Python Program For Pointing To Next Higher Value Node In A Linked List With An Arbitrary Pointer
Last Updated :
20 Mar, 2023
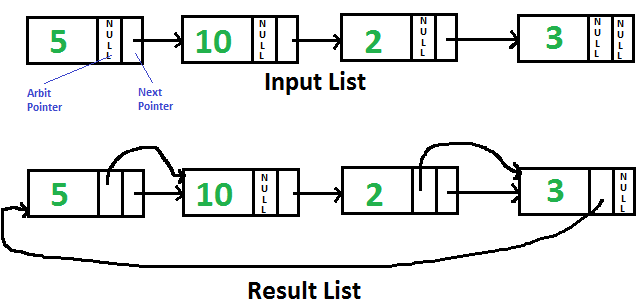
Given singly linked list with every node having an additional “arbitrary” pointer that currently points to NULL. Need to make the “arbitrary” pointer point to the next higher value node.
We strongly recommend to minimize your browser and try this yourself first
A Simple Solution is to traverse all nodes one by one, for every node, find the node which has the next greater value of the current node and change the next pointer. Time Complexity of this solution is O(n2).
An Efficient Solution works in O(nLogn) time. The idea is to use Merge Sort for linked list.
1) Traverse input list and copy next pointer to arbit pointer for every node.
2) Do Merge Sort for the linked list formed by arbit pointers.
Below is the implementation of the above idea. All of the merger sort functions are taken from here. The taken functions are modified here so that they work on arbit pointers instead of next pointers.
Python3
head = None
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.arbit = None
def printList(node, anode):
print("Traversal using Next Pointer")
while (node != None):
print(node.data, end = ", ")
node = node.next
print("Traversal using Arbit Pointer");
while (anode != None):
print(anode.data, end = ", ")
anode = anode.arbit
def populateArbit(start):
temp = start
while (temp != None):
temp.arbit = temp.next
temp = temp.next
return MergeSort(start)
def MergeSort(start):
if (start == None or start.arbit == None):
return start
middle = getMiddle(start)
nextofmiddle = middle.arbit
middle.arbit = None
left = MergeSort(start)
right = MergeSort(nextofmiddle)
sortedlist = SortedMerge(left, right)
return sortedlist
def getMiddle(source):
if (source == None):
return source
fastptr = source.arbit
slowptr = source
while (fastptr != None):
fastptr = fastptr.arbit
if (fastptr != None):
slowptr = slowptr.arbit
fastptr = fastptr.arbit
return slowptr
def SortedMerge(a, b):
result = None
if (a == None):
return b
elif (b == None):
return a
if (a.data <= b.data):
result = a
result.arbit = SortedMerge(a.arbit, b)
else:
result = b
result.arbit = SortedMerge(a, b.arbit)
return result
if __name__=='__main__':
head = Node(5)
head.next = Node(10)
head.next.next = Node(2)
head.next.next.next = Node(3)
ahead = populateArbit(head)
print("Result Linked List is:")
printList(head, ahead)
|
Output:
Result Linked List is:
Traversal using Next Pointer
5, 10, 2, 3,
Traversal using Arbit Pointer
2, 3, 5, 10,
Time Complexity: O(n log n), where n is the number of nodes in the Linked list.
Space Complexity: O(1). We are not using any extra space.
Please refer complete article on Point to next higher value node in a linked list with an arbitrary pointer for more details!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...