Python | Arithmetic operations in excel file using openpyxl
Last Updated :
19 May, 2021
Prerequisite: Reading & Writing to excel sheet using openpyxl
Openpyxl is a Python library using which one can perform multiple operations on excel files like reading, writing, arithmetic operations and plotting graphs. Let’s see how to perform different arithmetic operations using openpyxl.
- =SUM(cell1:cell2) : Adds all the numbers in a range of cells.
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = 200
sheet['A2'] = 300
sheet['A3'] = 400
sheet['A4'] = 500
sheet['A5'] = 600
sheet['A7'] = '= SUM(A1:A5)'
wb.save("sum.xlsx")
|

- =PRODUCT(cell1:cell2) : Multiplies all the numbers in the range of cells.
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = 2
sheet['A2'] = 3
sheet['A3'] = 4
sheet['A4'] = 5
sheet['A5'] = 6
sheet['A7'] = '= PRODUCT(A1:A5)'
wb.save("product.xlsx")
|

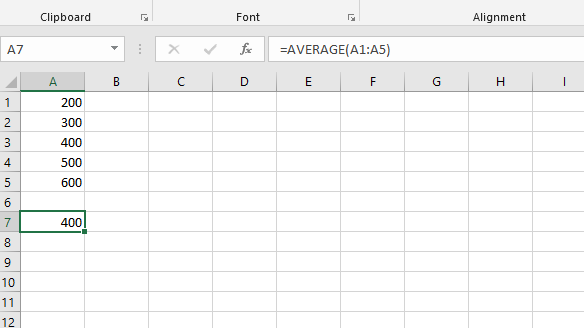
- =AVERAGE(cell1:cell2) : It gives the average (arithmetical mean) of all the numbers which is present in the given cell range.
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = 200
sheet['A2'] = 300
sheet['A3'] = 400
sheet['A4'] = 500
sheet['A5'] = 600
sheet['A7'] = '= AVERAGE(A1:A5)'
wb.save("average.xlsx")
|
- =QUOTIENT(num1, num2) : It returns the integer portion of a division.
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = '= QUOTIENT(64, 8)'
sheet['A2'] = '= QUOTIENT(25, 4)'
wb.save("quotient.xlsx")
|

- =MOD(num1, num2) : Returns the remainder after a number is divided by the divisor.
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = '= MOD(64, 8)'
sheet['A2'] = '= MOD(25, 4)'
wb.save("modulus.xlsx")
|

- =COUNT(cell1:cell2) : It counts the number of cells in a range that contain the number.
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = 200
sheet['A2'] = 300
sheet['A3'] = 400
sheet['A4'] = 500
sheet['A5'] = 600
sheet['A7'] = '= COUNT(A1:A6)'
wb.save("count.xlsx")
|

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...