Program for Decimal to Octal Conversion
Last Updated :
03 May, 2023
Given a decimal number as input, we need to write a program to convert the given decimal number into an equivalent octal number. i.e convert the number with base value 10 to base value 8. The base value of a number system determines the number of digits used to represent a numeric value. For example, the binary number system uses two digits 0 and 1, the octal number system uses 8 digits from 0-7 and the decimal number system uses 10 digits 0-9 to represent any numeric value.
Examples:
Input : 16
Output: 20
Input : 10
Output: 12
Input : 33
Output: 41
Algorithm:
- Store the remainder when the number is divided by 8 in an array.
- Divide the number by 8 now
- Repeat the above two steps until the number is not equal to 0.
- Print the array in reverse order now.
For Example:
If the given decimal number is 16.
Step 1: Remainder when 16 is divided by 8 is 0. Therefore, arr[0] = 0.
Step 2: Divide 16 by 8. New number is 16/8 = 2.
Step 3: Remainder, when 2 is divided by 8, is 2. Therefore, arr[1] = 2.
Step 4: Divide 2 by 8. New number is 2/8 = 0.
Step 5: Since number becomes = 0.
Stop repeating steps and print the array in reverse order. Therefore, the equivalent octal number is 20.
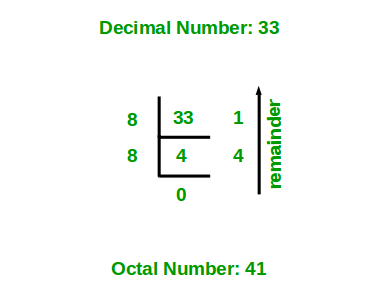
The below diagram shows an example of converting the decimal number 33 to an equivalent octal number.
Below is the implementation of the above idea.
C
#include <stdio.h>
void decToOctal(int n)
{
int octalNum[100];
int i = 0;
while (n != 0) {
octalNum[i] = n % 8;
n = n / 8;
i++;
}
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
printf("%d", octalNum[j]);
}
int main()
{
int n = 33;
decToOctal(n);
return 0;
}
|
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void decToOctal(int n)
{
int octalNum[100];
int i = 0;
while (n != 0) {
octalNum[i] = n % 8;
n = n / 8;
i++;
}
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
cout << octalNum[j];
}
int main()
{
int n = 33;
decToOctal(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static void decToOctal(int n)
{
int[] octalNum = new int[100];
int i = 0;
while (n != 0) {
octalNum[i] = n % 8;
n = n / 8;
i++;
}
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
System.out.print(octalNum[j]);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 33;
decToOctal(n);
}
}
|
Python3
def decToOctal(n):
octalNum = [0] * 100
i = 0
while (n != 0):
octalNum[i] = n % 8
n = int(n / 8)
i += 1
for j in range(i - 1, -1, -1):
print(octalNum[j], end="")
n = 33
decToOctal(n)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void decToOctal(int n)
{
int[] octalNum = new int[100];
int i = 0;
while (n != 0) {
octalNum[i] = n % 8;
n = n / 8;
i++;
}
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
Console.Write(octalNum[j]);
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 33;
decToOctal(n);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function decToOctal($n)
{
$octalNum;
$i = 0;
while ($n != 0)
{
$octalNum[$i] = $n % 8;
$n = (int)($n / 8);
$i++;
}
for ( $j = $i - 1; $j >= 0; $j--)
echo $octalNum[$j];
}
$n = 33;
decToOctal($n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function decToOctal(n)
{
let octalNum = new Array(100);
let i = 0;
while (n != 0) {
octalNum[i] = n % 8;
n = Math.floor(n / 8);
i++;
}
for (let j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
document.write(octalNum[j]);
}
let n = 33;
decToOctal(n);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(L) where L is the number of digits in octal number.
Another Approach: (O(1) space Complexity)
This problem can also be solved without using an array using the following algorithm:
- Initialize octal num to 0 and countVal to 1 and the decimal number as n
- Find the remainder when decimal number divided by 8
- Update octal number by octalNum + (remainder * countval)
- Increase countval by countval*10
- Divide decimal number by 8
- Repeat from the second step until the decimal number is zero
Below is the implementation of the above idea:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void decimaltoOctal(int deciNum)
{
int octalNum = 0, countval = 1;
int dNo = deciNum;
while (deciNum != 0) {
int remainder = deciNum % 8;
octalNum += remainder * countval;
countval = countval * 10;
deciNum /= 8;
}
cout << octalNum << endl;
}
int main()
{
int n = 33;
decimaltoOctal(n);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
void decimaltoOctal(int deciNum)
{
int octalNum = 0, countval = 1;
int dNo = deciNum;
while (deciNum != 0) {
int remainder = deciNum % 8;
octalNum += remainder * countval;
countval = countval * 10;
deciNum /= 8;
}
printf("%d", octalNum);
}
int main()
{
int n = 33;
decimaltoOctal(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static void octaltodecimal(int deciNum)
{
int octalNum = 0, countval = 1;
int dNo = deciNum;
while (deciNum != 0) {
int remainder = deciNum % 8;
octalNum += remainder * countval;
countval = countval * 10;
deciNum /= 8;
}
System.out.println(octalNum);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 33;
octaltodecimal(n);
}
}
|
Python3
def decimaltoOctal(deciNum):
octalNum = 0
countval = 1
dNo = deciNum
while (deciNum != 0):
remainder = deciNum % 8
octalNum += remainder * countval
countval = countval * 10
deciNum //= 8
print(octalNum)
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 33
decimaltoOctal(n)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void octaltodecimal(int deciNum)
{
int octalNum = 0, countval = 1;
while (deciNum != 0) {
int remainder = deciNum % 8;
octalNum += remainder * countval;
countval = countval * 10;
deciNum /= 8;
}
Console.Write(octalNum);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 33;
octaltodecimal(n);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function decimaltoOctal(deciNum)
{
let octalNum = 0, countval = 1;
let dNo = deciNum;
while (deciNum != 0) {
let remainder = Math.floor(deciNum % 8);
octalNum += remainder * countval;
countval = countval * 10;
deciNum = Math.floor(deciNum/8);
}
document.write(octalNum + "<br>");
}
let n = 33;
decimaltoOctal(n);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Using a predefined function
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void decToOct(int n)
{
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(n));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 33;
decToOct(n);
}
}
|
Python3
def decToOct(n):
print(oct(n));
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 33;
decToOct(n);
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
public static void decToOct(int n)
{
Console.WriteLine(Convert.ToString(n, 8));
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 33;
decToOct(n);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function decToOct(n)
{
document.write(n.toString(8));
}
var n = 33;
decToOct(n);
</script>
|
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string intToOctal(int n)
{
stringstream st;
st << oct << n;
return st.str();
}
int main()
{
int n = 43;
cout << intToOctal(n);
return 0;
}
|
Time complexity: O(1).
Space complexity: O(1).
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...