Progress Dialog in Android with Example
Last Updated :
14 Feb, 2022
In Android, a Progress Dialog is a type of alert message that can be invoked to appear on the screen to display the progress of an action that is loading. By default, a Progress Dialog has a title, a message, and a circular progress bar that keeps rotating. A sample Progress Dialog is shown in the below image.
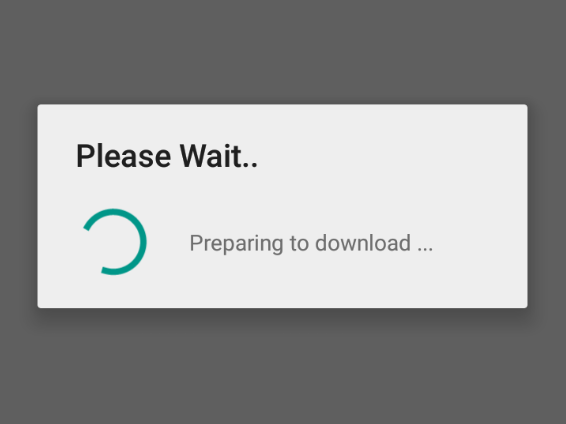
In this article, we will show you how you could create and display a similar-looking Progress Dialog in Android. Follow the below steps once the IDE is ready.
Step by Step Implementation
Step 1: Create a New Project in Android Studio
To create a new project in Android Studio please refer to How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio. We demonstrated the application in Kotlin, so make sure you select Kotlin as the primary language while creating a New Project.
Step 2: Working with the activity_main.xml file
Navigate to the app > res > layout > activity_main.xml and add the below code to that file. Below is the code for the activity_main.xml file. Add a Button as shown below. This button would be used to invoke the Progress Dialog.
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="click"/>
</RelativeLayout>
|
Step 3: Working with the MainActivity.kt file
Go to the MainActivity.kt file and refer to the following code. Below is the code for the MainActivity.kt file. Comments are added inside the code to understand the code in more detail.
Kotlin
package org.geeksforgeeks.basicprogressdialog
import android.app.ProgressDialog
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.WindowManager
import android.widget.Button
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val mButton = findViewById<Button>(R.id.button_1)
mButton.setOnClickListener {
val mProgressDialog = ProgressDialog(this)
mProgressDialog.setTitle("This is TITLE")
mProgressDialog.setMessage("This is MESSAGE")
mProgressDialog.show()
}
}
}
|
Output:
You can see that when Button is clicked, Progress Dialog appears on the screen. The back button can be pressed to exit Progress Dialog. However, Progress Dialog can be programmed to run until a task is complete while the back button can be disabled during the entire process.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...