Program to Find GCD or HCF of Two Numbers
Last Updated :
18 Jan, 2024
Given two numbers a and b, the task is to find the GCD of the two numbers.
Note: The GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) or HCF (Highest Common Factor) of two numbers is the largest number that divides both of them.
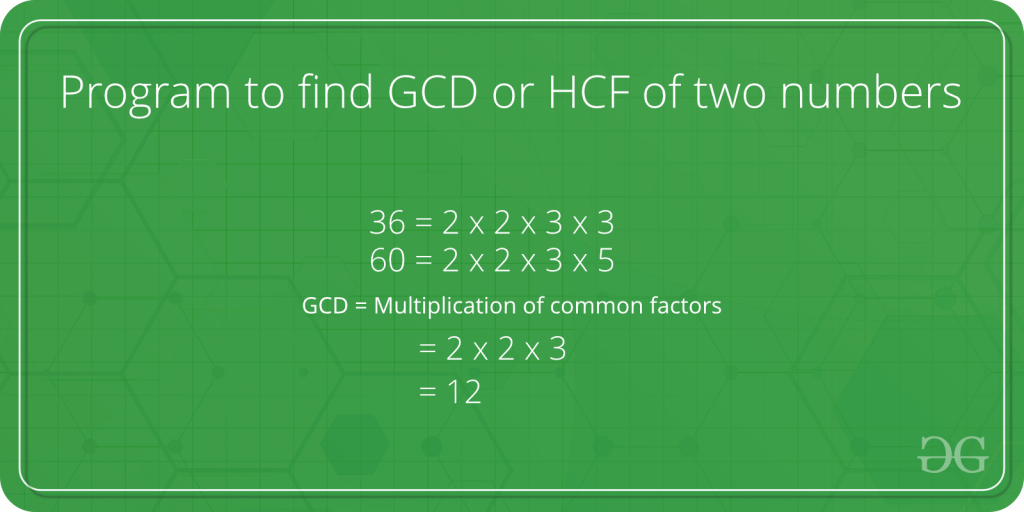
Examples:
Input: a = 20, b = 28
Output: 4
Explanation: The factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10 and 20. The factors of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14 and 28. Among these factors, 1, 2 and 4 are the common factors of both 20 and 28. The greatest among the common factors is 4.
Input: a = 60, b = 36
Output: 12
Naive Approach for GCD of two numbers:
The basic idea is to find the minimum of the two numbers and find its highest factor which is also a factor of the other number.
Below is the code implementation of the above idea:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
int result = min(a, b);
while (result > 0) {
if (a % result == 0 && b % result == 0) {
break;
}
result--;
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
cout << "GCD of " << a << " and " << b << " is "
<< gcd(a, b);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
int result = ((a < b) ? a : b);
while (result > 0) {
if (a % result == 0 && b % result == 0) {
break;
}
result--;
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
printf("GCD of %d and %d is %d ", a, b, gcd(a, b));
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
int result = Math.min(a, b);
while (result > 0) {
if (a % result == 0 && b % result == 0) {
break;
}
result--;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
System.out.print("GCD of " + a + " and " + b
+ " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Python3
def gcd(a, b):
result = min(a, b)
while result:
if a % result == 0 and b % result == 0:
break
result -= 1
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = 98
b = 56
print(f"GCD of {a} and {b} is {gcd(a, b)}")
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
int result = Math.Min(a, b);
while (result > 0) {
if (a % result == 0 && b % result == 0) {
break;
}
result--;
}
return result;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
Console.WriteLine("GCD of " + a + " and " + b
+ " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Javascript
function gcd(a,b)
{
let result = Math.min(a, b);
while (result > 0) {
if (a % result == 0 && b % result == 0) {
break;
}
result--;
}
return result;
}
let a = 98;
let b = 56;
console.log("GCD of ",a," and ",b," is ",gcd(a, b));
|
Output
GCD of 98 and 56 is 14
Time Complexity: O(min(a,b))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
The idea of this algorithm is, the GCD of two numbers doesn’t change if the smaller number is subtracted from the bigger number. This is the Euclidean algorithm by subtraction. It is a process of repeat subtraction, carrying the result forward each time until the result is equal to any one number being subtracted.
