Python MySQL – Where Clause
Last Updated :
23 Jan, 2022
Where clause is used in MySQL database to filter the data as per the condition required. You can fetch, delete or update a particular set of data in MySQL database by using where clause.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, …. columnN FROM [TABLE NAME] WHERE [CONDITION];
The above syntax is used for displaying a certain set of data following the condition.
Example: Consider the following database named college and having a table name as a student.
Schema of the database:
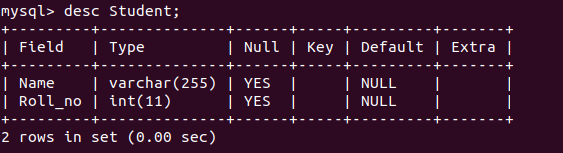
Database:
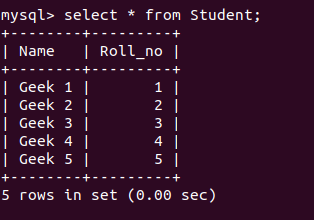
Where Clause In Python
Steps to use where clause in Python is:
- First form a connection between MySQL and Python program. It is done by importing mysql.connector package and using mysql.connector.connect() method, for passing the user name, password, host (optional default: localhost) and, database (optional) as parameters to it.
- Now, create a cursor object on the connection object created above by using cursor() method. A database cursor is a control structure that enables traversal over the records in a database.
- Then, execute the where clause statement by passing it through execute() method.
Python3
import mysql.connector
conn = mysql.connector.connect(user='your_username',
host='localhost',
password ='your_password',
database='College')
mycursor = conn.cursor();
sql = "select * from Student where Roll_no >= 3;"
mycursor.execute(sql)
myresult = mycursor.fetchall()
for x in myresult:
print(x)
conn.close()
|
OUTPUT:

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...