Python | tensorflow.bitcast() method
Last Updated :
23 Feb, 2023
TensorFlow is open-source python library designed by Google to develop Machine Learning models and deep learning neural networks.
bitcast() is method in tensorflow library which is used to bitcast a tensor from one type to another type. It doesn’t copy the data.
Syntax:
tf.bitcast(
input, type, name
)
Arguments:
1. input: It is the Tensor and the allowed type for this tensor are
bfloat16, half, float32, float64, int64, int32, uint8, uint16, uint32,
uint64, int8, int16, complex64, complex128, qint8, quint8, qint16, quint16, qint32.
2. type: It defines the dtype in which input need to be bitcasted.
3. name: It is an optional argument. It is used to give a name to operation.
Return: It returns a tensor of type type.
Note: bitcast can’t be used to cast real dtype to complex dtype. It will raise InvalidArgumentError.
Example 1:
Python3
import tensorflow
a = tensorflow.constant(0xffffffff, dtype=tensorflow.uint32)
print('a:',a)
b = tensorflow.bitcast(a, tensorflow.uint8)
print('b:',b)
|
Output:
a: tf.Tensor(4294967295, shape=(), dtype=uint32)
b: tf.Tensor([255 255 255 255], shape=(4,), dtype=uint8)
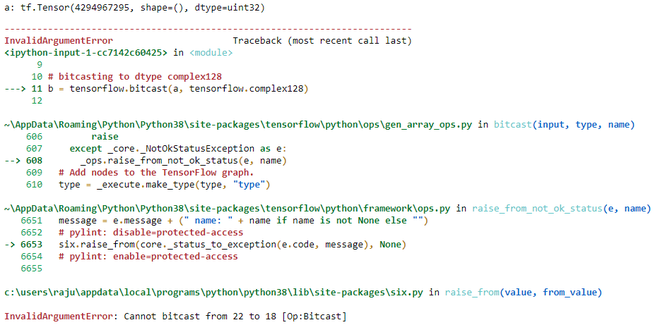
Example 2:
This example tries to bitcast a real dtype to complex dtype
Python3
import tensorflow
a = tensorflow.constant(0xffffffff, dtype=tensorflow.uint32)
print('a:',a)
b = tensorflow.bitcast(a, tensorflow.complex128)
|
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...