Pseudo-code:
gcd(a, b):
if a = b:
return a
if a > b:
return gcd(a – b, b)
else:
return gcd(a, b – a)
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b)
return gcd(a - b, b);
return gcd(a, b - a);
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
cout << "GCD of " << a << " and " << b << " is "
<< gcd(a, b);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b)
return gcd(a - b, b);
return gcd(a, b - a);
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
printf("GCD of %d and %d is %d ", a, b, gcd(a, b));
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class Test {
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b)
return gcd(a - b, b);
return gcd(a, b - a);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
System.out.println("GCD of " + a + " and " + b
+ " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Python3
def gcd(a, b):
if (a == 0):
return b
if (b == 0):
return a
if (a == b):
return a
if (a > b):
return gcd(a-b, b)
return gcd(a, b-a)
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = 98
b = 56
if(gcd(a, b)):
print('GCD of', a, 'and', b, 'is', gcd(a, b))
else:
print('not found')
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b)
return gcd(a - b, b);
return gcd(a, b - a);
}
public static void Main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
Console.WriteLine("GCD of " + a + " and " + b
+ " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Javascript
function gcd(a, b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b)
return gcd(a-b, b);
return gcd(a, b-a);
}
let a = 98, b = 56;
console.log("GCD of "+ a + " and " + b + " is " + gcd(a, b));
|
PHP
<?php
function gcd($a, $b)
{
if ($a == 0)
return $b;
if ($b == 0)
return $a;
if($a == $b)
return $a ;
if($a > $b)
return gcd( $a-$b , $b ) ;
return gcd( $a , $b-$a ) ;
}
$a = 98 ;
$b = 56 ;
echo "GCD of $a and $b is ", gcd($a , $b) ;
?>
|
Output
GCD of 98 and 56 is 14
Time Complexity: O(min(a,b))
Auxiliary Space: O(1) No space is used as it is a tail recursion.
Optimization by checking divisibility:
The above method can be optimized based on the following idea:
If we notice the previous approach, we can see at some point, one number becomes a factor of the other so instead of repeatedly subtracting till both become equal, we can check if it is a factor of the other.
Illustration:
See the below illustration for a better understanding:
Consider a = 98 and b = 56
a = 98, b = 56:
- a > b so put a = a-b and b remains same. So a = 98-56 = 42 & b= 56.
a = 42, b = 56:
- Since b > a, we check if b%a=0. Since answer is no, we proceed further.
- Now b>a. So b = b-a and a remains same. So b = 56-42 = 14 & a= 42.
a = 42, b = 14:
- Since a>b, we check if a%b=0. Now the answer is yes.
- So we print smaller among a and b as H.C.F . i.e. 42 is 3 times of 14.
So HCF is 14.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b) {
if (a % b == 0)
return b;
return gcd(a - b, b);
}
if (b % a == 0)
return a;
return gcd(a, b - a);
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
cout << "GCD of " << a << " and " << b << " is "
<< gcd(a, b);
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class GCD {
static int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b) {
if (a % b == 0)
return b;
return gcd(a - b, b);
}
if (b % a == 0)
return a;
return gcd(a, b - a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 98, b = 56;
System.out.println("GCD of " + a + " and " + b + " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Python3
def gcd(a, b):
if a == 0:
return b
if b == 0:
return a
if a == b:
return a
if a > b:
if a % b == 0:
return b
return gcd(a - b, b)
if b % a == 0:
return a
return gcd(a, b - a)
a = 98
b = 56
print(f"GCD of {a} and {b} is {gcd(a, b)}")
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static int GCD(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
if (a == b)
return a;
if (a > b)
{
if (a % b == 0)
return b;
return GCD(a - b, b);
}
if (b % a == 0)
return a;
return GCD(a, b - a);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
Console.WriteLine("GCD of " + a + " and " + b + " is " + GCD(a, b));
}
}
|
Javascript
function gcd(a, b) {
if (a === 0) {
return b;
}
if (b === 0) {
return a;
}
if (a === b) {
return a;
}
if (a > b) {
if (a % b === 0) {
return b;
}
return gcd(a - b, b);
}
if (b % a === 0) {
return a;
}
return gcd(a, b - a);
}
let a = 98;
let b = 56;
console.log(`GCD of ${a} and ${b} is ${gcd(a, b)}`);
|
Output
GCD of 98 and 56 is 14
Time Complexity: O(min(a, b))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Optimization using division:
Instead of the Euclidean algorithm by subtraction, a better approach can be used. We don’t perform subtraction here. we continuously divide the bigger number by the smaller number. More can be learned about this efficient solution by using the modulo operator in Euclidean algorithm.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
cout<<"GCD of "<<a<<" and "<<b<<" is "<<gcd(a, b);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
printf("GCD of %d and %d is %d ", a, b, gcd(a, b));
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class Test
{
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
System.out.println("GCD of " + a +" and " + b + " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Python3
def gcd(a,b):
if (b == 0):
return a
return gcd(b, a%b)
a = 98
b = 56
if(gcd(a, b)):
print('GCD of', a, 'and', b, 'is', gcd(a, b))
else:
print('not found')
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
public static void Main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
Console.WriteLine("GCD of "
+ a +" and " + b + " is "
+ gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function gcd(a, b){
if(b == 0){
return a;
}
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
let a = 98;
let b = 56;
document.write(`GCD of ${a} and ${b} is ${gcd(a, b)}`);
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function gcd($a, $b)
{
if($b==0)
return $a ;
return gcd( $b , $a % $b ) ;
}
$a = 98 ;
$b = 56 ;
echo "GCD of $a and $b is ", gcd($a , $b) ;
?>
|
Output
GCD of 98 and 56 is 14
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(log(min(a,b)))
- The derivation for this is obtained from the analysis of the worst-case scenario.
