Rust – Constants
Last Updated :
31 Mar, 2021
Constants are the value that can not be changed after assigning them. If we created a constant, then there is no way of changing its value. The keyword for declaring constant is const. In Rust, constants must be explicitly typed. The below syntax is used to initialize a constant value:
Syntax :
const VARIABLE_NAME:dataType = value;
Now let’s check out some examples for the same.
Example 1 :
Rust
fn main() {
const MARKS:i32 = 100;
const PI:f32 = 3.14;
const NAME:&str = "GFG";
println!("MARKS {}",MARKS);
println!("PI {}",PI);
println!("NAME {}",NAME);
}
|
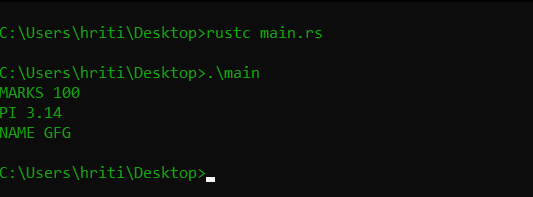
Output:
MARKS 100
PI 3.14
NAME GFG
Example 2:
Rust
fn main() {
const GFG:i32 = 100;
const GFG:i32 = 200;
println!("{}",GFG);
}
|
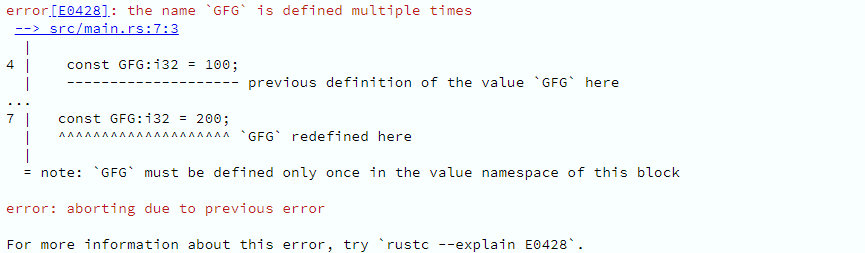
This will produce an error :
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...