortWithSetbits(arr, n, k);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(n*log(n))
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...