Similarities between TCP/IP model and OSI model
Last Updated :
24 Apr, 2023
Pre-Requisite: Layers of OSI Model, TCP/IP Model
OSI Model or Open Systems Interconnection is an architecture of 7 layers in which each layer has its work to perform whereas TCP/IP is a concise version of the OSI Model. TCP/IP Model consists of 4 layers rather than the 7 layers of the OSI Model. There are so many similarities between the TCP/IP model and the OSI model of the Networking subject. But here we are going to discuss a few of the points related to TCP/IP as follows.
OSI Model
Open systems interconnection (OSI model) consists of 7 layers and every layer has a certain function to it. Here are the layers from which the data is flowed before reaching its destination starting from the bottom layer and ending at the top layer when the data is transferred from one location to another location in the globe with the help of networking. These are the layers that are present in the OSI model of networking.
Layers of OSI Model
- Physical layer
- Data Link layer
- Network layer
- Transport layer
- Session layer
- Presentation layer
- Application layer
OSI Model
1. Physical Layer: Physical layer has the work of establishing the actual physical connection among the devices. It is the bottom layer of the OSI Model.
2. Data Link Layer: The Data Link Layer takes responsibility for the hop-to-hop or node-to-node delivery of the message.
3. Network Layer: The Network Layer has the characteristics of transmission of data from one host to another in different networks.
4. Transport Layer: The transport layer takes responsibility for Message Delivery across the points on the way to the destination.
5. Session Layer: The Session Layer has the responsibility of connection establishment, session management, and termination of the process.
6. Presentation Layer: The Presentation Layer has the work of encrypting and decrypting the data and making it accessible to the Application Layer.
7. Application Layer: The Application Layer is the topmost layer of the OSI Model where the User interacts with the system.
TCP/IP Model
The transmission control protocol is shortly called TCP/IP model. Which consists of 4 layers and every layer has a certain function to it. Here are the layers from which the data is flowed before reaching its destination starting from the bottom layer and ending at the top layer when the data is transferred from one location to another location in the globe with the help of networking. These are the layers that are present in the TCP/IP model.
Layers of TCP/IP Model
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Internet Layer
- Network Access Layer
1. Network Access Layer: The Network Access Layer comprises of Physical and Data Link Layer of the OSI Model. It has the work of transmitting the data among two devices within the same network.
2. Internet Layer: The Internet layer is similar to the Network Layer of the OSI Model. It helps in the movement of data packets from the destination to the source.
3. Transport Layer: The Transport Layer in TCP/IP Model is similar to the Transport Layer of the OSI Model. It works for reliability and error-free message delivery.
4. Application Layer: The Application Layer is the topmost layer of the Application Layer. It forms from the combination of the Application, Presentation, and Session Layer of the OSI Model. It works in providing access to the networks.

OSI and TCP/IP Model
Similarities Between TCP/IP Model and OSI Model
| Similarities |
TCP/IP and OSI Model |
| Model |
Both TCP/IP are logical models. |
| Structure |
Both are arranged layered wise which is also called an architectural model. These models have a stack of protocols it means the protocol is arranged in every layer. Both models have some set of protocols. |
| Networking |
Both TCP/IP defines standards for networking. |
| Framework |
Both TCP/IPs provide a framework for creating and implementing networking standards and devices. |
| Communication process |
Both TCP/IPs simplify and divide the network communication process into making their layers. |
| Similar components |
In Both TCP/IP models manufacturer allows making sets of devices and network components that can co-exist and work with the devices and components that are made by the other manufacturers. |
| functionality |
In both TCP/IP models, a single layer defines a particular functionality and set standards for that functionality only. |
| Troubleshooting |
Both the TCP/IP models simplify their troubleshooting process by dividing the layer’s complex functions into simpler components of the layer. |
| Ethernet standards |
Instead of defining the already defined standards and protocols in both the TCP/IP models. For example, the Ethernet standards were already defined by IEEE before proceeding to create these models. So instead of defining them again in both the models of IEEE Ethernet standards. |
Conclusion
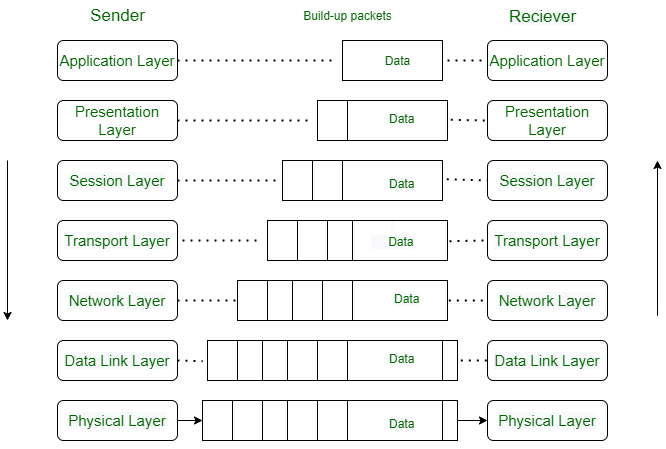
The TCP/IP model and the OSI model are two different conceptual frameworks used to describe how communications protocols work. One of the main similarities between the two models is that they both describe how information is transmitted between two devices across a network. Both models define a set of layers, each of which performs a specific set of functions to enable the transmission of data. Another similarity between the two models is that they both use the concept of encapsulation, in which data is packaged into a series of headers and trailers that contain information about the data being transmitted and how it should be handled by the network.
Despite these similarities, there are some key differences between the two models. One of the main differences is that the TCP/IP model is primarily used in the Internet and other networks that use the Internet Protocol (IP), while the OSI model is a more general framework that can be used to describe any network protocol. Additionally, the TCP/IP model has only four layers, while the OSI model has seven.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...