Python Tkinter – Scale Widget
Last Updated :
23 Dec, 2021
Tkinter is a GUI toolkit used in python to make user-friendly GUIs.Tkinter is the most commonly used and the most basic GUI framework available in python. Tkinter uses an object-oriented approach to make GUIs.
Note: For more information, refer to Python GUI – tkinter
Scale widget
The Scale widget is used whenever we want to select a specific value from a range of values. It provides a sliding bar through which we can select the values by sliding from left to right or top to bottom depending upon the orientation of our sliding bar.
Syntax:
S = Scale(root, bg, fg, bd, command, orient, from_, to, ..)
Optional parameters
- root – root window.
- bg – background colour
- fg – foreground colour
- bd – border
- orient – orientation(vertical or horizontal)
- from_ – starting value
- to – ending value
- troughcolor – set colour for trough.
- state – decides if the widget will be responsive or unresponsive.
- sliderlength – decides the length of the slider.
- label – to display label in the widget.
- highlightbackground – the colour of the focus when widget is not focused.
- cursor – The cursor on the widget which could be arrow, circle, dot etc.
Methods
- set(value) – set the value for scale.
- get() – get the value of scale.
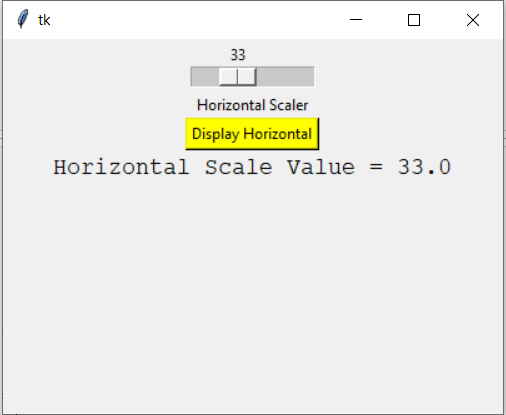
Example 1: Creating a horizontal bar
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.geometry("400x300")
v1 = DoubleVar()
def show1():
sel = "Horizontal Scale Value = " + str(v1.get())
l1.config(text = sel, font =("Courier", 14))
s1 = Scale( root, variable = v1,
from_ = 1, to = 100,
orient = HORIZONTAL)
l3 = Label(root, text = "Horizontal Scaler")
b1 = Button(root, text ="Display Horizontal",
command = show1,
bg = "yellow")
l1 = Label(root)
s1.pack(anchor = CENTER)
l3.pack()
b1.pack(anchor = CENTER)
l1.pack()
root.mainloop()
|
Output:
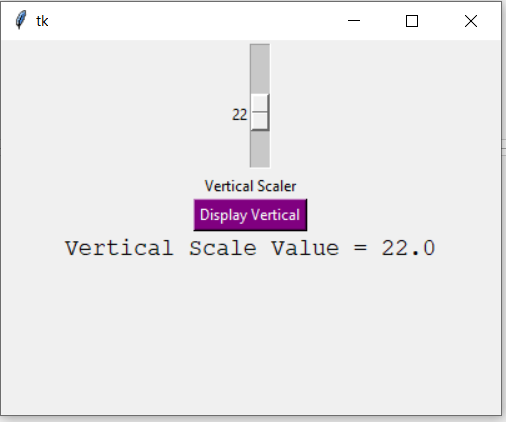
Example 2: Creating a vertical slider
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.geometry("400x300")
v2 = DoubleVar()
def show2():
sel = "Vertical Scale Value = " + str(v2.get())
l2.config(text = sel, font =("Courier", 14))
s2 = Scale( root, variable = v2,
from_ = 50, to = 1,
orient = VERTICAL)
l4 = Label(root, text = "Vertical Scaler")
b2 = Button(root, text ="Display Vertical",
command = show2,
bg = "purple",
fg = "white")
l2 = Label(root)
s2.pack(anchor = CENTER)
l4.pack()
b2.pack()
l2.pack()
root.mainloop()
|
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...