Python | Pandas Series.rolling()
Last Updated :
07 Feb, 2019
Pandas series is a One-dimensional ndarray with axis labels. The labels need not be unique but must be a hashable type. The object supports both integer and label-based indexing and provides a host of methods for performing operations involving the index.
Pandas Series.rolling() function is a very useful function. It Provides rolling window calculations over the underlying data in the given Series object.
Syntax: Series.rolling(window, min_periods=None, center=False, win_type=None, on=None, axis=0, closed=None)
Parameter :
window : Size of the moving window
min_periods : Minimum number of observations in window required to have a value
center : Set the labels at the center of the window.
win_type : Provide a window type.
on : str, optional
axis : int or str, default 0
closed : Make the interval closed on the ‘right’, ‘left’, ‘both’ or ‘neither’ endpoints.
Returns : a Window or Rolling sub-classed for the particular operation
Example #1: Use Series.rolling() function to find the rolling window sum of the underlying data for the given Series object. The size of the rolling window should be 2 and the weightage of each element should be same.
import pandas as pd
sr = pd.Series([10, 25, 3, 11, 24, 6])
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp']
sr.index = index_
print(sr)
|
Output :
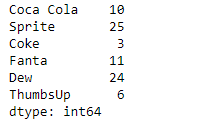
Now we will use Series.rolling() function to find the sum of the underlying data having a window size of 2.
result = sr.rolling(2).sum()
print(result)
|
Output :
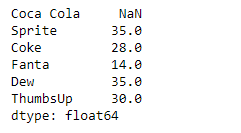
As we can see in the output, the Series.rolling() function has successfully returned a series object having found the sum of the underlying data over a window size of 2. Notice the first value is a missing value as there was no element previous to it so the sum could not be performed.
Example #2: Use Series.rolling() function to find the rolling window sum of the underlying data for the given Series object. The size of the rolling window should be 2 and the rolling window type should be ‘triang’.
import pandas as pd
sr = pd.Series([10, 25, 3, 11, 24, 6])
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp']
sr.index = index_
print(sr)
|
Output :
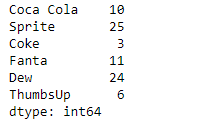
Now we will use Series.rolling() function to find the sum of the underlying data having a window size of 2.
result = sr.rolling(2, win_type ='triang').sum()
print(result)
|
Output :
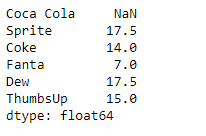
As we can see in the output, the Series.rolling() function has successfully returned a series object having found the sum of the underlying data over a window size of 2. Notice the first value is a missing value as there was no element previous to it so the sum could not be performed.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...