Shortest distance to every other character from given character
Last Updated :
30 Sep, 2022
Given a string S and a character X where ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com X\varepsilon S[i]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-14adebd94bb71f5deb98d9570ac3a560_l3.png) , for some
, for some 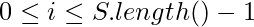 . The task is to return an array of distances representing the shortest distance from the character X to every other character in the string.
. The task is to return an array of distances representing the shortest distance from the character X to every other character in the string.
Examples:
Input: S = “geeksforgeeks”, X = ‘e’
Output: [1, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 2]
for S[0] = ‘g’ nearest ‘e’ is at distance = 1 i.e. S[1] = ‘e’.
similarly, for S[1] = ‘e’, distance = 0.
for S[6] = ‘o’, distance = 3 since we have S[9] = ‘e’, and so on.
Input: S = “helloworld”, X = ‘o’
Output: [4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3]
Approach 1: For each character at index i in S[], let us try to find the distance to the next character X going left to right, and from right to left. The answer will be the minimum of these two values.
- When going from left to right, we remember the index of the last character X we’ve seen. Then the answer is i – prev.
- When going from right to left, the answer is prev – i.
- We take the minimum of these two answers to create our final distance array.
- Finally, print the array.
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void shortestDistance(string S, char X)
{
int prev = INT_MAX;
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++)
{
if (S[i] == X)
prev = i;
if (prev == INT_MAX)
ans.push_back(INT_MAX);
else
ans.push_back(i - prev);
}
prev = INT_MAX;
for (int i = S.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (S[i] == X)
prev = i;
if (prev != INT_MAX)
ans[i] = min(ans[i], prev - i);
}
for (auto val: ans)
cout << val << ' ';
}
int main()
{
string S = "helloworld";
char X = 'o';
shortestDistance(S, X);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static void shortestDistance(String S, char X)
{
int prev = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Vector<Integer> ans = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++)
{
if (S.charAt(i) == X)
prev = i;
if (prev == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
ans.add(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
else
ans.add(i - prev);
}
prev = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = S.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (S.charAt(i) == X)
prev = i;
if (prev != Integer.MAX_VALUE)
ans.set(i, Math.min(ans.get(i), prev - i));
}
for (Integer val: ans)
System.out.print(val+" ");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String S = "geeksforgeeks";
char X = 'g';
shortestDistance(S, X);
}
}
|
Python3
def shortestDistance(S, X):
inf = float('inf')
prev = inf
ans = []
for i,j in enumerate(S):
if S[i] == X:
prev = i
if (prev == inf) :
ans.append(inf)
else :
ans.append(i - prev)
prev = inf
for i in range(len(S) - 1, -1, -1):
if S[i] == X:
prev = i
if (X != inf):
ans[i] = min(ans[i], prev - i)
return ans
S = "geeksforgeeks"
X = "g"
print(shortestDistance(S, X))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public static void shortestDistance(String S, char X){
int prev = int.MaxValue;
List<int> ans = new List<int>();
for (int i=0; i<S.Length; i++)
{
if (S[i] == X)
prev = i;
if (prev == int.MaxValue)
ans.Add(int.MaxValue);
else
ans.Add(i-prev);
}
prev = int.MaxValue;
for (int i=S.Length-1; i>=0; i--)
{
if (S[i] == X)
prev = i;
if (prev != int.MaxValue)
ans[i] = Math.Min(ans[i], prev-i);
}
foreach (var i in ans)
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String S = "geeksforgeeks";
char X = 'g';
shortestDistance(S, X);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function shortestDistance(S, X)
{
let prev = Number.MAX_VALUE;
let ans = [];
for (let i = 0; i < S.length; i++)
{
if (S[i] == X)
prev = i;
if (prev == Number.MAX_VALUE)
ans.push(Number.MAX_VALUE);
else
ans.push(i - prev);
}
prev = Number.MAX_VALUE;
for (let i = S.length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (S[i] == X)
prev = i;
if (prev != Number.MAX_VALUE)
ans[i] = Math.min(ans[i], prev - i);
}
for (let val of ans)
document.write(val + ' ');
}
let S = "helloworld";
let X = 'o';
shortestDistance(S, X);
</script>
|
Output4 3 2 1 0 1 0 1 2 3
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(|S|),
- Auxiliary Space: O(|S|) because extra space for vector ans is being used
Approach 2: Create a list holding the occurrence of the character and then create two pointers pointing two immediate locations in this list, now iterate over the string to find the difference between these two pointers and insert the minimum in the result list. If pointer 2 is nearer to the current character, move the pointers one step ahead.
- Create a list holding positions of the required character in the string and an empty list to hold the result array.
- Create two pointers to the list p1=0 and p2=0 if list length is 1 else p2=1
- Iterate over the string and compare the values at these pointers (v1=p1->value & v2=p2->value) with the current index(i).
- If i <= v1, then push v1-i in the result list.
