Reverse a Linked List in groups of given size
Last Updated :
10 Jan, 2023
Given a linked list, write a function to reverse every k nodes (where k is an input to the function).
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->NULL, K = 3
Output: 3->2->1->6->5->4->8->7->NULL
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->NULL, K = 5
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->8->7->6->NULL
Algorithm: reverse(head, k)
- Reverse the first sub-list of size k. While reversing keep track of the next node and previous node. Let the pointer to the next node be next and pointer to the previous node be prev. See this post for reversing a linked list.
- head->next = reverse(next, k) ( Recursively call for rest of the list and link the two sub-lists )
- Return prev ( prev becomes the new head of the list (see the diagrams of an iterative method of this post )
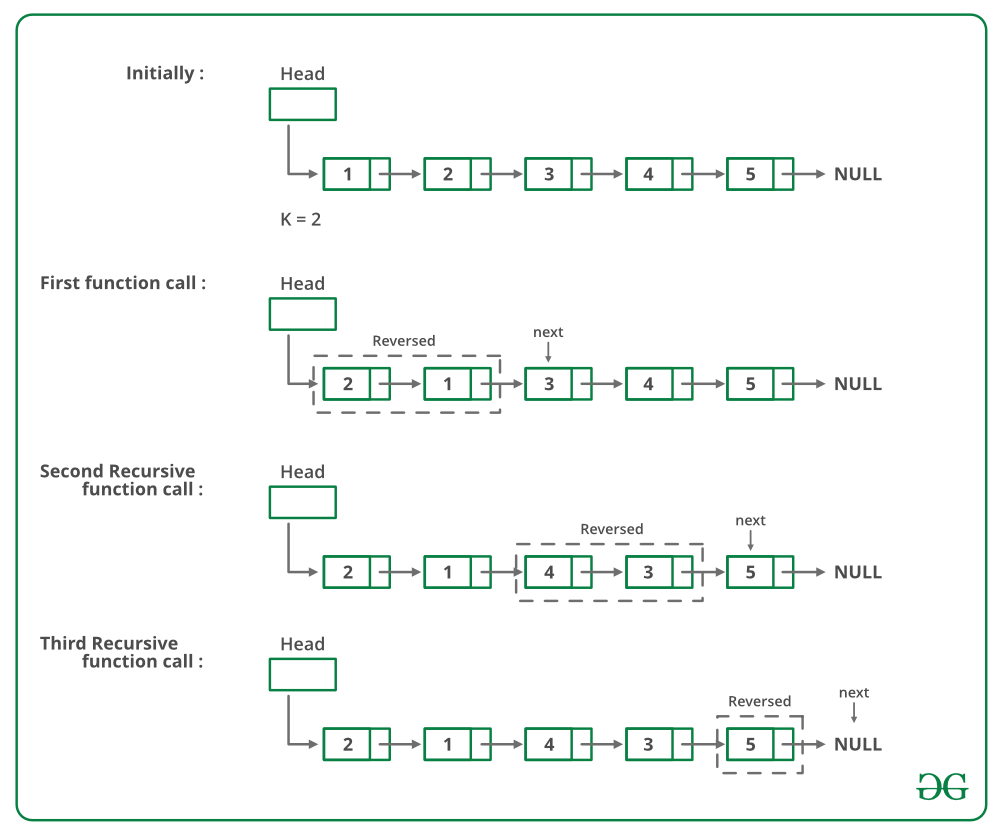
Below is image shows how the reverse function works:
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* reverse(Node* head, int k)
{
if (!head)
return NULL;
Node* current = head;
Node* next = NULL;
Node* prev = NULL;
int count = 0;
while (current != NULL && count < k) {
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
if (next != NULL)
head->next = reverse(next, k);
return prev;
}
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Given linked list \n";
printList(head);
head = reverse(head, 3);
cout << "\nReversed Linked list \n";
printList(head);
return (0);
}
|
C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node *reverse (struct Node *head, int k)
{
if (!head)
return NULL;
struct Node* current = head;
struct Node* next = NULL;
struct Node* prev = NULL;
int count = 0;
while (current != NULL && count < k)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
if (next != NULL)
head->next = reverse(next, k);
return prev;
}
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
int main(void)
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printf("\nGiven linked list \n");
printList(head);
head = reverse(head, 3);
printf("\nReversed Linked list \n");
printList(head);
return(0);
}
|
Java
class LinkedList {
Node head;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
Node reverse(Node head, int k)
{
if(head == null)
return null;
Node current = head;
Node next = null;
Node prev = null;
int count = 0;
while (count < k && current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
if (next != null)
head.next = reverse(next, k);
return prev;
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(9);
llist.push(8);
llist.push(7);
llist.push(6);
llist.push(5);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Given Linked List");
llist.printList();
llist.head = llist.reverse(llist.head, 3);
System.out.println("Reversed list");
llist.printList();
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def reverse(self, head, k):
if head == None:
return None
current = head
next = None
prev = None
count = 0
while(current is not None and count < k):
next = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = next
count += 1
if next is not None:
head.next = self.reverse(next, k)
return prev
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data,end=' ')
temp = temp.next
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(9)
llist.push(8)
llist.push(7)
llist.push(6)
llist.push(5)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print("Given linked list")
llist.printList()
llist.head = llist.reverse(llist.head, 3)
print ("\nReversed Linked list")
llist.printList()
|
C#
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
Node reverse(Node head, int k)
{
if(head == null)
return null;
Node current = head;
Node next = null;
Node prev = null;
int count = 0;
while (count < k && current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
if (next != null)
head.next = reverse(next, k);
return prev;
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(9);
llist.push(8);
llist.push(7);
llist.push(6);
llist.push(5);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
Console.WriteLine("Given Linked List");
llist.printList();
llist.head = llist.reverse(llist.head, 3);
Console.WriteLine("Reversed list");
llist.printList();
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
function reverse(head , k) {
if (head == null)
return null;
var current = head;
var next = null;
var prev = null;
var count = 0;
while (count < k && current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
if (next != null)
head.next = reverse(next, k);
