Root to leaf path sum equal to a given number
Last Updated :
28 Jul, 2023
Given a binary tree and a number, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given number. Return false if no such path can be found.
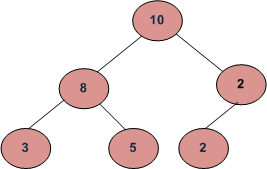
Example:
Input: 10 Sum = 23
/ \
8 2
/ \ /
3 5 2
Output: True
Explanation: Root to leaf path sum, existing in this tree are
21 –> 10 – 8 – 3
23 –> 10 – 8 – 5
14 –> 10 – 2 – 2
So it is possible to get sum = 23
Recursively move to left and right subtree and decrease sum by the value of the current node and if at any point the current node is equal to a leaf node and remaining sum is equal to zero then the answer is true
Follow the given steps to solve the problem using the above approach:
- Recursively move to the left and right subtree and at each call decrease the sum by the value of the current node
- If at any level the current node is a leaf node and the remaining sum is equal to zero then return true
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define bool int
class node {
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
bool hasPathSum(node* Node, int sum)
{
if (Node == NULL)
return 0;
bool ans = 0;
int subSum = sum - Node->data;
if (subSum == 0 && Node->left == NULL
&& Node->right == NULL)
return 1;
if (Node->left)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(Node->left, subSum);
if (Node->right)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(Node->right, subSum);
return ans;
}
node* newnode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
int main()
{
int sum = 21;
node* root = newnode(10);
root->left = newnode(8);
root->right = newnode(2);
root->left->left = newnode(3);
root->left->right = newnode(5);
root->right->left = newnode(2);
if (hasPathSum(root, sum))
cout << "There is a root-to-leaf path with sum "
<< sum;
else
cout << "There is no root-to-leaf path with sum "
<< sum;
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define bool int
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
bool hasPathSum(struct node* node, int sum)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
bool ans = 0;
int subSum = sum - node->data;
if (subSum == 0 && node->left == NULL
&& node->right == NULL)
return 1;
if (node->left)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(node->left, subSum);
if (node->right)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(node->right, subSum);
return ans;
}
struct node* newnode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main()
{
int sum = 21;
struct node* root = newnode(10);
root->left = newnode(8);
root->right = newnode(2);
root->left->left = newnode(3);
root->left->right = newnode(5);
root->right->left = newnode(2);
if (hasPathSum(root, sum))
printf("There is a root-to-leaf path with sum %d",
sum);
else
printf("There is no root-to-leaf path with sum %d",
sum);
getchar();
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
boolean hasPathSum(Node node, int sum)
{
if (root == null)
return false;
boolean ans = false;
int subSum = sum - node.data;
if (subSum == 0 && node.left == null
&& node.right == null)
return (ans = true);
if (node.left != null)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(node.left, subSum);
if (node.right != null)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(node.right, subSum);
return (ans);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int sum = 21;
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.right = new Node(2);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(2);
if (tree.hasPathSum(tree.root, sum))
System.out.println(
"There is a root to leaf path with sum "
+ sum);
else
System.out.println(
"There is no root to leaf path with sum "
+ sum);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def hasPathSum(node, s):
ans = 0
subSum = s - node.data
if(subSum == 0 and node.left == None and node.right == None):
return True
if node.left is not None:
ans = ans or hasPathSum(node.left, subSum)
if node.right is not None:
ans = ans or hasPathSum(node.right, subSum)
return ans
if __name__ == "__main__":
s = 21
root = Node(10)
root.left = Node(8)
root.right = Node(2)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.left.left = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(2)
if hasPathSum(root, s):
print("There is a root-to-leaf path with sum %d" % (s))
else:
print("There is no root-to-leaf path with sum %d" % (s))
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
public Node root;
public virtual bool haspathSum(Node node, int sum)
{
ans = false;
int subsum = sum - node.data;
if (subsum == 0 && node.left == null
&& node.right == null) {
return true;
}
if (node.left != null) {
ans = ans || haspathSum(node.left, subsum);
}
if (node.right != null) {
ans = ans || haspathSum(node.right, subsum);
}
return ans;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = 21;
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.right = new Node(2);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(2);
if (tree.haspathSum(tree.root, sum)) {
Console.WriteLine("There is a root to leaf "
+ "path with sum " + sum);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("There is no root to leaf "
+ "path with sum " + sum);
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
var root;
function hasPathSum(node , sum)
{
var ans = false;
var subSum = sum - node.data;
if(subSum == 0 && node.left == null && node.right == null)
return(ans = true);
if(node.left != null)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(node.left, subSum);
if(node.right != null)
ans = ans || hasPathSum(node.right, subSum);
return(ans);
}
var sum = 21;
var root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(2);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
if (hasPathSum(root, sum))
document.write(
"There is a root to leaf path with sum "
+ sum);
else
document.write(
"There is no root to leaf path with sum "
+ sum);
|
Output
There is a root-to-leaf path with sum 21
Time Complexity: O(N)
Space Complexity: O(N) or O(H)
Approach 2: Iterative Approach using Stack
In this approach, we use a stack to perform a preorder traversal of the binary tree. We maintain two stacks – one to store the nodes and another to store the sum of values along the path to that node. Whenever we encounter a leaf node, we check if the sum matches the target sum. If it does, we return true, otherwise, we continue traversing the tree.
