Sorted order printing of a given array that represents a BST
Last Updated :
28 Nov, 2022
Given an array that stores a complete Binary Search Tree, write a function that efficiently prints the given array in ascending order.
For example, given an array [4, 2, 5, 1, 3], the function should print 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
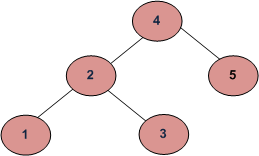
Solution:
Inorder traversal of BST prints it in ascending order. The only trick is to modify recursion termination condition in standard Inorder Tree Traversal.
Implementation:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void printSorted(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
if(start > end)
return;
printSorted(arr, start*2 + 1, end);
cout << arr[start] << " ";
printSorted(arr, start*2 + 2, end);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {4, 2, 5, 1, 3};
int arr_size = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
printSorted(arr, 0, arr_size-1);
getchar();
return 0;
}
|
C
#include<stdio.h>
void printSorted(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
if(start > end)
return;
printSorted(arr, start*2 + 1, end);
printf("%d ", arr[start]);
printSorted(arr, start*2 + 2, end);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {4, 2, 5, 1, 3};
int arr_size = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
printSorted(arr, 0, arr_size-1);
getchar();
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG{
private static void printSorted(int[] arr, int start,
int end) {
if(start > end)
return;
printSorted(arr, start*2 + 1, end);
System.out.print(arr[start] + " ");
printSorted(arr, start*2 + 2, end);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {4, 2, 5, 1, 3};
printSorted(arr, 0, arr.length-1);
}
}
|
Python3
def printSorted(arr, start, end):
if start > end:
return
printSorted(arr, start * 2 + 1, end)
print(arr[start], end = " ")
printSorted(arr, start * 2 + 2, end)
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [4, 2, 5, 1, 3]
arr_size = len(arr)
printSorted(arr, 0, arr_size - 1)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static private void printSorted(int []arr,
int start,
int end)
{
if(start > end)
return;
printSorted(arr, start * 2 + 1, end);
Console.Write(arr[start] + " ");
printSorted(arr, start * 2 + 2, end);
}
static public void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr= {4, 2, 5, 1, 3};
printSorted(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function printSorted($arr, $start, $end)
{
if($start > $end)
return;
printSorted($arr, $start * 2 + 1, $end);
echo($arr[$start] . " ");
printSorted($arr, $start * 2 + 2, $end);
}
$arr = array(4, 2, 5, 1, 3);
printSorted($arr, 0, sizeof($arr) - 1);
|
Javascript
<script>
function printSorted(arr, start, end)
{
if (start > end)
return;
printSorted(arr, start * 2 + 1, end);
document.write(arr[start] + " ");
printSorted(arr, start * 2 + 2, end);
}
var arr = [4, 2, 5, 1, 3];
printSorted(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(n), As we are visiting every element just once.
Auxiliary Space: O(h), Here h is the height of the tree and the extra space is used in the recursion call stack.
Please write comments if you find the above solution incorrect, or find better ways to solve the same problem.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...