Sort an Array of Points by their distance from a reference Point
Last Updated :
09 Sep, 2022
Given an array arr[] containing N points and a reference point P, the task is to sort these points according to their distance from the given point P.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {{5, 0}, {4, 0}, {3, 0}, {2, 0}, {1, 0}}, P = (0, 0)
Output: (1, 0) (2, 0) (3, 0) (4, 0) (5, 0)
Explanation:
Distance between (0, 0) and (1, 0) = 1
Distance between (0, 0) and (2, 0) = 2
Distance between (0, 0) and (3, 0) = 3
Distance between (0, 0) and (4, 0) = 4
Distance between (0, 0) and (5, 0) = 5
Hence, the sorted array of points will be: {(1, 0) (2, 0) (3, 0) (4, 0) (5, 0)}
Input: arr[] = {{5, 0}, {0, 4}, {0, 3}, {2, 0}, {1, 0}}, P = (0, 0)
Output: (1, 0) (2, 0) (0, 3) (0, 4) (5, 0)
Explanation:
Distance between (0, 0) and (1, 0) = 1
Distance between (0, 0) and (2, 0) = 2
Distance between (0, 0) and (0, 3) = 3
Distance between (0, 0) and (0, 4) = 4
Distance between (0, 0) and (5, 0) = 5
Hence, the sorted array of points will be: {(1, 0) (2, 0) (0, 3) (0, 4) (5, 0)}
Approach: The idea is to store each element at its distance from the given point P in a pair and then sort all the elements of the vector according to the distance stored.
- For each of the given points:
Distance = 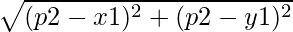
- Append the distance in an array
- Sort the array of distance and print the points based on the sorted distance.
- Time Complexity: As in the above approach, there is sorting of an array of length N, which takes O(N*logN) time in the worst case. Hence, the Time Complexity will be O(N*log N).
- Auxiliary Space Complexity: As in the above approach, there is extra space used to store the distance and the points as pairs. Hence, the auxiliary space complexity will be O(N).
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool compare(pair<int, pair<int, int> > a,
pair<int, pair<int, int> > b)
{
if (a.first == b.first) {
return 0;
}
else {
return (a.first < b.first) ? -1 : 1;
}
}
void sortArr(vector<vector<int> > arr, int n, vector<int> p)
{
vector<pair<int, pair<int, int> > > vp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int dist = pow((p[0] - arr[i][0]), 2)
+ pow((p[1] - arr[i][1]), 2);
vp.push_back(make_pair(
dist, make_pair(arr[i][0], arr[i][1])));
}
sort(vp.begin(), vp.end(), compare);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << "(" << vp[i].second.first << ", "
<< vp[i].second.second << ") " << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > arr
= { { 5, 5 }, { 6, 6 }, { 1, 0 },
{ 2, 0 }, { 3, 1 }, { 1, -2 } };
int n = 6;
vector<int> p = { 0, 0 };
sortArr(arr, n, p);
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static void sortArr(int[][] arr, int n, int[] p)
{
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> vp = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int dist = (int)Math.pow((p[0] - arr[i][0]), 2)
+ (int)Math.pow((p[1] - arr[i][1]), 2);
ArrayList<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<Integer> ();
l1.add(dist);
l1.add(arr[i][0]);
l1.add(arr[i][1]);
vp.add(l1);
}
Collections.sort(vp, new Comparator<ArrayList<Integer>> () {
@Override
public int compare(ArrayList<Integer> a, ArrayList<Integer> b) {
return a.get(0).compareTo(b.get(0));
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print("(" + vp.get(i).get(1) + ", "
+ vp.get(i).get(2) +") ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] arr = { { 5, 5 }, { 6, 6 }, { 1, 0 },
{ 2, 0 }, { 3, 1 }, { 1, -2 } };
int n = 6;
int[] p = { 0, 0 };
sortArr(arr, n, p);
}
}
|
Python3
import functools
def sortFunction(a, b) :
if (a[0] == b[0]):
return 0;
else :
if (a[0] < b[0]):
return -1
return 1;
def sortArr(arr, n, p):
vp = [0 for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
dist = pow((p[0] - arr[i][0]), 2) + pow((p[1] - arr[i][1]), 2);
vp[i] = [dist, [arr[i][0], arr[i][1]]];
vp.sort(key=functools.cmp_to_key(sortFunction));
for i in range(n):
print("(", vp[i][1][0], ", ", vp[i][1][1], ") ", sep = "", end = " ");
arr = [[ 5, 5 ], [ 6, 6 ], [ 1, 0], [ 2, 0 ], [ 3, 1 ], [ 1, -2 ]];
n = 6;
p = [ 0, 0 ];
sortArr(arr, n, p);
|
C#
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static void sortArr(int[, ] arr, int n, int[] p)
{
List<List<int>> vp = new List<List<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int dist = (int)Math.Pow((p[0] - arr[i, 0]), 2)
+ (int)Math.Pow((p[1] - arr[i, 1]), 2);
List<int> l1 = new List<int>();
l1.Add(dist);
l1.Add(arr[i, 0]);
l1.Add(arr[i, 1]);
vp.Add(l1);
}
vp = vp.OrderBy(ele => ele[0]).ToList();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Console.Write("(" + vp[i][1] + ", "
+ vp[i][2] +") ");
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] arr = new [,] { { 5, 5 }, { 6, 6 }, { 1, 0 },
{ 2, 0 }, { 3, 1 }, { 1, -2 } };
int n = 6;
int[] p = { 0, 0 };
sortArr(arr, n, p);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function sortFunction(a, b) {
if (a[0] === b[0]) {
return 0;
}
else {
return (a[0] < b[0]) ? -1 : 1;
}
}
function sortArr(arr, n, p)
{
var vp = new Array(n);
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var dist = Math.pow((p[0] - arr[i][0]), 2)
+ Math.pow((p[1] - arr[i][1]), 2);
vp[i] = [dist, [arr[i][0], arr[i][1]]];
}
vp.sort(sortFunction);
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
document.write("(" + vp[i][1][0] + ", " + vp[i][1][1] + ") ");
}
}
var arr = [[ 5, 5 ], [ 6, 6 ], [ 1, 0], [ 2, 0 ], [ 3, 1 ], [ 1, -2 ]];
var n = 6;
var p = [ 0, 0 ];
sortArr(arr, n, p);
</script>
|
Output:
(1, 0) (2, 0) (1, -2) (3, 1) (5, 5) (6, 6)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...