Python | Pandas Series.slice_shift()
Last Updated :
05 Feb, 2019
Pandas series is a One-dimensional ndarray with axis labels. The labels need not be unique but must be a hashable type. The object supports both integer- and label-based indexing and provides a host of methods for performing operations involving the index.
Pandas Series.slice_shift() function is equivalent to shift without copying data. The shifted data will not include the dropped periods and the shifted axis will be smaller than the original.
Syntax: Series.slice_shift(periods=1, axis=0)
Parameter :
periods : Number of periods to move, can be positive or negative
Returns : shifted : same type as caller
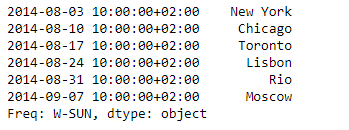
Example #1: Use Series.slice_shift() function to shift the data of the given Series object by 2 periods.
import pandas as pd
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
sr.index = didx
print(sr)
|
Output :
Now we will use Series.slice_shift() function to shift the data in the given series object by 2 periods.
sr.slice_shift(periods = 2)
|
Output :

As we can see in the output, the Series.slice_shift() function has successfully shifted the data over the index. Notice the first two index labels are dropped.
Example #2: Use Series.slice_shift() function to shift the data of the given Series object by -2 periods.
import pandas as pd
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
sr.index = didx
print(sr)
|
Output :

Now we will use Series.slice_shift() function to shift the data in the given series object by -2 periods.
sr.slice_shift(periods = -2)
|
Output :

As we can see in the output, the Series.slice_shift() function has successfully shifted the data over the index. Notice the last two index labels are dropped and the data has been shifted upward.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...