Quadratic Probing in Hashing
Last Updated :
24 Jan, 2023
Hashing is an improvement technique over the Direct Access Table. The idea is to use a hash function that converts a given phone number or any other key to a smaller number and uses the small number as the index in a table called a hash table.
A function that converts a given big number to a small practical integer value. The mapped integer value is used as an index in the hash table. In simple terms, a hash function maps a big number or string to a small integer that can be used as an index in the hash table. In this article, the collision technique, quadratic probing is discussed:
Quadratic Probing:
Quadratic probing is an open-addressing scheme where we look for the i2‘th slot in the i’th iteration if the given hash value x collides in the hash table.
How Quadratic Probing is done?
Let hash(x) be the slot index computed using the hash function.
- If the slot hash(x) % S is full, then we try (hash(x) + 1*1) % S.
- If (hash(x) + 1*1) % S is also full, then we try (hash(x) + 2*2) % S.
- If (hash(x) + 2*2) % S is also full, then we try (hash(x) + 3*3) % S.
- This process is repeated for all the values of i until an empty slot is found.
For example: Let us consider a simple hash function as “key mod 7” and sequence of keys as 50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73, 101
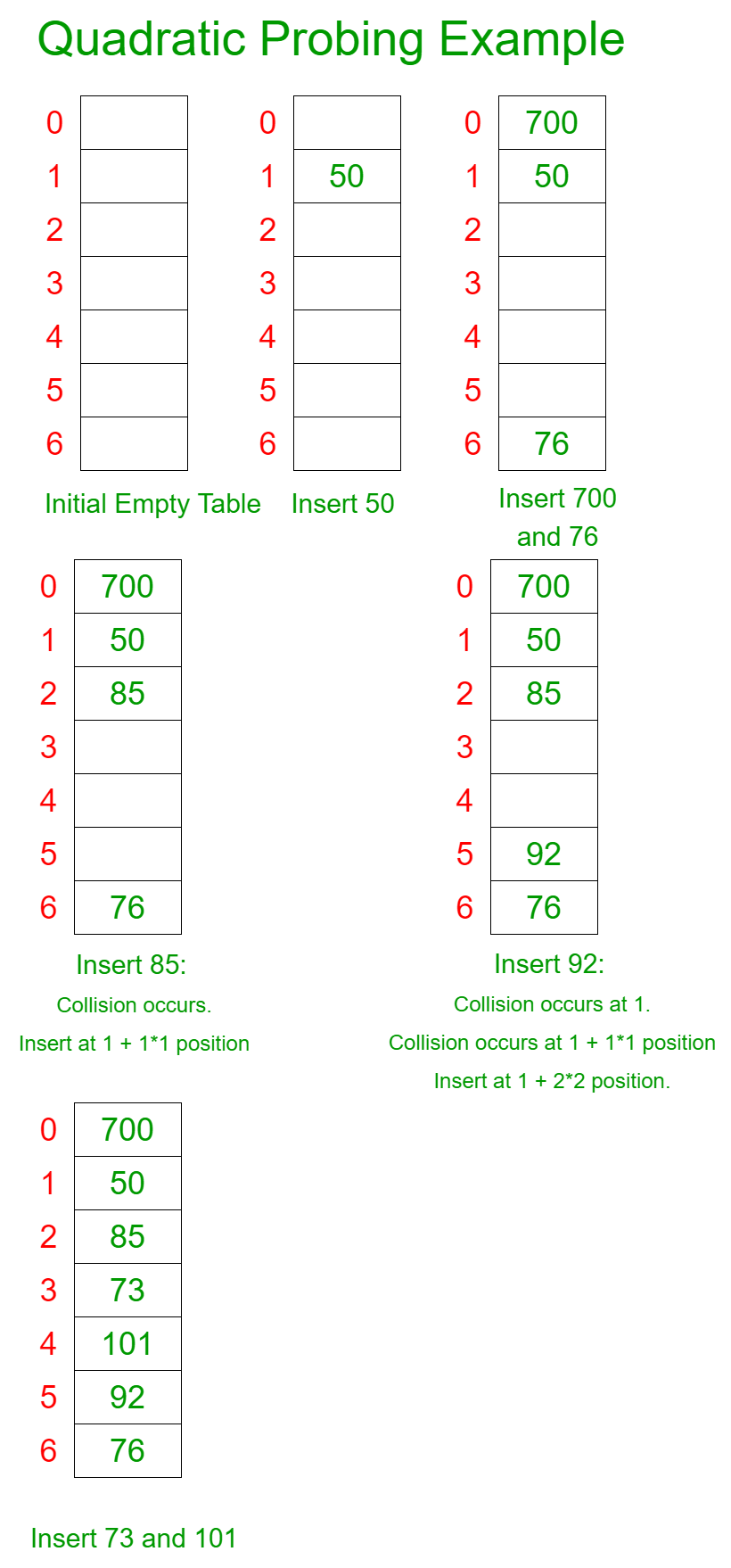
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
}
void hashing(int table[], int tsize, int arr[], int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int hv = arr[i] % tsize;
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else {
for (int j = 0; j < tsize; j++) {
int t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1) {
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table, N);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73, 101 };
int N = 7;
int L = 7;
int hash_table[7];
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
static void hashing(int table[], int tsize, int arr[],
int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int hv = arr[i] % tsize;
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else {
for (int j = 0; j < tsize; j++) {
int t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1) {
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73, 101 };
int N = 7;
int L = 7;
int hash_table[] = new int[L];
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
}
}
|
Python3
def printArray(arr, n):
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
def hashing(table, tsize, arr, N):
for i in range(N):
hv = arr[i] % tsize
if (table[hv] == -1):
table[hv] = arr[i]
else:
for j in range(tsize):
t = (hv + j * j) % tsize
if (table[t] == -1):
table[t] = arr[i]
break
printArray(table, N)
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [50, 700, 76,
85, 92, 73, 101]
N = 7
L = 7
hash_table = [0] * 7
for i in range(L):
hash_table[i] = -1
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void printArray(int[] arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
static void hashing(int[] table, int tsize, int[] arr,
int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int hv = arr[i] % tsize;
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else {
for (int j = 0; j < tsize; j++) {
int t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1) {
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73, 101 };
int N = 7;
int L = 7;
int[] hash_table = new int[L];
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function printArray(arr)
{
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
function hashing(table, tsize,
arr, N)
{
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
let hv = arr[i] % tsize;
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else {
for (let j = 0; j < tsize; j++) {
let t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1) {
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table);
}
let arr = [ 50, 700, 76, 85,
92, 73, 101 ];
let N = 7;
let L = 7;
let hash_table = [];
for (let i = 0; i < L; i++) {
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
</script>
|
Output
700 50 85 73 101 92 76
Time Complexity: O(N * L), where N is the length of the array and L is the size of the hash table.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...