Public Key Infrastructure
Last Updated :
09 Jun, 2022
Public key infrastructure or PKI is the governing body behind issuing digital certificates. It helps to protect confidential data and gives unique identities to users and systems. Thus, it ensures security in communications.
The public key infrastructure uses a pair of keys: the public key and the private key to achieve security. The public keys are prone to attacks and thus an intact infrastructure is needed to maintain them.
Managing Keys in the Cryptosystem:
The security of a cryptosystem relies on its keys. Thus, it is important that we have a solid key management system in place. The 3 main areas of key management are as follows:
- A cryptographic key is a piece of data that must be managed by secure administration.
- It involves managing the key life cycle which is as follows:
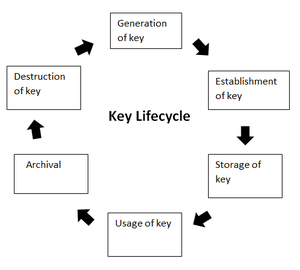
- Public key management further requires:
- Keeping the private key secret: Only the owner of a private key is authorized to use a private key. It should thus remain out of reach of any other person.
- Assuring the public key: Public keys are in the open domain and can be publicly accessed. When this extent of public accessibility, it becomes hard to know if a key is correct and what it will be used for. The purpose of a public key must be explicitly defined.
PKI or public key infrastructure aims at achieving the assurance of public key.
Public Key Infrastructure:
Public key infrastructure affirms the usage of a public key. PKI identifies a public key along with its purpose. It usually consists of the following components:
- A digital certificate also called a public key certificate
- Private Key tokens
- Registration authority
- Certification authority
- CMS or Certification management system
Working on a PKI:
Let us understand the working of PKI in steps.
- PKI and Encryption: The root of PKI involves the use of cryptography and encryption techniques. Both symmetric and asymmetric encryption uses a public key. The challenge here is – “how do you know that the public key belongs to the right person or to the person you think it belongs to?”. There is always a risk of MITM(Man in the middle). This issue is resolved by a PKI using digital certificates. It gives identities to keys in order to make the verification of owners easy and accurate.
- Public Key Certificate or Digital Certificate: Digital certificates are issued to people and electronic systems to uniquely identify them in the digital world. Here are a few noteworthy things about a digital certificate. Digital certificates are also called X.509 certificates. This is because they are based on the ITU standard X.509.
- The Certification Authority (CA) stores the public key of a user along with other information about the client in the digital certificate. The information is signed and a digital signature is also included in the certificate.
- The affirmation for the public key then thus be retrieved by validating the signature using the public key of the Certification Authority.
- Certifying Authorities: A CA issues and verifies certificates. This authority makes sure that the information in a certificate is real and correct and it also digitally signs the certificate. A CA or Certifying Authority performs these basic roles:
- Generates the key pairs – This key pair generated by the CA can be either independent or in collaboration with the client.
- Issuing of the digital certificates – When the client successfully provides the right details about his identity, the CA issues a certificate to the client. Then CA further signs this certificate digitally so that no changes can be made to the information.
- Publishing of certificates – The CA publishes the certificates so that the users can find them. They can do this by either publishing them in an electronic telephone directory or by sending them out to other people.
- Verification of certificate – CA gives a public key that helps in verifying if the access attempt is authorized or not.
- Revocation – In case of suspicious behavior of a client or loss of trust in them, the CA has the power to revoke the digital certificate.
Classes of a Digital Certificate:
A digital certificate can be divided into four broad categories. These are :
- Class 1: These can be obtained by only providing the email address.
- Class 2: These need more personal information.
- Class 3: This first checks the identity of the person making a request.
- Class 4: They are used by organizations and governments.
Process of creation of certificate:
The creation of a certificate takes place as follows:
- Private and public keys are created.
- CA requests identifying attributes of the owner of a private key.
- Public key and attributes are encoded into a CSR or Certificate Signing Request.
- Key owner signs that CSR to prove the possession of a private key.
- CA signs the certificate after validation.
Creation of Trust layers among CA Hierarchies:
Each CA has its own certificate. Thus, trust is built hierarchically where one CA issues certificates to other CAs. Moreover, there is a root certificate that is self-signed. For a root CA, the issuer and the subject are not two separate parties but a single party.
Security of Root CA:
As you saw above, the ultimate authority is the root CA. Hence, the security of root CA is of huge importance. If the private key of a root CA is not taken care of, then it might turn into a catastrophe. This is because anyone disguised as the root CA can then issue certificates. To meet security standards, a root CA should be offline 99.9% of the time. However, it does need to come online to create public and private keys and to issue new certificates. Ideally, these activities should be performed 2-4 times a year.
Use of PKI in Today’s Digital Age:
Today, there are an enormous number of applications that need require authentication. Certifications are needed at millions of places. This can not be done without a Public key infrastructure. The importance of PKI, depending on the use case and needs, has evolved over time. Here is a part of that track.
- For the very first time during the period of 1995 to 2002, the use of PKI was limited to the most important and high-value certificates. This included the certificates of eCommerce websites that enabled them to display the lock icon in the search bar. The goal was to make consumers confident about the security and authenticity of various websites.
- The second episode of PKI emerged around 2003 to 2010 when enterprises came into the picture. It was at this time that employees received laptops and the use of mobile phones was rising. Thus, employees needed access to the organization’s assets even outside the office. That is when the use of PKI looked like the best way for authentication.
- The third phase started in 2011 and is continuing to date. With the advent of new technologies like IoT(Internet of Things) and need the to scale PKI, the use, as well as the challenges in using PKI, have increased tremendously. Today, millions of certificates are issued to authenticate mobile workforces. However, managing this huge number of certificates is quite challenging.
- S/MIME, Document Signing, code or app signing also uses PKI.
Challenges that a PKI Solves:
PKI owes its popularity to the various problems its solves. Some use cases of PKI are:
- Securing web browsers and communicating networks by SSL/TLS certifications.
- Maintaining Access Rights over Intranets and VPNs.
- Data Encryption
- Digitally Signed Software
- Wi-fi Access Without Passwords
Other than these, one of the most important use cases of PKI is based around IoT(Internet of Things). Here are two industries that are using PKI for IoT devices:
- Auto Manufacturers: Cars these days have features like GPS, call for services, assistants, etc. These require communication paths where a lot of data is passed. Making these connections secure is very important to avoid malicious parties hacking into the cars. This is where PKI comes in.
- Medical device Manufacturers: Devices like surgical robots require high security. Also, FDA mandates that any next-generation medical device must be updatable so that bugs can be removed and security issues can be dealt with. PKI is used to issues certificates to such devices.
Disadvantages of PKI:
- Speed: Since PKI uses super complex algorithms to create a secure key pair. So it eventually slows down the process and data transfer.
- Private Key Compromise: Even though PKI can’t be hacked very easily but a private key can be hacked by a professional hacker, since PKI uses Public and Private key to encrypt and decrypt data so with user’s private key in hand and public key which is easily available the information can be decrypted easily.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...