Scalability and Elasticity in Cloud Computing
Last Updated :
16 Jan, 2023
Prerequisite – Cloud Computing
Cloud Elasticity: Elasticity refers to the ability of a cloud to automatically expand or compress the infrastructural resources on a sudden up and down in the requirement so that the workload can be managed efficiently. This elasticity helps to minimize infrastructural costs. This is not applicable for all kinds of environments, it is helpful to address only those scenarios where the resource requirements fluctuate up and down suddenly for a specific time interval. It is not quite practical to use where persistent resource infrastructure is required to handle the heavy workload.
The versatility is vital for mission basic or business basic applications where any split the difference in the exhibition may prompts enormous business misfortune. Thus, flexibility comes into picture where extra assets are provisioned for such application to meet the presentation prerequisites.
It works such a way that when number of client access expands, applications are naturally provisioned the extra figuring, stockpiling and organization assets like central processor, Memory, Stockpiling or transfer speed what’s more, when fewer clients are there it will naturally diminish those as
per prerequisite.
The Flexibility in cloud is a well-known highlight related with scale-out arrangements (level scaling), which takes into consideration assets to be powerfully added or eliminated when required.
It is for the most part connected with public cloud assets which is generally highlighted in pay-per-use or pay-more only as costs arise administrations.
The Flexibility is the capacity to develop or contract framework assets (like process, capacity or organization) powerfully on a case by case basis to adjust to responsibility changes in the
applications in an autonomic way.
It makes make most extreme asset use which bring about reserve funds in foundation costs in general.
Relies upon the climate, flexibility is applied on assets in the framework that isn’t restricted to equipment, programming, network, QoS and different arrangements.
The versatility is totally relying upon the climate as now and again it might become negative characteristic where execution of certain applications probably ensured execution.
It is most commonly used in pay-per-use, public cloud services. Where IT managers are willing to pay only for the duration to which they consumed the resources.
Example: Consider an online shopping site whose transaction workload increases during festive season like Christmas. So for this specific period of time, the resources need a spike up. In order to handle this kind of situation, we can go for a Cloud-Elasticity service rather than Cloud Scalability. As soon as the season goes out, the deployed resources can then be requested for withdrawal.
Cloud Scalability: Cloud scalability is used to handle the growing workload where good performance is also needed to work efficiently with software or applications. Scalability is commonly used where the persistent deployment of resources is required to handle the workload statically.
Example: Consider you are the owner of a company whose database size was small in earlier days but as time passed your business does grow and the size of your database also increases, so in this case you just need to request your cloud service vendor to scale up your database capacity to handle a heavy workload.
It is totally different from what you have read above in Cloud Elasticity. Scalability is used to fulfill the static needs while elasticity is used to fulfill the dynamic need of the organization. Scalability is a similar kind of service provided by the cloud where the customers have to pay-per-use. So, in conclusion, we can say that Scalability is useful where the workload remains high and increases statically.
Types of Scalability:
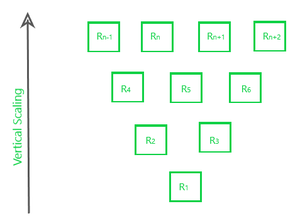
1. Vertical Scalability (Scale-up) –
In this type of scalability, we increase the power of existing resources in the working environment in an upward direction.
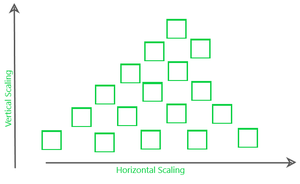
2. Horizontal Scalability: In this kind of scaling, the resources are added in a horizontal row.

3. Diagonal Scalability –
It is a mixture of both Horizontal and Vertical scalability where the resources are added both vertically and horizontally.
Difference Between Cloud Elasticity and Scalability :
| |
Cloud Elasticity |
Cloud Scalability |
| 1 |
Elasticity is used just to meet the sudden up and down in the workload for a small period of time. |
Scalability is used to meet the static increase in the workload. |
| 2 |
Elasticity is used to meet dynamic changes, where the resources need can increase or decrease. |
Scalability is always used to address the increase in workload in an organization. |
| 3 |
Elasticity is commonly used by small companies whose workload and demand increases only for a specific period of time. |
Scalability is used by giant companies whose customer circle persistently grows in order to do the operations efficiently. |
| 4 |
It is a short term planning and adopted just to deal with an unexpected increase in demand or seasonal demands. |
Scalability is a long term planning and adopted just to deal with an expected increase in demand. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...