RFID Full Form
Last Updated :
21 Feb, 2023
RFID or Radio Frequency Identification is an automatic identification method that uses wireless non-contact radio frequency waves in which data is digitally encoded in RFID tags or smart labels which can be read by reader through radio waves. The transfer of data takes place between a reader and a movable thing that can be identified & track. RFID can be considered similar to barcodes as data read from tags are stored in database or you can say device which captures label’s data, stores data in a database. The major difference between barcodes or QR codes and RFID is that RFID tag data can be read outside line-of-sight whereas traditional barcodes can’t. RFID doesn’t require any physical contact between reader or scanner and tagged item. There is a microchip placed inside a label which is used to transfer data when label is exposed to radio waves. RFID tags are mainly used in industries for tracking progress of a product. RFID System : RFID System composed of RFID Reader & RFID Tags.
- RFID Reader – It is a device used to communicate with RFID Tag which consists of one or more antennas, used to emit radio waves & receive signals back, from RFID Tag. The RFID reader is also called as interrogator as it used to interrogate RFID Tag.
-
- RFID Tags – RFID Tags consists of 2 parts:
- Integrated Circuit : It is used for storing & processing data.
- Antenna : It is used for transmitting receiving signal.
- Active Tag : These have their own power supply and allows a read range of about 100 feet.
- Passive Tag : A reader inductively gives power to Passive Tags as they don’t have their own power supply. Passive Tags are most widely used Tag and their read range is approximately 30 feet.
What is RFID?
Radio Recurrence Distinguishing proof (RFID) is an abbreviation for Radio Recurrence ID.
The guideline is the non-contact information correspondence between the RFID peruser and the RFID tag to accomplish the motivation behind recognizing the objective, which is a sort of programmed distinguishing proof innovation.
Direct non-contact two-way information correspondence through radio recurrence, and utilize radio recurrence to peruse and compose recording media (electronic labels or radio recurrence cards), to accomplish the reason for recognizing targets and information trade, which is viewed as the most possible improvement in the 21st 100 years. One of the data innovation.
Classification of RFID System : RFID System is classified into 2 Fields, Near Field RFID and Far Field RFID.
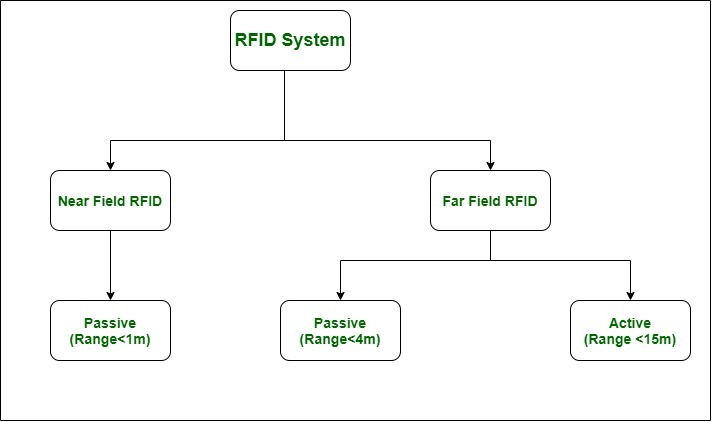
- Near Field RFID – Near Field RFID has small, Omni-directional reader antenna & tag read range between 5mm to 10cm depending on frequency & antenna.
- Far Field RFID – Far Field RFID has resonant, directional antenna & tag range that can reach up to 22.1m.
Components of RFID system:
An RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) system typically consists of the following components:
- RFID Tag: Also known as a transponder, this is a small wireless device that contains a microchip
and an antenna. The tag stores information about the item it is attached to, such as its unique identification number and other relevant data.
- RFID Reader: Also known as an interrogator, this is a device that emits radio waves and can read
the information stored on an RFID tag. It is connected to a computer or other device that processes the data received from the tag.
- Antenna: This is a device that transmits and receives radio waves between the RFID tag and reader. It can be integrated into the RFID tag or reader, or it can be a separate component.
- Middleware: This is software that sits between the RFID reader and the back-end computer system. It helps to manage and process the data received from the RFID tags, and can also provide additional functionality such as filtering and error checking.
- Back-end System: This is the computer system that stores and processes the data received from the RFID tags. It can be a simple database or a more complex system, depending on the application.
- Power supply: Some RFID systems require an external power supply to function, while others use batteries or are powered by the reader through a process known as backscatter.
- Accessories: Depending on the application, additional accessories such as mounts, cases, and antennas may be required to optimize the performance of the RFID system.
In summary, RFID system is composed of RFID tags, RFID readers, antennas, middleware, back-
end system, power supply and accessories. The RFID tag is a wireless device that contains a
microchip and an antenna, it stores information about the item it is attached to, the RFID reader or interrogator emits radio waves and can read the information stored on the tag, the antenna transmits and receives radio waves between the RFID tag and reader, middleware helps to manage and process the data received, the back-end system stores and processes the data received and power supply is a necessary component to power the system.
Applications of RFID :
- Document tracking.
- Controlling access to restricted areas
- Asset tracking
- Personnel tracking
- Inventory management
- ID badging
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing
- Healthcare
RFID FEATURE’S:
- Applicability: RFID innovation depends on electromagnetic waves and doesn’t need actual contact between the two gatherings.
- This permits it to lay out associations paying little mind to clean, haze, plastic, paper, wood, and different deterrents, and impart straightforwardly.
- Proficiency: The perusing and composing velocity of the RFID framework is incredibly quick, and a commonplace RFID transmission process is normally under 100 milliseconds.
- High-recurrence RFID perusers might recognize and peruse the substance of various labels simultaneously, which significantly works on the proficiency of data transmission.
- Uniqueness: Each RFID tag is novel.
- Through the balanced correspondence between RFID labels and items, the ensuing course of every item can be plainly followed.
- Effortlessness: RFID labels have a straightforward construction, high acknowledgment rate and basic understanding hardware.
- Particularly as NFC innovation is continuously promoted on cell phones, every client’s cell phone will turn into the least complex RFID peruser.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...