Program to construct a DFA which accepts the language L = {aN | N ≥ 1}
Last Updated :
28 Jun, 2021
Prerequisite: Finite Automata
Given a string S of size N, the task is to design a Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) for accepting the language L = {aN | N ? 1}. The regular language L is {a, aa, aaa, aaaaaaa…, }. If the given string follows the given language L, then print “Accepted”. Otherwise, print “Not Accepted”.
Examples:
Input: S = “aaabbb”
Output: Not Accepted
Explanation: String must only contain a.
Input: S = “aa”
Output: Accepted
Approach: The idea by which the automata lead to acceptance of string is stated below in steps:
- The automata will accept all the strings containing only the character ‘a’. If the user tried to input any character other than ‘a’, the machine will reject it.
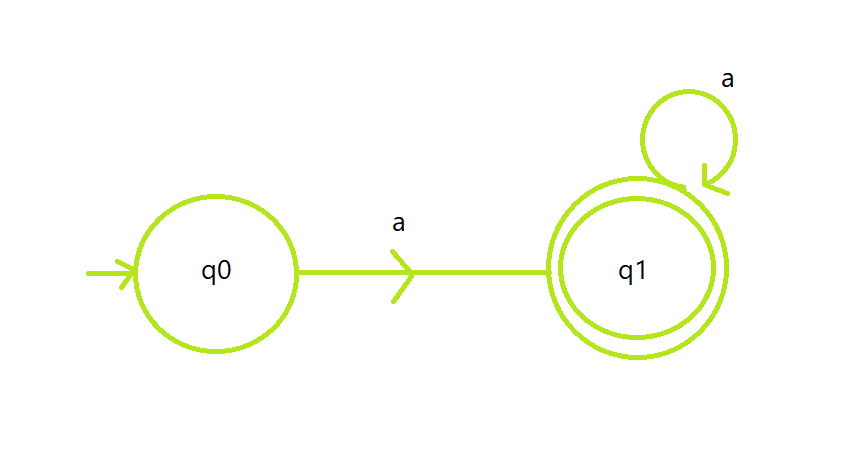
- Let the state q0 is the initial state represent the set of all strings of length 0, state q1 is the final state represent the set of all strings from 1 to N.
- State q1 contains a self-loop of a which indicates that it can be repeated as required.
- The logic for code is very basic as it has only a for loop which counts the number of a’s in a given string, if the count of a is the same as N then it will be accepted. Otherwise, the string will be rejected.
DFA State Transition Diagram:
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void isAcceptedDFA(string s, int N)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (s[i] == 'a')
count++;
}
if (count == N && count != 0) {
cout << "Accepted";
}
else {
cout << "Not Accepted";
}
}
int main()
{
string S = "aaaaa";
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.size());
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static void isAcceptedDFA(String s, int N)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (s.charAt(i) == 'a')
count++;
}
if (count == N && count != 0)
{
System.out.print("Accepted");
}
else
{
System.out.print("Not Accepted");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String S = "aaaaa";
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.length());
}
}
|
Python3
def isAcceptedDFA(s, N):
count = 0
for i in range(N):
if (s[i] == 'a'):
count += 1
if (count == N and count != 0):
print ("Accepted")
else :
print ("Not Accepted")
if __name__ == '__main__':
S = "aaaaa"
isAcceptedDFA(S, len(S))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static void isAcceptedDFA(String s, int N)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (s[i] == 'a')
count++;
}
if (count == N && count != 0)
{
Console.Write("Accepted");
}
else
{
Console.Write("Not Accepted");
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String S = "aaaaa";
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.Length);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function isAcceptedDFA(s, N) {
var count = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (s[i] === "a") count++;
}
if (count === N && count !== 0) {
document.write("Accepted");
}
else {
document.write("Not Accepted");
}
}
var S = "aaaaa";
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.length);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...