ShellSort
Last Updated :
11 Mar, 2024
Shell sort is mainly a variation of Insertion Sort. In insertion sort, we move elements only one position ahead. When an element has to be moved far ahead, many movements are involved. The idea of ShellSort is to allow the exchange of far items. In Shell sort, we make the array h-sorted for a large value of h. We keep reducing the value of h until it becomes 1. An array is said to be h-sorted if all sublists of every h’th element are sorted.
Algorithm:
Step 1 − Start
Step 2 − Initialize the value of gap size, say h.
Step 3 − Divide the list into smaller sub-part. Each must have equal intervals to h.
Step 4 − Sort these sub-lists using insertion sort.
Step 5 – Repeat this step 2 until the list is sorted.
Step 6 – Print a sorted list.
Step 7 – Stop.
Following is the implementation of ShellSort.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int shellSort(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int gap = n/2; gap > 0; gap /= 2)
{
for (int i = gap; i < n; i += 1)
{
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap)
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
int main()
{
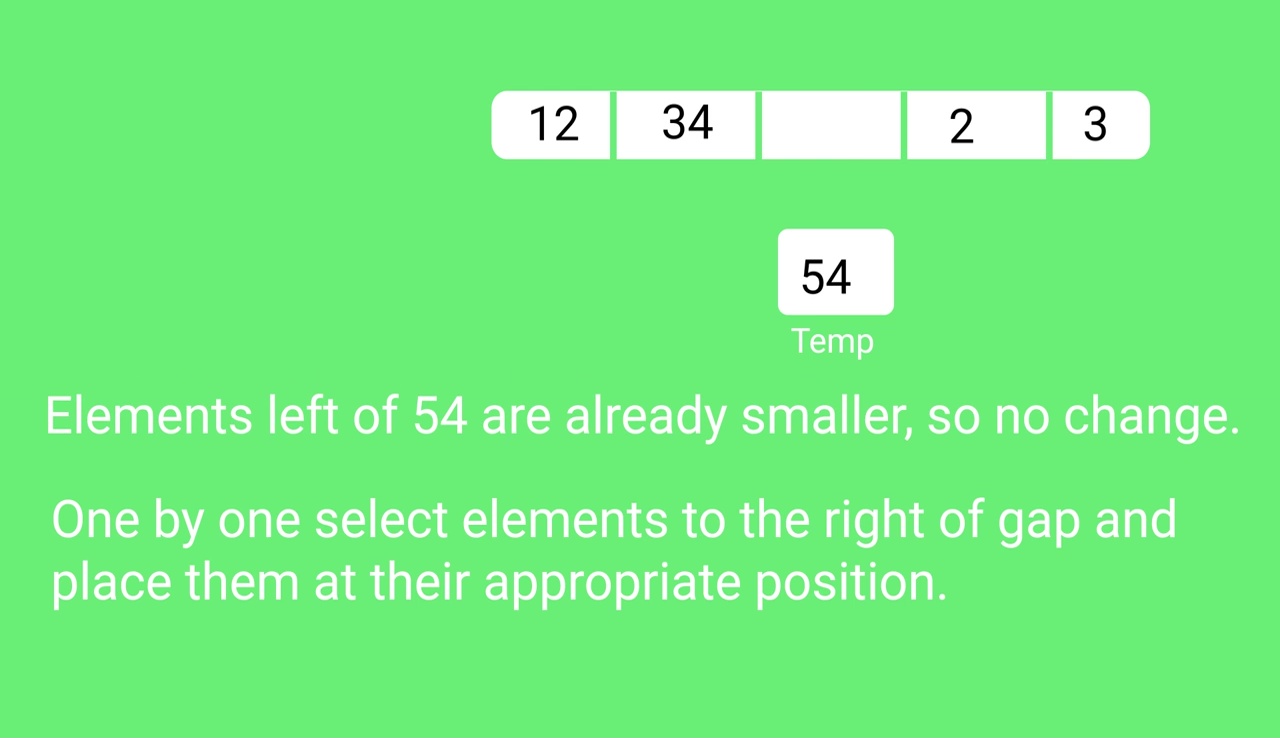
int arr[] = {12, 34, 54, 2, 3}, i;
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Array before sorting: \n";
printArray(arr, n);
shellSort(arr, n);
cout << "\nArray after sorting: \n";
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class ShellSort
{
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
int sort(int arr[])
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int gap = n/2; gap > 0; gap /= 2)
{
for (int i = gap; i < n; i += 1)
{
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap)
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = {12, 34, 54, 2, 3};
System.out.println("Array before sorting");
printArray(arr);
ShellSort ob = new ShellSort();
ob.sort(arr);
System.out.println("Array after sorting");
printArray(arr);
}
}
|
C#
using System;
class ShellSort
{
static void printArray(int []arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
int sort(int []arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int gap = n/2; gap > 0; gap /= 2)
{
for (int i = gap; i < n; i += 1)
{
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap)
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = {12, 34, 54, 2, 3};
Console.Write("Array before sorting :\n");
printArray(arr);
ShellSort ob = new ShellSort();
ob.sort(arr);
Console.Write("Array after sorting :\n");
printArray(arr);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function printArray(arr)
{
let n = arr.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i)
