Pyplot in Matplotlib
Last Updated :
03 Jan, 2024
Python is the most used language for Matplotlib is a plotting library for creating static, animated, and interactive visualizations in Python. Matplotlib can be used in Python scripts, the Python and IPython shell, web application servers, and various graphical user interface toolkits like Tkinter, awxPython, etc.
Note: For more information, refer to Python Matplotlib – An Overview
Installing Matplotlib
To use Pyplot we must first download the Matplotlib module. For this write the following command:
pip install matplotlib
Pyplot in Matplotlib Syntax
Syntax: matplotlib.pyplot.plot(*args, scalex=True, scaley=True, data=None, **kwargs)
Parameters:
This function accepts parameters that enable us to set axes scales and format the graphs. These parameters are mentioned below :-
- plot(x, y): plot x and y using default line style and color.
- plot.axis([xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]): scales the x-axis and y-axis from minimum to maximum values
- plot.(x, y, color=’green’, marker=’o’, linestyle=’dashed’, linewidth=2, markersize=12):
x and y co-ordinates are marked using circular markers of size 12 and green color line with — style of width 2
- plot.xlabel(‘X-axis’): names x-axis
- plot.ylabel(‘Y-axis’): names y-axis
- plot(x, y, label = ‘Sample line ‘): plotted Sample Line will be displayed as a legend
What is Pyplot in Matplotlib?
Pyplot is a Matplotlib module that provides a MATLAB-like interface. Matplotlib is designed to be as usable as MATLAB, with the ability to use Python and the advantage of being free and open-source. Each pyplot function makes some changes to a figure: e.g., creates a figure, creates a plotting area in a figure, plots some lines in a plotting area, decorates the plot with labels, etc. The various plots we can utilize using Pyplot are Line Plot, Histogram, Scatter, 3D Plot, Image, Contour, and Polar
Plotting in Matplotlib
We will import the matplotlib library and then plot some example data points. The plot function marks the x-coordinates(1, 2, 3, 4) and y-coordinates(1, 4, 9, 16) in a linear graph with specified scales.
Python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 9, 16])
plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 20])
plt.show()
|
Output
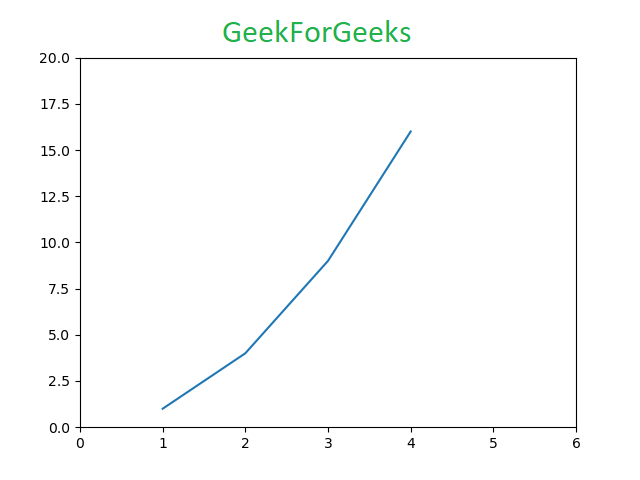
Matplotlib Pyplot Examples
There are various ways to create Matplotlib Pyplot . here we are discussing some generally used methods for create Matplotlib Pyplot those are following.
- Linear Plot using matplotlib.pyplot
- Linear Plot with Line Formatting
- Scatter Plot with Color Mapping
For the sake of example, we will use Electricity Power Consumption datasets of India and Bangladesh. Here, we are using Google Public Data as a data source.
We will plot power consumption in kWh by India and Bangladesh with years as X-axis.
Linear Plot using matplotlib.pyplot
In this example code uses Matplotlib to plot the per capita electricity consumption of India and Bangladesh from 1972 to 2012. Two lines represent the countries, with different colors. The plot includes axis labels, a title, and a legend for clarity.
Python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
year = [1972, 1982, 1992, 2002, 2012]
e_india = [100.6, 158.61, 305.54, 394.96, 724.79]
e_bangladesh = [10.5, 25.21, 58.65, 119.27, 274.87]
with different colored labels of two countries
plt.plot(year, e_india, color ='orange',
label ='India')
plt.plot(year, e_bangladesh, color ='g',
label ='Bangladesh')
plt.xlabel('Years')
plt.ylabel('Power consumption in kWh')
plt.title('Electricity consumption per capita\
of India and Bangladesh')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
|
Output :
.png)
Line Plot
Linear Plot with Line Formatting
In this example we will plot the same plot but with a variation in the lines plotted. We can use dashed line or a line with markers.
Python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
year = [1972, 1982, 1992, 2002, 2012]
e_india = [100.6, 158.61, 305.54,
394.96, 724.79]
e_bangladesh = [10.5, 25.21, 58.65,
119.27, 274.87]
plt.plot(year, e_india, color ='orange',
marker ='o', markersize = 12,
label ='India')
plt.plot(year, e_bangladesh, color ='g',
linestyle ='dashed', linewidth = 2,
label ='Bangladesh')
plt.xlabel('Years')
plt.ylabel('Power consumption in kWh')
plt.title('Electricity consumption per \
capita of India and Bangladesh')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
|
Output:
.png)
Line Plot with Line Formatting
Scatter Plot with Color Mapping
In this example Python code uses Matplotlib and NumPy to generate a scatter plot with random data. The `x` and `y` arrays represent the coordinates, and the `colors` array provides color values. The plot includes a color mapping using the ‘viridis’ colormap, a color bar for reference, and axis labels. Finally, the plot is displayed using `plt.show()`.
Python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(42)
x = np.random.rand(50)
y = np.random.rand(50)
colors = np.random.rand(50)
plt.scatter(x, y, c=colors, cmap='viridis', s=100, alpha=0.8)
cbar = plt.colorbar()
cbar.set_label('Color Value')
plt.title('Scatter Plot with Color Mapping')
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.show()
|
Output:
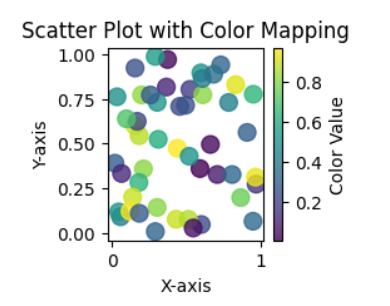
Scatter Plot with Color Mapping
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...