Python OpenCV | cv2.blur() method
Last Updated :
04 Jan, 2023
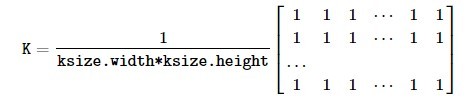
OpenCV-Python is a library of Python bindings designed to solve computer vision problems. cv2.blur() method is used to blur an image using the normalized box filter. The function smooths an image using the kernel which is represented as:
Syntax: cv2.blur(src, ksize[, dst[, anchor[, borderType]]])
Parameters:
src: It is the image whose is to be blurred.
ksize: A tuple representing the blurring kernel size.
dst: It is the output image of the same size and type as src.
anchor: It is a variable of type integer representing anchor point and it’s default value Point is (-1, -1) which means that the anchor is at the kernel center.
borderType: It depicts what kind of border to be added. It is defined by flags like cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, cv2.BORDER_REFLECT, etc
Return Value: It returns an image.
Image used for all the below examples:

Example #1:
import cv2
path = r'C:\Users\Rajnish\Desktop\geeksforgeeks\geeks.png'
image = cv2.imread(path)
window_name = 'Image'
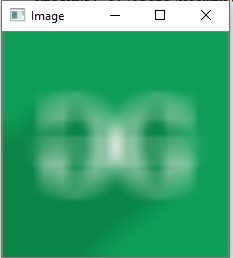
ksize = (10, 10)
image = cv2.blur(image, ksize)
cv2.imshow(window_name, image)
|
Output:

Example #2:
import cv2
path = r'C:\Users\Rajnish\Desktop\geeksforgeeks\geeks.png'
image = cv2.imread(path)
window_name = 'Image'
ksize = (30, 30)
image = cv2.blur(image, ksize, cv2.BORDER_DEFAULT)
cv2.imshow(window_name, image)
|
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...