Python | sympy.lucas() method
Last Updated :
26 Jul, 2019
With the help of
sympy.lucas() method, we can find
Lucas numbers in SymPy.
lucas(n) -
Lucas numbers satisfy a recurrence relation similar to that of the Fibonacci sequence, in which each term is the sum of the preceding two. They are generated by choosing the initial values
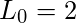
and
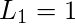
and the recurrence relation
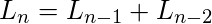
.
Syntax: lucas(n)
Parameter:
n – It denotes the number upto which lucus number is to be calculated.
Returns: Returns the nth lucas number.
Example #1:
from sympy import *
n = 7
print("Value of n = {}".format(n))
nth_lucas = lucas(n)
print("Value of nth lucas number : {}".format(nth_lucas))
|
Output:
Value of n = 7
Value of nth lucas number : 29
Example #2:
from sympy import *
n = 10
print("Value of n = {}".format(n))
n_lucas = [lucas(x) for x in range(11)]
print("N lucas number are : {}".format(n_lucas))
|
Output:
Value of n = 10
N lucas number are : [2, 1, 3, 4, 7, 11, 18, 29, 47, 76, 123]
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...