Reversing a queue using recursion
Last Updated :
26 Dec, 2022
Given a queue, write a recursive function to reverse it.
Standard operations allowed :
enqueue(x) : Add an item x to rear of queue.
dequeue() : Remove an item from front of queue.
empty() : Checks if a queue is empty or not.
Examples :
Input : Q = [5, 24, 9, 6, 8, 4, 1, 8, 3, 6]
Output : Q = [6, 3, 8, 1, 4, 8, 6, 9, 24, 5]
Explanation : Output queue is the reverse of the input queue.
Input : Q = [8, 7, 2, 5, 1]
Output : Q = [1, 5, 2, 7, 8]
Recursive Algorithm :
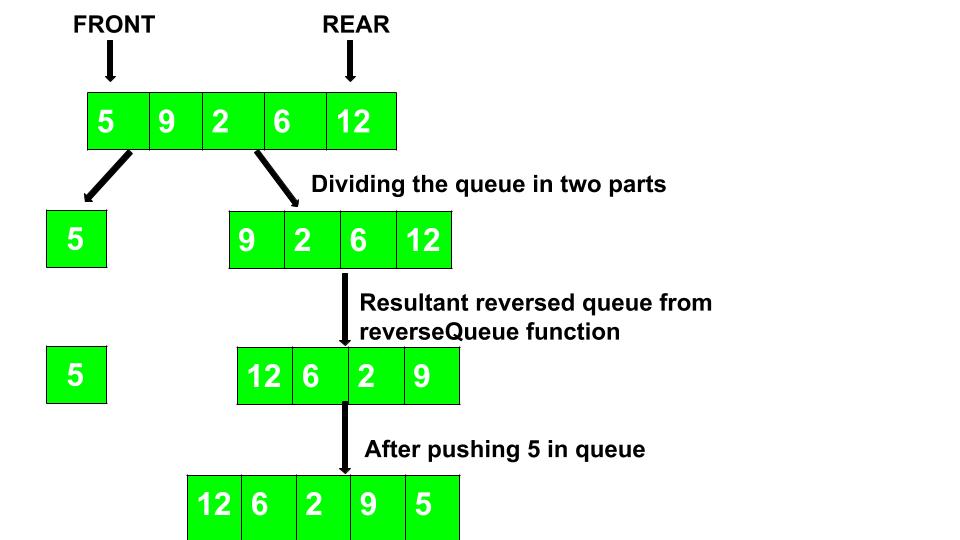
- The pop element from the queue if the queue has elements otherwise return empty queue.
- Call reverseQueue function for the remaining queue.
- Push the popped element in the resultant reversed queue.
Pseudo Code :
queue reverseFunction(queue)
{
if (queue is empty)
return queue;
else {
data = queue.front()
queue.pop()
queue = reverseFunction(queue);
q.push(data);
return queue;
}
}
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void printQueue(queue<long long int> Queue)
{
while (!Queue.empty()) {
cout << Queue.front() << " ";
Queue.pop();
}
}
void reverseQueue(queue<long long int>& q)
{
if (q.empty())
return;
long long int data = q.front();
q.pop();
reverseQueue(q);
q.push(data);
}
int main()
{
queue<long long int> Queue;
Queue.push(56);
Queue.push(27);
Queue.push(30);
Queue.push(45);
Queue.push(85);
Queue.push(92);
Queue.push(58);
Queue.push(80);
Queue.push(90);
Queue.push(100);
reverseQueue(Queue);
printQueue(Queue);
}
|
Java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Queue_reverse {
static Queue<Integer> queue;
static void Print()
{
while (!queue.isEmpty())
{
System.out.print(queue.peek() + " ");
queue.remove();
}
}
static Queue<Integer> reverseQueue(Queue<Integer> q)
{
if (q.isEmpty())
return q;
int data = q.peek();
q.remove();
q = reverseQueue(q);
q.add(data);
return q;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(56);
queue.add(27);
queue.add(30);
queue.add(45);
queue.add(85);
queue.add(92);
queue.add(58);
queue.add(80);
queue.add(90);
queue.add(100);
queue = reverseQueue(queue);
Print();
}
}
|
Python3
from queue import Queue
def reverse_queue(queue: Queue):
if queue.empty():
return
item = queue.queue[0]
queue.get()
reverse_queue(queue)
queue.put(item)
def print_queue(queue: Queue):
while not queue.empty():
print(queue.queue[0], end=" ")
queue.get()
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
q = Queue()
q.put(56)
q.put(27)
q.put(30)
q.put(45)
q.put(85)
q.put(92)
q.put(58)
q.put(80)
q.put(90)
q.put(100)
reverse_queue(q)
print_queue(q)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static void printQueue(Queue<long> queue)
{
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
Console.Write(queue.Peek() + " ");
queue.Dequeue();
}
}
static void reverseQueue(ref Queue<long> q)
{
if (q.Count == 0)
return;
long data = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
reverseQueue(ref q);
q.Enqueue(data);
}
static void Main()
{
Queue<long> queue = new Queue<long>();
queue.Enqueue(56);
queue.Enqueue(27);
queue.Enqueue(30);
queue.Enqueue(45);
queue.Enqueue(85);
queue.Enqueue(92);
queue.Enqueue(58);
queue.Enqueue(80);
queue.Enqueue(90);
queue.Enqueue(100);
reverseQueue(ref queue);
printQueue(queue);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function printQueue(queue)
{
while (queue.length != 0)
{
document.write(queue[0] + " ");
queue.shift();
}
}
function reverseQueue(q)
{
if (q.length == 0)
return;
let data = q[0];
q.shift();
reverseQueue(q);
q.push(data);
}
let queue = [];
queue.push(56);
queue.push(27);
queue.push(30);
queue.push(45);
queue.push(85);
queue.push(92);
queue.push(58);
queue.push(80);
queue.push(90);
queue.push(100);
reverseQueue(queue);
printQueue(queue);
</script>
|
Output
100 90 80 58 92 85 45 30 27 56
Complexity analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(n).
- Auxiliary Space: O(n), since recursion uses stack internally
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...