Read Only Memory (ROM)
Last Updated :
19 Apr, 2024
In a computer system, memory is a very essential part of the computer system and is used to store information for instant or permanent use. Based on computer memory working features, memory is divided into two types i.e. Volatile and Non-Volatile Memory. Before understanding ROM, we will first understand what exactly volatile and non-volatile memory is. Non-volatile memory is a type of computer memory that is used to retain stored information during power is removed. It is less expensive than volatile memory. It has a large storage capacity. ROM (read-only memory), and flash memory are examples of non-volatile memory. Whereas volatile memory is a temporary memory. In this memory, the data is stored till the system is capable of, but once the power of the system is turned off the data within the volatile memory is deleted automatically. RAM is an example of volatile memory.
What is Read-Only Memory (ROM)?
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory. It is a non-volatile memory that is used to store important information which is used to operate the system. As its name refers to read-only memory, we can only read the programs and data stored on it. It is also a primary memory unit of the computer system. It contains some electronic fuses that can be programmed for a piece of specific information. The information is stored in the ROM in binary format. It is also known as permanent memory.
Block Diagram of ROM
As shown in below diagram, there are k input lines and n output lines in it. The input address from which we wish to retrieve the ROM content is taken using the k input lines. Since each of the k input lines can have a value of 0 or 1, there are a total of 2 k addresses that can be referred to by these input lines, and each of these addresses contains n bits of information that is output from the ROM.
A ROM of this type is designated as a 2k x n ROM.
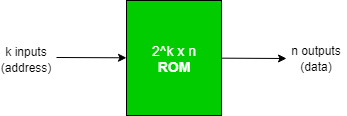
Block Diagram of ROM
Internal Structure of ROM
The internal structure of ROM have two basic components.
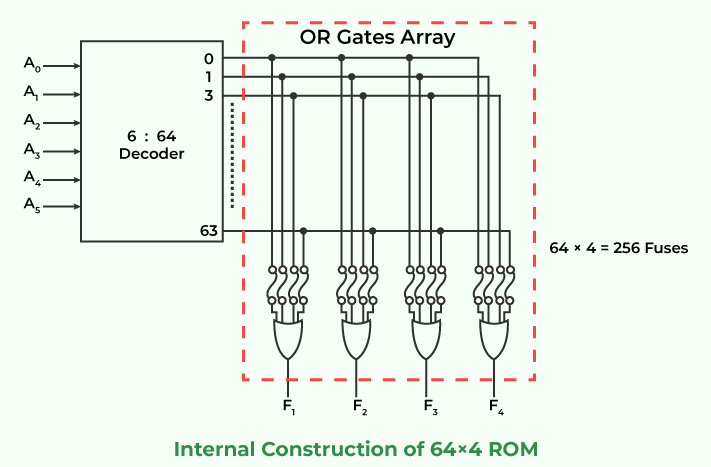
Internal Structure of ROM
A circuit known as a decoder converts an encoded form, such as binary coded decimal, or BCD, into a decimal form. As a result, the output is the binary equivalent of the input. The outputs of the decoder will be the output of every OR gate in the ROM. Let’s use a 64 x 4 ROM as an example. This read-only memory has 64 words with a 4 bit length. As a result, there would be four output lines. Since there are only six input lines and there are 64 words in this ROM, we can specify 64 addresses or minimum terms by choosing one of the 64 words that are available on the output lines from the six input lines. Each address entered has a unique selected word.
Working of ROM
A small, long-lasting battery within the computer powers the ROM, which is made up of two primary components: the OR logic gates and the decoder. In ROM, the decoder receives binary input and produces decimal output. The decoder’s decimal output serves as the input for ROM’s OR gates. ROM chips have a grid of columns and rows that may be switched on and off. If they are turned on, the value is 1, and the lines are connected by a diode. When the value is 0, the lines are not connected. Each element in the arrangement represents one storage element on the memory chip. The diodes allow only one direction of flow, with a specific threshold known as forward break over. This determines the current required before the diode passes the flow on. Silicon-based circuitry typically has a forward break-over voltage of 0.6 V. ROM chips sometimes transmit a charge that exceeds the forward break over to the column with a specified row that is grounded to a specific cell. When a diode is present in the cell, the charge transforms to the binary system, and the cell is “on” with a value of 1.
