Routing for Mobile Hosts
Last Updated :
21 Jan, 2021
Millions of people use computers while on go, from the truly mobile situations with a wireless device in moving cars, to nomadic situations in which laptop computers are used in a series of a different location. We use the term mobile hosts to mean either category, as distinct from stationary hosts that never move. The mobile hosts introduce a new complication to route packets to the mobile hosts, the network first has to find it.
Assumed model :
The model of the world that we will consider is one in which all hosts are assumed to have a permanent home location that never changes. Each host has a permanent home address that can be used to determine home location. Like the telephone number 1-212-5551212 indicates the United States (country code 1) and Manhattan (212).
Feature :
- The basic idea used for mobile routing on the internet and cellular network is for the mobile hosts to tell the host at the home location.
- This host, which acts on behalf of the mobile host called a home agent.
- Once it knows where the mobile host currently located, it can forward packets so that they are delivered. The figure shows mobile routing in action.
- The local address called care-of address.
- Once it has this address it can tell its home agent where it is now. It does this by sending registration message to home agent with care of address.
Description of Diagram :
The message is shown with a dashed line in the figure indicate that it is a control message, not a data message. The sender sends a data packet to the mobile host using its permanent address. This packet is routed by the network to the host home location because the home addresses belong there. It encapsulates the packet with a new header and sends this bundle to the care-of address. This mechanism is called tunneling. It is very important on the internet, so we will look at it in more detail later.
Diagram :
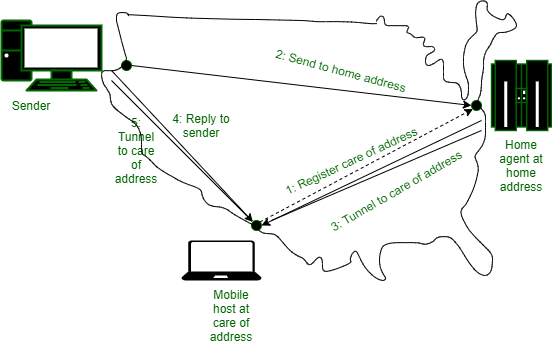
- When the encapsulated packet arrives at the care-of address, the mobile host unwraps it and retrieves the packet from the sender.
- The overall route is called triangle routing because it way is circuitous if the remote location is far from the home location.
- As part of the step, 4 senders learns the current care-of address.
- Subsequent packets can be routed directly to the mobile host by tunneling them to the care-of address (step 5) bypassing the home location.
- If connectivity lost for any reason as the mobile moves, the home address can always be used to reach the mobile.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...