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
document.write("<br>");
}
function sort(arr)
{
let n = arr.length;
for (let gap = Math.floor(n/2); gap > 0; gap = Math.floor(gap/2))
{
for (let i = gap; i < n; i += 1)
{
let temp = arr[i];
let j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap)
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
return arr;
}
let arr = [12, 34, 54, 2, 3];
document.write("Array before sorting<br>");
printArray(arr);
arr = sort(arr);
document.write("Array after sorting<br>");
printArray(arr);
</script>
|
Python3
def shellSort(arr, n):
gap=n//2
while gap>0:
j=gap
while j<n:
i=j-gap
while i>=0:
if arr[i+gap]>arr[i]:
break
else:
arr[i+gap],arr[i]=arr[i],arr[i+gap]
i=i-gap
j+=1
gap=gap//2
arr2 = [12, 34, 54, 2, 3]
print("input array:",arr2)
shellSort(arr2,len(arr2))
print("sorted array",arr2)
|
Output
Array before sorting:
12 34 54 2 3
Array after sorting:
2 3 12 34 54
Time Complexity: Time complexity of the above implementation of Shell sort is O(n2). In the above implementation, the gap is reduced by half in every iteration. There are many other ways to reduce gaps which leads to better time complexity. See this for more details.
Worst Case Complexity
The worst-case complexity for shell sort is O(n2)
Best Case Complexity
When the given array list is already sorted the total count of comparisons of each interval is equal to the size of the given array.
So best case complexity is Ω(n log(n))
Average Case Complexity
The Average Case Complexity: O(n*log n)~O(n1.25)
Space Complexity
The space complexity of the shell sort is O(1).
Questions:
1. Which is more efficient shell or heap sort?
Ans. As per big-O notation, shell sort has O(n^{1.25}) average time complexity whereas, heap sort has O(N log N) time complexity. According to a strict mathematical interpretation of the big-O notation, heap sort surpasses shell sort in efficiency as we approach 2000 elements to be sorted.
Note:- Big-O is a rounded approximation and analytical evaluation is not always 100% correct, it depends on the algorithms’ implementation which can affect actual run time.
Shell Sort Applications
1. Replacement for insertion sort, where it takes a long time to complete a given task.
2. To call stack overhead we use shell sort.
3. when recursion exceeds a particular limit we use shell sort.
4. For medium to large-sized datasets.
5. In insertion sort to reduce the number of operations.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shellsort
Snapshots:





Other Sorting Algorithms on GeeksforGeeks/GeeksQuiz:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...