return prev;
}
function push(new_data) {
new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
function printList() {
temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
document.write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
document.write("<br/>");
}
push(9);
push(8);
push(7);
push(6);
push(5);
push(4);
push(3);
push(2);
push(1);
document.write("Given Linked List<br/>");
printList();
head = reverse(head, 3);
document.write("Reversed list<br/>");
printList();
</script>
|
Output
Given linked list
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Reversed Linked list
3 2 1 6 5 4 9 8 7
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(n).
Traversal of list is done only once and it has ‘n’ elements.
- Auxiliary Space: O(n/k).
For each Linked List of size n, n/k or (n/k)+1 calls will be made during the recursion.
We can solve this question in O(1) Space Complexity.
Approach – 2 Space Optimized – Iterative
The following steps are required for this Algorithm:
- Create a dummy node and point it to the head of input i.e dummy->next = head.
- Calculate the length of the linked list which takes O(N) time, where N is the length of the linked list.
- Initialize three-pointers prev, curr, next to reverse k elements for every group.
- Iterate over the linked lists till next!=NULL.
- Points curr to the prev->next and next to the curr next.
- Then, Using the inner for loop reverse the particular group using these four steps:
- curr->next = next->next
- next->next = prev->next
- prev->next = next
- next = curr->next
7. This for loop runs for k-1 times for all groups except the last remaining element, for the last remaining element it runs for the remaining length of the linked list – 1.
8. Decrement count after for loop by k count -= k, to determine the length of the remaining linked list.
9. Change prev position to curr, prev = curr.
Here is the code for the above algorithm.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* reverse(Node* head, int k)
{
if (!head || k == 1)
return head;
Node* dummy = new Node();
dummy->data = -1;
dummy->next = head;
Node *prev = dummy, *curr = dummy, *next = dummy;
int count = 0;
while (curr) {
curr = curr->next;
count++;
}
while (next) {
curr = prev->next;
next = curr->next;
int toLoop = count > k ? k : count - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < toLoop; i++) {
curr->next = next->next;
next->next = prev->next;
prev->next = next;
next = curr->next;
}
prev = curr;
count -= k;
}
return dummy->next;
}
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Given linked list \n";
printList(head);
head = reverse(head, 3);
cout << "\nReversed Linked list \n";
printList(head);
return (0);
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node* reverse(Node* head, int k)
{
if (!head || k == 1)
return head;
Node* dummy = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
dummy->data = -1;
dummy->next = head;
Node *prev = dummy, *curr = dummy, *next = dummy;
int count = 0;
while (curr) {
curr = curr->next;
count++;
}
while (next) {
curr = prev->next;
next = curr->next;
int toLoop = count > k ? k : count - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < toLoop; i++) {
curr->next = next->next;
next->next = prev->next;
prev->next = next;
next = curr->next;
}
prev = curr;
count -= k;
}
return dummy->next;
}
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printf("Given linked list \n");
printList(head);
head = reverse(head, 3);
printf("\nReversed Linked list \n");
printList(head);
return (0);
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int a)
{
data = a;
next = null;
}
}
class GFG {
static Node push(Node head, int val)
{
Node newNode = new Node(val);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return head;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
return head;
}
static Node reverse(Node head, int k)
{
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
Node dummy = new Node(-1);
dummy.next = head;
Node prev = dummy;
Node curr = dummy;
Node next = dummy;
int count = 0;
while (curr != null) {
count++;
curr = curr.next;
}
while (next != null) {
curr = prev.next;
next = curr.next;
int toLoop
= count > k
? k
: count - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < toLoop; i++) {
curr.next = next.next;
next.next = prev.next;
prev.next = next;
next = curr.next;
}
prev = curr;
count -= k;
}
return dummy.next;
}
static void print(Node head)
{
while (head.next != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println(head.data);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
