Prerequisite : Gaussian Elimination to Solve Linear Equations
Introduction : The Gauss-Jordan method, also known as Gauss-Jordan elimination method is used to solve a system of linear equations and is a modified version of Gauss Elimination Method.
It is similar and simpler than Gauss Elimination Method as we have to perform 2 different process in Gauss Elimination Method i.e.
- Formation of upper triangular matrix, and
- Back substitution
But in case of Gauss-Jordan Elimination Method, we only have to form a reduced row echelon form (diagonal matrix). Below given is the flow-chart of Gauss-Jordan Elimination Method.
Flow Chart of Gauss-Jordan Elimination Method :

Examples :
Input : 2y + z = 4
x + y + 2z = 6
2x + y + z = 7
Output :
Final Augmented Matrix is :
1 0 0 2.2
0 2 0 2.8
0 0 -2.5 -3
Result is : 2.2 1.4 1.2
Explanation : Below given is the explanation of the above example.
- Input Augmented Matrix is :
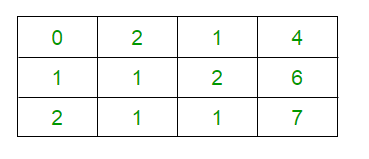
- Interchanging R1 and R2, we get
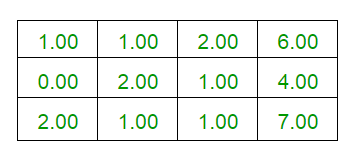
- Performing the row operation R3 <- R3 - (2*R1)
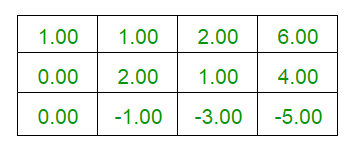
- Performing the row operations R1 <- R1 - ((1/2)* R2) and R3 <- R3 + ((1/2)*R2)
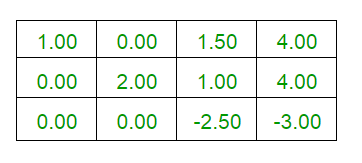
- Performing R1 <- R1 + ((3/5)*R3) and R2 <- R2 + ((2/5)*R3)
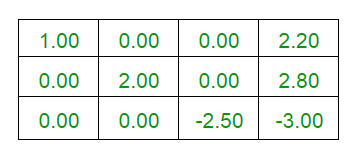
- Unique Solutions are :

Implementation:
// C++ Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
// Elimination Method
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define M 10
// Function to print the matrix
void PrintMatrix(float a[][M], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// function to reduce matrix to reduced
// row echelon form.
int PerformOperation(float a[][M], int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0, c, flag = 0, m = 0;
float pro = 0;
// Performing elementary operations
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i][i] == 0)
{
c = 1;
while ((i + c) < n && a[i + c][i] == 0)
c++;
if ((i + c) == n) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (j = i, k = 0; k <= n; k++)
swap(a[j][k], a[j+c][k]);
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Excluding all i == j
if (i != j) {
// Converting Matrix to reduced row
// echelon form(diagonal matrix)
float pro = a[j][i] / a[i][i];
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
a[j][k] = a[j][k] - (a[i][k]) * pro;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
// Function to print the desired result
// if unique solutions exists, otherwise
// prints no solution or infinite solutions
// depending upon the input given.
void PrintResult(float a[][M], int n, int flag)
{
cout << "Result is : ";
if (flag == 2)
cout << "Infinite Solutions Exists" << endl;
else if (flag == 3)
cout << "No Solution Exists" << endl;
// Printing the solution by dividing constants by
// their respective diagonal elements
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i][n] / a[i][i] << " ";
}
}
// To check whether infinite solutions
// exists or no solution exists
int CheckConsistency(float a[][M], int n, int flag)
{
int i, j;
float sum;
// flag == 2 for infinite solution
// flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum = sum + a[i][j];
if (sum == a[i][j])
flag = 2;
}
return flag;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
float a[M][M] = {{ 0, 2, 1, 4 },
{ 1, 1, 2, 6 },
{ 2, 1, 1, 7 }};
// Order of Matrix(n)
int n = 3, flag = 0;
// Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n);
if (flag == 1)
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag);
// Printing Final Matrix
cout << "Final Augmented Matrix is : " << endl;
PrintMatrix(a, n);
cout << endl;
// Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag);
return 0;
}
// Java Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
// Elimination Method
class GFG {
static int M = 10;
// Function to print the matrix
static void PrintMatrix(float a[][], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
// function to reduce matrix to reduced
// row echelon form.