- What we do is we ask what are the 2 least numbers that take 1 step, those would be (1,1). If we want to increase the number of steps to 2 while keeping the numbers as low as possible as we can take the numbers to be (1,2). Similarly, for 3 steps, the numbers would be (2,3), 4 would be (3,5), 5 would be (5,8).
- So we can notice a pattern here, for the nth step the numbers would be (fib(n), fib(n+1)). So the worst-case time complexity would be O(n) where a ? fib(n) and b ? fib(n+1).
- Now Fibonacci series is an exponentially growing series where the ratio of nth/(n-1)th term approaches (sqrt(5)+1)/2 which is also called the golden ratio. So we can see that the time complexity of the algorithm increases linearly as the terms grow exponentially hence the time complexity would be log(min(a,b)).
Auxiliary Space: O(log(min(a,b))
Iterative implementation for GCD of two numbers using Euclidean Algorithm:
Below is the iterative way to find the GCD of two numbers using Euclidean algorithm.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
while (a > 0 && b > 0) {
if (a > b) {
a = a % b;
}
else {
b = b % a;
}
}
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
return a;
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
cout << "GCD of " << a << " and " << b << " is "
<< gcd(a, b);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
while (a > 0 && b > 0) {
if (a > b) {
a = a % b;
}
else {
b = b % a;
}
}
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
return a;
}
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
printf("GCD of %d and %d is %d ", a, b, gcd(a, b));
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class Test {
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
while (a > 0 && b > 0) {
if (a > b) {
a = a % b;
}
else {
b = b % a;
}
}
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
return a;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
System.out.println("GCD of " + a + " and " + b
+ " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Python3
def gcd(a, b):
while(a > 0 and b > 0):
if (a > b):
a = a % b
else:
b = b % a
if (a == 0):
return b
return a
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = 98
b = 56
if(gcd(a, b)):
print('GCD of', a, 'and', b, 'is', gcd(a, b))
else:
print('not found')
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
while (a > 0 && b > 0) {
if (a > b) {
a = a % b;
}
else {
b = b % a;
}
}
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
return a;
}
public static void Main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
Console.WriteLine("GCD of " + a + " and " + b
+ " is " + gcd(a, b));
}
}
|
Javascript
function gcd(a, b){
while (a > 0 && b > 0) {
if (a > b) {
a = a % b;
}
else {
b = b % a;
}
}
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
return a;
}
let a = 98;
let b = 56;
console.log(`GCD of ${a} and ${b} is ${gcd(a, b)}`);
|
Output
GCD of 98 and 56 is 14
Time Complexity: O(log(min(a,b)))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
GCD of two numbers using inbuilt function:
Languages like C++ have inbuilt functions to calculate GCD of two numbers.
Below is the implementation using inbuilt functions.
C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
cout << "The gcd of a and b is " << __gcd(a, b) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
int gcd = gcd(a, b);
System.out.println("The gcd of a and b is " + gcd);
}
public static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
BigInteger bigA = BigInteger.valueOf(Math.abs(a));
BigInteger bigB = BigInteger.valueOf(Math.abs(b));
BigInteger gcd = bigA.gcd(bigB);
return gcd.intValue();
}
}
|
Python3
import math
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = 98
b = 56
gcd_result = math.gcd(a, b)
print("The gcd of a and b is", gcd_result)
|
C#
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int a = 98, b = 56;
Console.WriteLine($"The gcd of a and b is {GCD(a, b)}");
}
static int GCD(int a, int b)
{
return Math.Abs(b == 0 ? a : GCD(b, a % b));
}
}
|
Javascript
function gcd(a, b) {
if (b === 0) {
return a;
} else {
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
}
const a = 98;
const b = 56;
console.log("The gcd of a and b is " + gcd(a, b));
|
Output
The gcd of a and b is 14
Time Complexity: O(log(min(a, b)))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Please refer GCD of more than two (or array) numbers to find HCF of more than two numbers.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...