int k = 3;
head = push(head, 1);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 5);
head = push(head, 6);
head = push(head, 7);
head = push(head, 8);
head = push(head, 9);
System.out.println("Given Linked List");
print(head);
System.out.println("Reversed list");
Node newHead = reverse(head, k);
print(newHead);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def reverse(head, k):
if not head or k == 1:
return head
dummy = Node(-1)
dummy.next = head
prev = dummy
curr = dummy
next = dummy
count = 0
toLoop = 0
i = 0
while curr:
curr = curr.next
count += 1
while next:
curr = prev.next
next = curr.next
toLoop = count > k and k or count - 1
for i in range(1, toLoop):
curr.next = next.next
next.next = prev.next
prev.next = next
next = curr.next
prev = curr
count -= k
return dummy.next
def printList(node):
while node is not None:
print(node.data, end=" ")
node = node.next
head = Node(1)
head.next = Node(2)
head.next.next = Node(3)
head.next.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next.next = Node(5)
head.next.next.next.next.next = Node(6)
head.next.next.next.next.next.next = Node(7)
head.next.next.next.next.next.next.next = Node(8)
head.next.next.next.next.next.next.next.next = Node(9)
print("Given linked list")
printList(head)
head = reverse(head, 3)
print("\nReversed Linked list")
printList(head)
|
C#
using System;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int a)
{
data = a;
next = null;
}
}
class GFG {
static Node push(Node head, int val)
{
Node newNode = new Node(val);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return head;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
return head;
}
static Node reverse(Node head, int k)
{
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
Node dummy = new Node(-1);
dummy.next = head;
Node prev = dummy;
Node curr = dummy;
Node next = dummy;
int count = 0;
while (curr != null) {
count++;
curr = curr.next;
}
while (next != null) {
curr = prev.next;
next = curr.next;
int toLoop
= count > k
? k
: count - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < toLoop; i++) {
curr.next = next.next;
next.next = prev.next;
prev.next = next;
next = curr.next;
}
prev = curr;
count -= k;
}
return dummy.next;
}
static void print(Node head)
{
while (head.next != null) {
Console.Write(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine(head.data);
}
public static void Main()
{
Node head = null;
int K = 3;
head = push(head, 1);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 5);
head = push(head, 6);
head = push(head, 7);
head = push(head, 8);
head = push(head, 9);
Console.WriteLine("Given linked list");
print(head);
Console.WriteLine("Reversed Linked list");
Node newHead = reverse(head, K);
print(newHead);
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node{
constructor(a){
this.data = a;
this.next = null;
}
}
function push(head, val){
newNode = new Node(val);
if(head==null){
head = newNode;
return head;
}
temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
return head;
}
function reverse(head, k){
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
var dummy = new Node(-1);
dummy.next = head;
var prev = dummy;
var curr = dummy;
var next = dummy;
let count = 0;
while(curr!=null){
count++;
curr = curr.next;
}
while(next!=null){
curr = prev.next;
next = curr.next;
let toLoop = count > k ? k : count - 1;
for(let i=1;i<toLoop;i++){
curr.next = next.next;
next.next = prev.next;
prev.next = next;
next = curr.next;
}
prev = curr;
count -= k;
}
return dummy.next;
}
function print(head){
while(head.next!=null){
console.log(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
console.log(head.data+"<br>");
}
var head = null;
let k = 3;
head = push(head, 1);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 5);
head = push(head, 6);
head = push(head, 7);
head = push(head, 8);
head = push(head, 9);
console.log("Given linked list<br>");
print(head);
console.log("Reversed linked list<br>");
var newHead = reverse(head, k);
print(newHead);
|
Output
Given linked list
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Reversed Linked list
3 2 1 6 5 4 9 8 7
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N) : While loop takes O(N/K) time and inner for loop takes O(K) time. So N/K * K = N. Therefore TC O(N)
Space Complexity: O(1) : No extra space is used.
Please write comments if you find the above code/algorithm incorrect, or find other ways to solve the same problem.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...