static int PerformOperation(float a[][], int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0, c, flag = 0, m = 0;
float pro = 0;
// Performing elementary operations
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i][i] == 0)
{
c = 1;
while ((i + c) < n && a[i + c][i] == 0)
c++;
if ((i + c) == n)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (j = i, k = 0; k <= n; k++)
{
float temp =a[j][k];
a[j][k] = a[j+c][k];
a[j+c][k] = temp;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// Excluding all i == j
if (i != j)
{
// Converting Matrix to reduced row
// echelon form(diagonal matrix)
float p = a[j][i] / a[i][i];
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
a[j][k] = a[j][k] - (a[i][k]) * p;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
// Function to print the desired result
// if unique solutions exists, otherwise
// prints no solution or infinite solutions
// depending upon the input given.
static void PrintResult(float a[][], int n, int flag)
{
System.out.print("Result is : ");
if (flag == 2)
System.out.println("Infinite Solutions Exists");
else if (flag == 3)
System.out.println("No Solution Exists");
// Printing the solution by dividing constants by
// their respective diagonal elements
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(a[i][n] / a[i][i] +" ");
}
}
// To check whether infinite solutions
// exists or no solution exists
static int CheckConsistency(float a[][], int n, int flag)
{
int i, j;
float sum;
// flag == 2 for infinite solution
// flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum = sum + a[i][j];
if (sum == a[i][j])
flag = 2;
}
return flag;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float a[][] = {{ 0, 2, 1, 4 },
{ 1, 1, 2, 6 },
{ 2, 1, 1, 7 }};
// Order of Matrix(n)
int n = 3, flag = 0;
// Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n);
if (flag == 1)
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag);
// Printing Final Matrix
System.out.println("Final Augmented Matrix is : ");
PrintMatrix(a, n);
System.out.println("");
// Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
// C# Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
// Elimination Method
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int M = 10;
// Function to print the matrix
static void PrintMatrix(float [,]a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
Console.Write(a[i, j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// function to reduce matrix to reduced
// row echelon form.
static int PerformOperation(float [,]a, int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0, c, flag = 0;
// Performing elementary operations
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i, i] == 0)
{
c = 1;
while ((i + c) < n && a[i + c, i] == 0)
c++;
if ((i + c) == n)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (j = i, k = 0; k <= n; k++)
{
float temp = a[j, k];
a[j, k] = a[j + c, k];
a[j + c, k] = temp;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// Excluding all i == j
if (i != j)
{
// Converting Matrix to reduced row
// echelon form(diagonal matrix)
float p = a[j, i] / a[i, i];
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
a[j, k] = a[j, k] - (a[i, k]) * p;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
// Function to print the desired result
// if unique solutions exists, otherwise
// prints no solution or infinite solutions
// depending upon the input given.
static void PrintResult(float [,]a,
int n, int flag)
{
Console.Write("Result is : ");
if (flag == 2)
Console.WriteLine("Infinite Solutions Exists");
else if (flag == 3)
Console.WriteLine("No Solution Exists");
// Printing the solution by dividing
// constants by their respective
// diagonal elements
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(a[i, n] / a[i, i] + " ");
}
}
// To check whether infinite solutions
// exists or no solution exists
static int CheckConsistency(float [,]a,
int n, int flag)
{
int i, j;
float sum;
// flag == 2 for infinite solution
// flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum = sum + a[i, j];
if (sum == a[i, j])
flag = 2;
}
return flag;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
float [,]a = {{ 0, 2, 1, 4 },
{ 1, 1, 2, 6 },
{ 2, 1, 1, 7 }};
// Order of Matrix(n)
int n = 3, flag = 0;
// Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n);
if (flag == 1)
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag);
// Printing Final Matrix
Console.WriteLine("Final Augmented Matrix is : ");
PrintMatrix(a, n);
Console.WriteLine("");
// Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script>
// JavaScript Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
// Elimination Method
let M = 10;
// Function to print the matrix
function PrintMatrix(a,n)
{
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (let j = 0; j <= n; j++)
document.write(a[i][j] + " ");
document.write("<br>");
}
}
// function to reduce matrix to reduced
// row echelon form.
