Six Sigma in Software Engineering
Last Updated :
30 Aug, 2019
Six Sigma is the process of producing high and improved quality output. This can be done in two phases – identification and elimination. The cause of defects is identified and appropriate elimination is done which reduces variation in whole processes. A six sigma method is one in which 99.99966% of all the products to be produced have the same features and are of free from defects.
Characteristics of Six Sigma:
The Characteristics of Six Sigma are as follows:
- Statistical Quality Control:
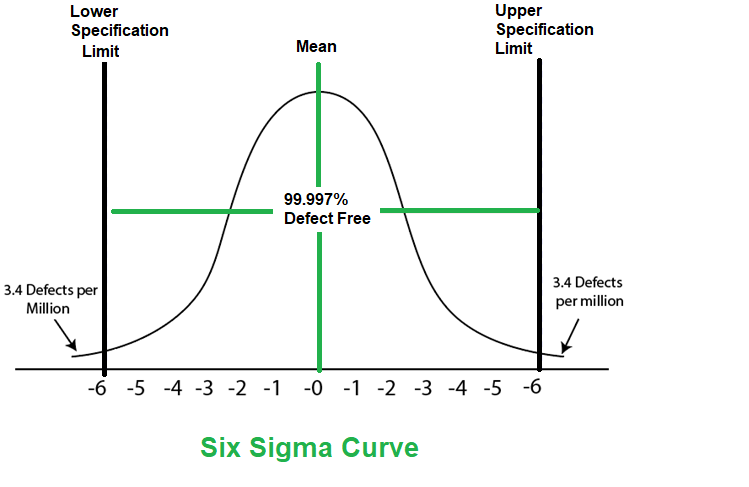
Six Sigma is derived from the Greek Letter ? which denote Standard Deviation in statistics. Standard Deviation is used for measuring the quality of output.
- Methodical Approach:
The Six Sigma is a systematic approach of application in DMAIC and DMADV which can be used to improve the quality of production. DMAIC means for Design-Measure- Analyze-Improve-Control. While DMADV stands for Design-Measure-Analyze-Design-Verify.
- Fact and Data-Based Approach:
The statistical and methodical method shows the scientific basis of the technique.

- Project and Objective-Based Focus:
The Six Sigma process is implemented to focus on the requirements and conditions.
- Customer Focus:
The customer focus is fundamental to the Six Sigma approach. The quality improvement and control standards are based on specific customer requirements.
- Teamwork Approach to Quality Management:
The Six Sigma process requires organizations to get organized for improving quality.
Six Sigma Methodologies:
Two methodologies used in the Six Sigma projects are DMAIC and DMADV.
- DMAIC is used to enhance an existing business process. The DMAIC project methodology has five phases:
- Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Improve
- Control
- DMADV is used to create new product designs or process designs. The DMADV project methodology also has five phases:
- Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Design
- Verify
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...