Features of ROM
- ROM is a non-volatile memory.
- Information stored in ROM is permanent.
- Information and programs stored on it, we can only read and cannot modified.
- Information and programs are stored on ROM in binary format.
- It is used in the start-up process of the computer.
Types of Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Now we will discuss the types of ROM one by one:
- MROM (Masked read-only memory): We know that ROM is as old as semiconductor technology. MROM was the very first ROM that consists of a grid of word lines and bit lines joined together transistor switches. This type of ROM data is physically encoded in the circuit and only be programmed during fabrication. It was not so expensive.
- PROM (Programmable read-only memory): PROM is a form of digital memory. In this type of ROM, each bit is locked by a fuse or anti-fuse. The data stored in it are permanently stored and can not be changed or erasable. It is used in low-level programs such as firmware or microcode.
- EPROM (Erasable programmable read-only memory): EPROM also called EROM, is a type of PROM but it can be reprogrammed. The data stored in EPROM can be erased and reprogrammed again by ultraviolet light. Reprogrammed of it is limited. Before the era of EEPROM and flash memory, EPROM was used in microcontrollers.
- EEPROM (Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory): As its name refers, it can be programmed and erased electrically. The data and program of this ROM can be erased and programmed about ten thousand times. The duration of erasing and programming of the EEPROM is near about 4ms to 10ms. It is used in microcontrollers and remote keyless systems.
Advantages of ROM
- It is cheaper than RAM and it is non-volatile memory.
- It is more reliable as compared to RAM.
- Its circuit is simple as compared to RAM.
- It doesn’t need refreshing time because it is static.
- It is easy to test.
Disadvantages of ROM
- It is a read-only memory, so it cannot be modified.
- It is slower as compared to RAM.
Difference Between RAM and ROM
|
RAM
|
ROM
|
|
RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
|
ROM stands for Read Only Memory.
|
|
You can modify , edit or erase data in RAM.
|
Data in ROM can not modified or erased, you can only read data of ROM.
|
|
RAM is a volatile memory that stores data as long as power supply is given.
|
ROM is a non-volatile memory that retian data even after the power is turned off.
|
|
Speed of RAM is more then speed of ROM.
|
ROM is slower then RAM.
|
|
RAM is costly as compared to ROM.
|
ROM is cheap as compared to RAM.
|
|
A RAM chip can store only a few gigabytes (GB) of data.
|
A ROM chip can store multiple megabytes (MB) of data.
|
|
CPU can easily access data stored in RAM.
|
CPU cannot easily access data stored in ROM.
|
|
RAM is used for the temporary storage of data currently being processed by the CPU.
|
ROM is used to store firmware, BIOS, and other data that needs to be retained.
|
Frequently Asked Question on ROM – FAQs
Can I store my data in ROM?
No, During manufacturing ROM is pre-programmed. ROM cannot be easily modified by Programmers. It is designed to reserve data that must unchanged, firmware and, system instructions.
How long can data be retained in ROM?
Data saved in ROM can be saved for many years, maybe even decades. The information saved in the ROM chip endures for a long time as lengthy as the physical integrity of the chip is preserved.
In which format information stored on ROM?
In Binary format information stored on ROM.
Why ROM is called non-volatile memory?
ROM is called non- volatile memory because ROM does not lose information when power is removed.
Is data in ROM secure?
Yes, data or information saved in ROM is secure from unauthorized modifications. Since ROM is read-only, the data cannot be easily changed. ROM provide safety for critical instructions and data.
What kind of circuits are used in ROM?
ROM is a combinational circuit. It is a combination of different ICs.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...