function PerformOperation(a,n)
{
let i, j, k = 0, c, flag = 0, m = 0;
let pro = 0;
// Performing elementary operations
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i][i] == 0)
{
c = 1;
while ((i + c) < n && a[i + c][i] == 0)
c++;
if ((i + c) == n)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (j = i, k = 0; k <= n; k++)
{
let temp =a[j][k];
a[j][k] = a[j+c][k];
a[j+c][k] = temp;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// Excluding all i == j
if (i != j)
{
// Converting Matrix to reduced row
// echelon form(diagonal matrix)
let p = a[j][i] / a[i][i];
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
a[j][k] = a[j][k] - (a[i][k]) * p;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
// Function to print the desired result
// if unique solutions exists, otherwise
// prints no solution or infinite solutions
// depending upon the input given.
function PrintResult(a,n,flag)
{
document.write("Result is : ");
if (flag == 2)
document.write("Infinite Solutions Exists<br>");
else if (flag == 3)
document.write("No Solution Exists<br>");
// Printing the solution by dividing constants by
// their respective diagonal elements
else {
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(a[i][n] / a[i][i] +" ");
}
}
// To check whether infinite solutions
// exists or no solution exists
function CheckConsistency(a,n,flag)
{
let i, j;
let sum;
// flag == 2 for infinite solution
// flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum = sum + a[i][j];
if (sum == a[i][j])
flag = 2;
}
return flag;
}
// Driver code
let a=[[ 0, 2, 1, 4 ],
[ 1, 1, 2, 6 ],
[ 2, 1, 1, 7 ]];
// Order of Matrix(n)
let n = 3, flag = 0;
// Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n);
if (flag == 1)
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag);
// Printing Final Matrix
document.write("Final Augmented Matrix is : <br>");
PrintMatrix(a, n);
document.write("<br>");
// Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag);
// This code is contributed by rag2127
</script>
# Python3 Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
# Elimination Method
M = 10
# Function to print the matrix
def PrintMatrix(a, n):
for i in range(n):
print(*a[i])
# function to reduce matrix to reduced
# row echelon form.
def PerformOperation(a, n):
i = 0
j = 0
k = 0
c = 0
flag = 0
m = 0
pro = 0
# Performing elementary operations
for i in range(n):
if (a[i][i] == 0):
c = 1
while ((i + c) < n and a[i + c][i] == 0):
c += 1
if ((i + c) == n):
flag = 1
break
j = i
for k in range(1 + n):
temp = a[j][k]
a[j][k] = a[j+c][k]
a[j+c][k] = temp
for j in range(n):
# Excluding all i == j
if (i != j):
# Converting Matrix to reduced row
# echelon form(diagonal matrix)
p = a[j][i] / a[i][i]
k = 0
for k in range(n + 1):
a[j][k] = a[j][k] - (a[i][k]) * p
return flag
# Function to print the desired result
# if unique solutions exists, otherwise
# prints no solution or infinite solutions
# depending upon the input given.
def PrintResult(a, n, flag):
print("Result is : ")
if (flag == 2):
print("Infinite Solutions Exists<br>")
elif (flag == 3):
print("No Solution Exists<br>")
# Printing the solution by dividing constants by
# their respective diagonal elements
else:
for i in range(n):
print(a[i][n] / a[i][i], end=" ")
# To check whether infinite solutions
# exists or no solution exists
def CheckConsistency(a, n, flag):
# flag == 2 for infinite solution
# flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3
for i in range(n):
sum = 0
for j in range(n):
sum = sum + a[i][j]
if (sum == a[i][j]):
flag = 2
return flag
# Driver code
a = [[0, 2, 1, 4], [1, 1, 2, 6], [2, 1, 1, 7]]
# Order of Matrix(n)
n = 3
flag = 0
# Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n)
if (flag == 1):
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag)
# Printing Final Matrix
print("Final Augmented Matrix is : ")
PrintMatrix(a, n)
print()
# Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag)
# This code is contributed by phasing17
Output
Final Augmented Matrix is : 1 0 0 2.2 0 2 0 2.8 0 0 -2.5 -3 Result is : 2.2 1.4 1.2
Applications :
- Solving System of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination Method can be used for finding the solution of a systems of linear equations which is applied throughout the mathematics.
- Finding Determinant: The Gaussian Elimination can be applied to a square matrix in order to find determinant of the matrix.
- Finding Inverse of Matrix: The Gauss-Jordan Elimination method can be used in determining the inverse of a square matrix.
- Finding Ranks and Bases: Using reduced row echelon form, the ranks as well as bases of square matrices can be computed by Gaussian elimination method.