Python program to implement Half Subtractor
Last Updated :
25 Mar, 2023
Prerequisite: Half Subtractor in Digital Logic
Given two inputs of Half Adder A, B. The task is to implement the Half Subtractor circuit and Print output i.e Difference and Borrow of two inputs.
The half subtractor is also a building block for subtracting two binary numbers. It has two inputs and two outputs. This circuit is used to subtract two single bit binary numbers A and B. The difference and borrow are the two output states of the half subtractor.
Examples:
Input: A=0; B=1
Output: Difference: 1
Borrow: 1
Explanation: According to logical expression Difference=A XOR B i.e 0 XOR 1 =1, Borrow=Ā AND B i.e 1 AND 1 =1
Input: A=1; B=1
Output: Difference: 0
Borrow: 1
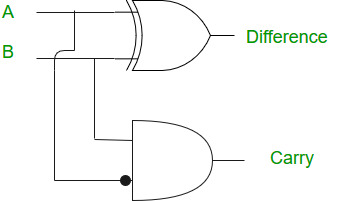
Logical Expression:
Difference = A XOR B
Borrow = Ā AND B
Logical Diagram:
Truth Table:
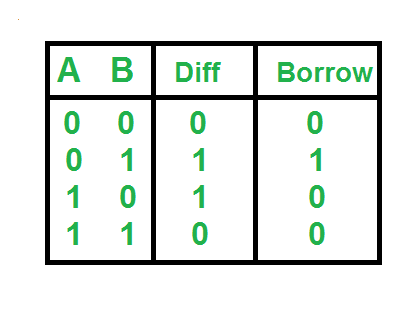
Approach:
- We take two inputs A and B.
- XOR operation on A and B gives the value of the Difference.
- AND operation on Ā and B gives the value of Borrow.
Implementation:
Python3
def getResult(A, B):
Difference = A ^ B
A = not(A)
Borrow = A & B
print("Difference:", Difference)
print("Borrow:", Borrow)
A = 0
B = 1
getResult(A, B)
|
Output:
Difference: 1
Borrow: 1
Method#2: List comprehension:
Algorithm:
- Assign values to A and B.
- Calculate the difference and borrow using XOR and NOT-AND operations, respectively.
- Store the results in the result list.
- Print the results.
Python3
A = 0
B = 1
result = [(A ^ B), int(not(A) and B)]
print("Difference:", result[0])
print("Borrow:", result[1])
|
Output
Difference: 1
Borrow: 1
Time Complexity: O(1)
The time complexity of this code is constant, as it does not depend on the size of the input. It only performs a few operations to calculate the difference and borrow.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
The space complexity of this code is also constant, as it only uses a fixed amount of memory to store the input variables and the result list, which contains two integers.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...