Python Pytorch arrange() method
Last Updated :
05 Aug, 2021
PyTorch is an open-source machine learning library developed by Facebook. It is used for deep neural network and natural language processing purposes.
The function torch.arrange() returns a 1-D tensor of size 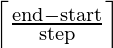
with values from the interval 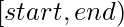 taken with common difference step beginning from start.
taken with common difference step beginning from start.
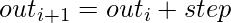
Syntax: torch.arrange(start=0, end, step=1, out=None)
Parameters:
start: the starting value for the set of points. Default: 0.
end: the ending value for the set of points
step: the gap between each pair of adjacent points. Default: 1.
out(Tensor, optional): the output tensor
Return type: A tensor
Code #1:
Python3
import torch
a = torch.arrange(3)
print("a = ", a)
b = torch.arrange(1, 6)
print("b = ", b)
c = torch.arrange(1, 5, 0.5)
print("c = ", c)
|
Output:
a = tensor([0, 1, 2])
b = tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
c = tensor([1.0000, 1.5000, 2.0000, 2.5000, 3.0000, 3.5000, 4.0000, 4.5000])
Note that the non-integer step is subject to floating-point rounding errors when comparing against end; to avoid inconsistency, we advise adding a small epsilon to the end in such cases.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...