Python Program For Flattening A Multilevel Linked List
Last Updated :
13 Feb, 2023
Given a linked list where in addition to the next pointer, each node has a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the below figure. You are given the head of the first level of the list. Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level linked list. You need to flatten the list in a way that all nodes at the first level should come first, then nodes of the second level, and so on.
Each node is a C struct with the following definition.
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.child = None
|
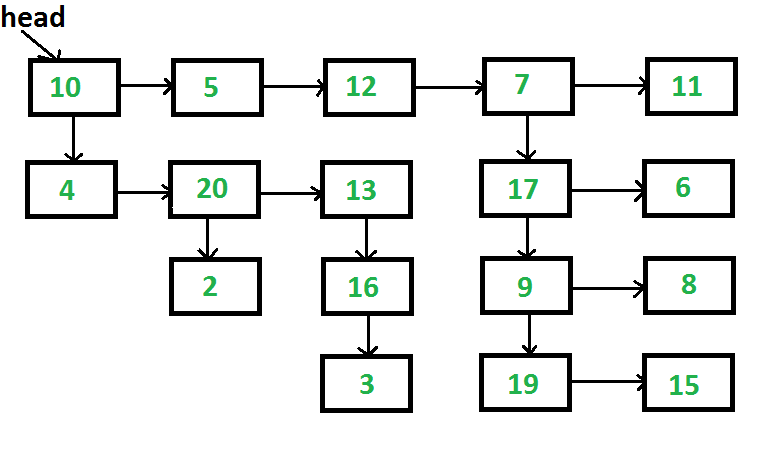
The above list should be converted to 10->5->12->7->11->4->20->13->17->6->2->16->9->8->3->19->15
The problem clearly says that we need to flatten level by level. The idea of a solution is, we start from the first level, process all nodes one by one, if a node has a child, then we append the child at the end of the list, otherwise, we don’t do anything. After the first level is processed, all next-level nodes will be appended after the first level. The same process is followed for the appended nodes.
1) Take the "cur" pointer, which will point to the head
of the first level of the list
2) Take the "tail" pointer, which will point to the end of
the first level of the list
3) Repeat the below procedure while "curr" is not NULL.
I) If the current node has a child then
a) Append this new child list to the "tail"
tail->next = cur->child
b) Find the last node of the new child list and update
the "tail"
tmp = cur->child;
while (tmp->next != NULL)
tmp = tmp->next;
tail = tmp;
II) Move to the next node. i.e. cur = cur->next
Following is the implementation of the above algorithm.
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.child = None
def newNode(data):
return Node(data)
def flattenlist(head):
if not head:
return
temp = head
while(temp.next != None):
temp = temp.next
currNode = head
while(currNode != temp):
if(currNode.child):
temp.next = currNode.child
tmp = currNode.child
while(tmp.next):
tmp = tmp.next
temp = tmp
currNode = currNode.next
def printList(head):
if not head:
return
while(head):
print("{}".format(head.data),
end = " ")
head = head.next
if __name__=='__main__':
child13 = newNode(16)
child13.child = newNode(3)
head1 = newNode(4)
head1.next = newNode(20)
head1.next.child = newNode(2)
head1.next.next = newNode(13)
head1.next.next.child = child13
child9 = newNode(19)
child9.next = newNode(15)
child17 = newNode(9)
child17.next = newNode(8)
child17.child = child9
head2 = newNode(17)
head2.next = newNode(6)
head2.child = child17
head = newNode(10)
head.child = head1
head.next = newNode(5)
head.next.next = newNode(12)
head.next.next.next = newNode(7)
head.next.next.next.child = head2
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(11)
flattenlist(head)
print("Flattened list is: ", end = "")
printList(head)
|
Output:
10 5 12 7 11 4 20 13 17 6 2 16 9 8 3 19 15
Time Complexity: Since every node is visited at most twice, the time complexity is O(n) where n is the number of nodes in given linked list.
Space Complexity : O(1)
Please refer complete article on Flatten a multilevel linked list for more details!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...