SortedSet Interface in Java with Examples
Last Updated :
11 Mar, 2024
The SortedSet interface present in java.util package extends the Set interface present in the collection framework. It is an interface that implements the mathematical set. This interface contains the methods inherited from the Set interface and adds a feature that stores all the elements in this interface to be stored in a sorted manner.
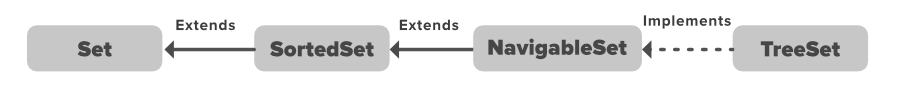
In the above image, the navigable set extends the sorted set interface. Since a set doesn’t retain the insertion order, the navigable set interface provides the implementation to navigate through the Set. The class which implements the navigable set is a TreeSet which is an implementation of a self-balancing tree. Therefore, this interface provides us with a way to navigate through this tree.
Declaration: The SortedSet interface is declared as:
public interface SortedSet extends Set
Example of a Sorted Set:
import java.util.*;
class SortedSetExample{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
ts.add("India");
ts.add("Australia");
ts.add("South Africa");
ts.add("India");
System.out.println(ts);
ts.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Set after removing "
+ "Australia:" + ts);
System.out.println("Iterating over set:");
Iterator<String> i = ts.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
|
Output:
[Australia, India, South Africa]
Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa]
Iterating over set:
India
South Africa
Note: All the elements of a SortedSet must implement the Comparable interface (or be accepted by the specified Comparator) and all such elements must be mutually comparable. Mutually Comparable simply means that two objects accept each other as the argument to their compareTo method.
Creating SortedSet Objects
Since SortedSet is an interface, objects cannot be created of the type SortedSet. We always need a class which extends this list in order to create an object. And also, after the introduction of Generics in Java 1.5, it is possible to restrict the type of object that can be stored in the SortedSet. This type-safe set can be defined as:
// Obj is the type of the object to be stored in SortedSet
SortedSet<Obj> set = new TreeSet<Obj> ();
Performing Various Operations on SortedSet
Since SortedSet is an interface, it can be used only with a class which implements this interface. TreeSet is the class which implements the SortedSet interface. Now, let’s see how to perform a few frequently used operations on the TreeSet.
1. Adding Elements: In order to add an element to the SortedSet, we can use the add() method. However, the insertion order is not retained in the TreeSet. Internally, for every element, the values are compared and sorted in the ascending order. We need to keep a note that duplicate elements are not allowed and all the duplicate elements are ignored. And also, Null values are not accepted by the SortedSet.
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("C");
ts.add("A");
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
|
2. Accessing the Elements: After adding the elements, if we wish to access the elements, we can use inbuilt methods like contains(), first(), last(), etc.
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("C");
ts.add("A");
System.out.println("Sorted Set is " + ts);
String check = "D";
System.out.println("Contains " + check
+ " " + ts.contains(check));
System.out.println("First Value " + ts.first());
System.out.println("Last Value " + ts.last());
}
}
|
Output:
Sorted Set is [A, B, C]
Contains D false
First Value A
Last Value C
3. Removing the Values: The values can be removed from the SortedSet using the remove() method.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("C");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("D");
ts.add("E");
System.out.println("Initial TreeSet " + ts);
ts.remove("B");
System.out.println("After removing element " + ts);
}
}
|
Output:
Initial TreeSet [A, B, C, D, E]
After removing element [A, C, D, E]
4. Iterating through the SortedSet: There are various ways to iterate through the SortedSet. The most famous one is to use the enhanced for loop.
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
ts.add("C");
ts.add("D");
ts.add("E");
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("Z");
for (String value : ts)
System.out.print(value
+ ", ");
System.out.println();
}
}
|
Output:
A, B, C, D, E, Z,
The class which implements the SortedSet interface is TreeSet.
TreeSet: TreeSet class which is implemented in the collections framework is an implementation of the SortedSet Interface and SortedSet extends Set Interface. It behaves like a simple set with the exception that it stores elements in a sorted format. TreeSet uses a tree data structure for storage. Objects are stored in sorted, ascending order. But we can iterate in descending order using method TreeSet.descendingIterator(). Let’s see how to create a sortedset object using this class.
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
ts.add("India");
ts.add("Australia");
ts.add("South Africa");
ts.add("India");
System.out.println(ts);
ts.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Set after removing "
+ "Australia:" + ts);
System.out.println("Iterating over set:");
Iterator<String> i = ts.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
|
Output:
[Australia, India, South Africa]
Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa]
Iterating over set:
India
South Africa
Methods of SortedSet Interface
The following are the methods present in the SortedSet interface. Here, the “*” represents that the methods are part of the Set interface.
| Method |
Description |
| *add(element) |
This method is used to add a specific element to the set. The function adds the element only if the specified element is not already present in the set else the function returns False if the element is already present in the Set. |
| *addAll(collection) |
This method is used to append all of the elements from the mentioned collection to the existing set. The elements are added randomly without following any specific order. |
| *clear() |
This method is used to remove all the elements from the set but not delete the set. The reference for the set still exists. |
| comparator() |
This method returns the comparator used to order the elements in this set, or null if this set uses the natural ordering of its elements. |
| *contains(element) |
This method is used to check whether a specific element is present in the Set or not. |
| *containsAll(collection) |
This method is used to check whether the set contains all the elements present in the given collection or not. This method returns true if the set contains all the elements and returns false if any of the elements are missing. |
| first() |
This method returns the first(lowest) element present in this set. |
| hashCode() |
This method is used to get the hashCode value for this instance of the Set. It returns an integer value which is the hashCode value for this instance of the Set. |
| headSet(element) |
This method returns the elements which are less than the element that are present in the sorted set. |
| *isEmpty() |
This method is used to check if a SortedSet is empty or not. |
| last() |
This method returns the last(highest) element present in the set. |
| *remove(element) |
This method is used to remove the given element from the set. This method returns True if the specified element is present in the Set otherwise it returns False. |
| *removeAll(collection) |
This method is used to remove all the elements from the collection which are present in the set. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
| *retainAll(collection) |
This method is used to retain all the elements from the set which are mentioned in the given collection. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
| *size() |
This method is used to get the size of the set. This returns an integer value which signifies the number of elements. |
| subSet(element1, element2) |
This method returns a sorted subset from the set containing the elements between element1 and element2. |
| tailSet(element) |
This method returns the elements which are greater than or equal to the element that are present in the sorted set. |
| *toArray() |
This method is used to form an array of the same elements as that of the Set. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...