- Else if i <= v2
- if i is nearer to v1, then push i-v1 in the result list
- Else push v2-i in the result list and move pointer one step forward if possible
- Else push i-v1 into the result list
- Return result list
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> shortestToChar(string s, char c)
{
vector<int> list;
vector<int> res;
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (s[i] == c) {
list.push_back(i);
}
}
int p1, p2, v1, v2;
int l = list.size() - 1;
p1 = 0;
p2 = l > 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
v1 = list[p1];
v2 = list[p2];
if (i <= v1) {
res.push_back(v1 - i);
}
else if (i <= v2) {
if (i - v1 < v2 - i) {
res.push_back(i - v1);
}
else {
res.push_back(v2 - i);
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2 < l ? (p2 + 1) : p2;
}
}
else {
res.push_back(i - v2);
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
string s = "geeksforgeeks";
char c = 'e';
vector<int> res = shortestToChar(s, c);
for (auto i : res)
cout << i << " ";
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
void shortestToChar(char s[], char c, int* res)
{
int list[MAX_SIZE];
int len = 0;
int l = 0;
while (s[len] != '\0') {
if (s[len] == c) {
list[l] = len;
l++;
}
len++;
}
int p1, p2, v1, v2;
l = l - 1;
p1 = 0;
p2 = l > 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
v1 = list[p1];
v2 = list[p2];
if (i <= v1) {
res[i] = (v1 - i);
}
else if (i <= v2) {
if (i - v1 < v2 - i) {
res[i] = (i - v1);
}
else {
res[i] = (v2 - i);
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2 < l ? (p2 + 1) : p2;
}
}
else {
res[i] = (i - v2);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char s[] = "geeksforgeeks";
char c = 'e';
int res[MAX_SIZE];
shortestToChar(s, c, res);
int i = 0;
while (s[i] != '\0')
printf("%d ", res[i++]);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static ArrayList<Integer> shortestToChar(String s,
char c)
{
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == c) {
list.add(i);
}
}
int p1, p2, v1, v2;
int l = list.size() - 1;
p1 = 0;
p2 = l > 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
v1 = list.get(p1);
v2 = list.get(p2);
if (i <= v1) {
res.add(v1 - i);
}
else if (i <= v2) {
if (i - v1 < v2 - i) {
res.add(i - v1);
}
else {
res.add(v2 - i);
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2 < l ? (p2 + 1) : p2;
}
}
else {
res.add(i - v2);
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s = "geeksforgeeks";
char c = 'e';
ArrayList<Integer> res = shortestToChar(s, c);
for (Integer i : res)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static List<int> shortestToChar(string s, char c)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>();
List<int> res = new List<int>();
int len = s.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (s[i] == c) {
list.Add(i);
}
}
int p1, p2, v1, v2;
int l = list.Count - 1;
p1 = 0;
p2 = l > 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
v1 = list[p1];
v2 = list[p2];
if (i <= v1) {
res.Add(v1 - i);
}
else if (i <= v2) {
if (i - v1 < v2 - i) {
res.Add(i - v1);
}
else {
res.Add(v2 - i);
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2 < l ? (p2 + 1) : p2;
}
}
else {
res.Add(i - v2);
}
}
return res;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s = "geeksforgeeks";
char c = 'e';
List<int> res = shortestToChar(s, c);
foreach(var i in res) Console.Write(i + " ");
}
}
|
Python3
def shortestToChar(s,c):
list = []
res = []
Len = len(s)
for i in range(Len):
if (s[i] == c):
list.append(i)
l = len(list) - 1
p1 = 0
p2 = 1 if l > 0 else 0
for i in range(Len):
v1 = list[p1]
v2 = list[p2]
if (i <= v1):
res.append(v1 - i)
elif (i <= v2):
if (i - v1 < v2 - i):
res.append(i - v1)
else:
res.append(v2 - i)
p1 = p2
p2 = (p2 + 1) if (p2<l) else p2
else:
res.append(i - v2)
return res
s = "geeksforgeeks"
c = 'e'
res = shortestToChar(s, c)
for i in res:
print(i,end = " ")
|
Javascript
<script>
function shortestToChar(s,c)
{
let list = [];
let res = [];
let len = s.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (s[i] == c) {
list.push(i);
}
}
let p1, p2, v1, v2;
let l = list.length - 1;
p1 = 0;
p2 = l > 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
v1 = list[p1];
v2 = list[p2];
if (i <= v1) {
res.push(v1 - i);
}
else if (i <= v2) {
if (i - v1 < v2 - i) {
res.push(i - v1);
}
else {
res.push(v2 - i);
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2 < l ? (p2 + 1) : p2;
}
}
else {
res.push(i - v2);
}
}
return res;
}
let s = "geeksforgeeks";
let c = 'e';
let res = shortestToChar(s, c);
for (let i of res)
document.write(i , end = " ");
</script>
|
Output1 0 0 1 2 3 3 2 1 0 0 1 2
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(n),
- Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...