Python – tensorflow.raw_ops.Cos()
Last Updated :
06 Mar, 2023
TensorFlow is open-source python library designed by Google to develop Machine Learning models and deep learning neural networks. TensorFlow raw_ops provides low level access to all TensorFlow operations. Cos() is used to find element wise cosine of x.
Syntax: tf.raw_ops.Cos(x, name)
Parameters:
- x: It’s the input tensor. Allowed dtype for this tensor are bfloat16, half, float32, float64.
- name(optional): It defines the name for the operation.
Returns: It returns a tensor of same dtype as x.
Note: It only takes keyword arguments.
Example 1:
Python3
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype = tf.float64)
print('Input: ', a)
res = tf.raw_ops.Cos(x = a)
print('Result: ', res)
|
Output:
Input: tf.Tensor([1. 2. 3. 4. 5.], shape=(5, ), dtype=float64)
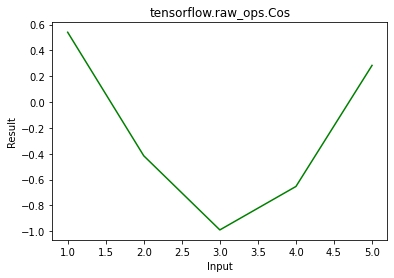
Result: tf.Tensor([ 0.54030231 -0.41614684 -0.9899925 -0.65364362 0.28366219], shape=(5, ), dtype=float64)
Example 2: Visualization
Python3
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype = tf.float64)
res = tf.raw_ops.Cos(x = a)
plt.plot(a, res, color ='green')
plt.title('tensorflow.raw_ops.Cos')
plt.xlabel('Input')
plt.ylabel('Result')
plt.show()
|
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...