- Check if the root node is NULL. If it is, return false, since there is no path to follow.
- Create two stacks, one for the nodes and one for the sums. Push the root node onto the node stack and its data onto the sum stack.
- While the node stack is not empty, do the following:
- Pop a node from the node stack and its corresponding sum from the sum stack.
- Check if the node is a leaf node (i.e., it has no left or right child). If it is, check if the sum equals the target sum. If it does, return true, since we have found a path that adds up to the target sum.
- If the node has a left child, push it onto the node stack and push the sum plus the left child’s data onto the sum stack.
- If the node has a right child, push it onto the node stack and push the sum plus the right child’s data onto the sum stack.
- If we reach this point, it means we have exhausted all paths and haven’t found any that add up to the target sum. Return false.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* left, *right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
bool hasPathSum(Node* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL) return false;
stack<Node*> s;
stack<int> sums;
s.push(root);
sums.push(root->data);
while (!s.empty()) {
Node* node = s.top(); s.pop();
int sum = sums.top(); sums.pop();
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) {
if (sum == targetSum) return true;
}
if (node->left != NULL) {
s.push(node->left);
sums.push(sum + node->left->data);
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
s.push(node->right);
sums.push(sum + node->right->data);
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
Node* root = new Node(10);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->right = new Node(2);
root->left->left = new Node(3);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(2);
int targetSum = 23;
if (hasPathSum(root, targetSum)) {
cout << "There is a root-to-leaf path with sum "
<< targetSum;
}
else {
cout << "There is no root-to-leaf path with sum "
<< targetSum;
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Stack;
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class PathSum {
public static boolean hasPathSum(Node root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null)
return false;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> sums = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
sums.push(root.data);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node = stack.pop();
int sum = sums.pop();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
if (sum == targetSum)
return true;
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
sums.push(sum + node.left.data);
}
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
sums.push(sum + node.right.data);
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(2);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
int targetSum = 23;
if (hasPathSum(root, targetSum)) {
System.out.println("There is a root-to-leaf path with sum " + targetSum);
} else {
System.out.println("There is no root-to-leaf path with sum " + targetSum);
}
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.data = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
def hasPathSum(root, targetSum):
if not root:
return False
s = [root]
sums = [root.data]
while s:
node = s.pop()
sum_val = sums.pop()
if not node.left and not node.right:
if sum_val == targetSum:
return True
if node.left:
s.append(node.left)
sums.append(sum_val + node.left.data)
if node.right:
s.append(node.right)
sums.append(sum_val + node.right.data)
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(10)
root.left = Node(8)
root.right = Node(2)
root.left.left = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(2)
targetSum = 23
if hasPathSum(root, targetSum):
print("There is a root-to-leaf path with sum", targetSum)
else:
print("There is no root-to-leaf path with sum", targetSum)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int val)
{
data = val;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class PathSum
{
public static bool HasPathSum(Node root, int targetSum)
{
if (root == null)
return false;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<int> sums = new Stack<int>();
stack.Push(root);
sums.Push(root.data);
while (stack.Count > 0)
{
Node node = stack.Pop();
int sum = sums.Pop();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
{
if (sum == targetSum)
return true;
}
if (node.left != null)
{
stack.Push(node.left);
sums.Push(sum + node.left.data);
}
if (node.right != null)
{
stack.Push(node.right);
sums.Push(sum + node.right.data);
}
}
return false;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(2);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
int targetSum = 23;
if (HasPathSum(root, targetSum))
{
Console.WriteLine("There is a root-to-leaf path with sum " + targetSum);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("There is no root-to-leaf path with sum " + targetSum);
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function hasPathSum(root, targetSum) {
if (root === null) {
return false;
}
const stack = [];
const sums = [];
stack.push(root);
sums.push(root.data);
while (stack.length > 0) {
const node = stack.pop();
const sum = sums.pop();
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
if (sum === targetSum) {
return true;
}
}
if (node.left !== null) {
stack.push(node.left);
sums.push(sum + node.left.data);
}
if (node.right !== null) {
stack.push(node.right);
sums.push(sum + node.right.data);
}
}
return false;
}
const root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(2);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
const targetSum = 23;
if (hasPathSum(root, targetSum)) {
console.log("There is a root-to-leaf path with sum " + targetSum);
} else {
console.log("There is no root-to-leaf path with sum " + targetSum);
}
|
Output
There is a root-to-leaf path with sum 23
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O( N)
References: http://cslibrary.stanford.edu/110/BinaryTrees.html
Author: Tushar Roy
Please write comments if you find any bug in above code/algorithm, or find other ways to solve the same problem
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...