What is Reconstitution of a partnership firm?
Reconstitution of a partnership firm refers to a change in the structure of a partnership business. This change can occur as a result of several factors, such as the admission of new partners, retirement of existing partners, or the death of a partner. Reconstitution can also involve changes in the profit-sharing ratio, capital contribution, or the addition of new partners to the firm.
The reconstitution of a partnership firm is usually governed by the terms of the partnership agreement or by the provisions of relevant laws and regulations. The process of reconstitution can be complex and may require the drafting of new partnership agreements, the transfer of ownership rights, and the adjustment of financial accounts. In order to ensure a smooth reconstitution process, it is important for the partners to carefully consider the implications of the changes and to seek professional advice as needed.
Reasons for Reconstitution of a Partnership Firm
1. Admission of New Partners: The addition of new partners can be a major reason for reconstitution. This may occur when a firm wants to bring in new talent, expertise, or capital to expand its operations.
2. Retirement of Partners: Retirement of partners can also lead to reconstitution, as the remaining partners may need to rearrange the ownership and management of the firm.
3. Death of a Partner: The death of a partner can trigger reconstitution if the remaining partners need to reorganize the ownership and management of the firm.
4. Change in the Profit-sharing Ratio: Changes in the profit-sharing ratio between partners can also lead to reconstitution, as the partners may need to renegotiate their respective roles and responsibilities in the firm.
5. Capital Contribution: A change in the capital contribution of the partners can also trigger reconstitution, as the partners may need to adjust the financial accounts of the firm to reflect the changes.
6. Dissolution and Winding up: Reconstitution may also occur in the context of dissolving a partnership and winding up its affairs.
7. Business expansion or contraction: Reconstitution may be necessary when a firm wants to expand or contract its operations, as the partners may need to reorganize the ownership and management of the firm to accommodate the changes.
8. Changes in the business environment: External factors, such as changes in the economy, competition, or regulations, can also lead to reconstitution, as the partners may need to adapt to the changing business environment.
Change in Profit Sharing Ratio amongst the Existing Partners
A change in the profit-sharing ratio amongst the existing partners of a partnership firm refers to an alteration in the distribution of profits among the partners. This can occur for several reasons, such as changes in the contributions, responsibilities, or skills of the partners, or a desire to reflect changes in the business environment. A change in the profit-sharing ratio can have significant implications for the partners, as it affects the distribution of profits, the allocation of expenses, and the taxation of the partnership.
To implement a change in the profit-sharing ratio, the partners typically need to renegotiate the terms of the partnership agreement and update the financial records of the firm. This may involve amending the partnership deed, adjusting the capital accounts, and updating the tax returns of the partnership.
It is important for the partners to carefully consider the implications of a change in the profit-sharing ratio and to seek professional advice as needed. The partners should ensure that the change is fair and equitable, and that it aligns with the goals and objectives of the partnership. Additionally, they should ensure that the change is in compliance with relevant laws and regulations and that it does not negatively affect the financial stability or reputation of the firm.
Meaning of Sacrificing Partner Ratio and Gaining Partner Ratio
Sacrificing Partner Ratio and Gaining Partner Ratio are terms used in the context of changes in the profit-sharing ratio among the partners of a partnership firm.
The Sacrificing Partner Ratio refers to the percentage of the profit or loss that a partner is willing to forgo in order to accommodate a change in the profit-sharing ratio. For example, if a partner agrees to reduce their share of the profits from 50% to 40%, their sacrificing ratio would be 10%.
The Gaining Partner Ratio refers to the percentage of the profit or loss that a partner is receiving as a result of the change in the profit-sharing ratio. For example, if a partner’s share of the profits increases from 30% to 40%, their gaining ratio would be 10%.
In essence, the sacrificing partner ratio and the gaining partner ratio represent the impact of the change in the profit-sharing ratio on the individual partners. They are used to determine the distribution of profits, losses, and expenses among the partners and to ensure that the change in the profit-sharing ratio is fair and equitable.
|
| Meaning | Sacrificing ratio refers to the ratio in which the old partners sacrifice their share in the profits for the new partner or any other partner of the business. | Gaining ratio refers to the ratio in which the remaining or continuing partners acquires the share of profit from the retiring partner. |
| Objective | Sacrificing ratio is usually calculated at the time of admission of a new partner for the adjustment of the goodwill to be brought by a new partner. | Gaining Ratio is usually calculated at the time of retirement or death of a partner to pay the amount of goodwill to the retiring partner in the gaining ratio. |
| Procedure | The sacrificing ratio is calculated when a new partner is admitted to the company. | Gaining ratio is calculated when one of the partners leaves or retires from the company or in the case of the death of any partner. |
| Computation | The old ratio is subtracted from the new ratio in calculating the Sacrificing Ratio. | The new ratio is subtracted from the old ratio in the calculation of the Gaining ratio. |
| Capital Effect | The capital account of the sacrificing partners will be increased by the amount received in the form of goodwill contributed to the company by the new partner. | The capital account of the remaining partners will be decreased for the amount paid in the form of goodwill to the retiring partner. |
| Formula | Sacrificing Ratio is calculated as:
Sacrificing Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
| Gaining Ratio is calculated as:
Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio
|
Examples of Sacrificing and Gaining Ratio:
Illustration 1:
M and N are partners sharing profit and loss in the ratio of 5:4. Q is admitted into the firm as a partner. They decided to share future profit and loss in the ratio of 4:3:2. Calculate the sacrificing ratio.
Solution:
Sacrificing ratio = Old ratio – New ratio
M’s old share = 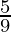
M’s new share = 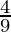
M’s sacrificing share = M’s old share – M’s new share
= 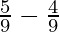
= 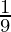
N’s old share = 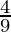
N’s new share = 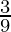
M’s sacrificing share = N’s old share – N’s new share
= 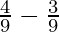
= 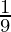
Sacrificing ratio = 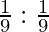
= 1:1
Illustration 2:
Kamal, Indu, and Rocky were partners in a firm sharing profit in a ratio of 4: 3: 2. Indu retires, and Kamal and Rocky decide to share the future profits and losses in the ratio of 5: 4. Calculate the Gaining ratio of the remaining partners.
Solution:
Old Ratio of Kamal, Indu, and Rocky = 4: 3: 2
New Ratio of Kamal and Rocky = 5: 4.
So, Gain of a Partner = New Share − Old Share
Gaining Ratio of Kamal = 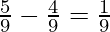
Gaining Ratio of Rocky = 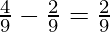
Therefore, the Gaining Ratio between Kamal and Rocky = 1 : 2
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...