Python | Pandas Dataframe.at[ ]
Last Updated :
16 Jul, 2021
Python is a great language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric Python packages. Pandas is one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much easier.
Pandas at[] is used to return data in a dataframe at the passed location. The passed location is in the format [position, Column Name]. This method works in a similar way to Pandas loc[ ] but at[ ] is used to return an only single value and hence works faster than it.
Syntax: Dataframe.at[position, label]
Parameters:
position: Position of element in column
label: Column name to be used
Return type: Single element at passed position
To download the data set used in following example, click here.
In the following examples, the data frame used contains data of some NBA players. The image of data frame before any operations is attached below.
Example #1:
In this example, A dataframe is created by passing URL of csv to Pandas .read_csv() method. After that 2nd value in Name column is returned using .at[ ] method.
Python3
import pandas as pd
position = 2
label = 'Name'
output = data.at[position, label]
print(output)
|
Output:
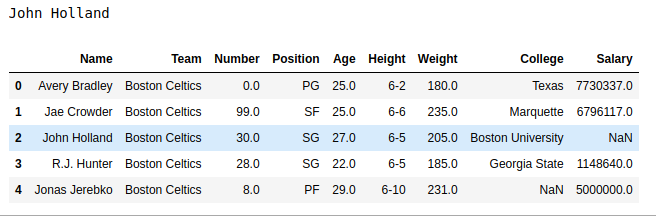
As shown in the output image, the output can be compared and it can be seen that the Value at 2nd position in the Name column is similar to output.
Note:
- Unlike, .loc[ ], This method only returns single value. Hence dataframe.at[3:6, label] will return an error.
- Since this method only works for single values, it is faster than .loc[] method.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...