Probability that the sum of all numbers obtained on throwing a dice N times lies between two given integers
Last Updated :
15 Nov, 2021
Given three integers N, A, and B, the task is to calculate the probability that the sum of numbers obtained on throwing the dice exactly N times lies between A and B.
Examples:
Input: N = 1, A = 2, B = 3
Output: 0.333333
Explanation: Ways to obtained the sum 2 by N ( = 1) throws of a dice is 1 {2}. Therefore, required probability = 1/6 = 0.33333
Input: N = 2, A = 3, B = 4
Output: 0.138889
Recursive Approach: Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Calculate probabilities for all the numbers between A and B and add them to get the answer.
- Call function find(N, sum) to calculate the probability for each number from a to b, where a number between a and b will be passed as sum.
- Base cases are:
- If the sum is either greater than 6 * N or less than N, then return 0 as it’s impossible to have sum greater than N * 6 or less than N.
- If N is equal to 1 and sum is in between 1 and 6, then return 1/6.
- Since at every state any number out of 1 to 6 in a single throw of dice may come, therefore recursion call should be made for the (sum up to that state – i) where 1≤ i ≤ 6.
- Return the resultant probability.
Recursion call:
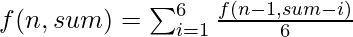
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long double find(int N, int sum)
{
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
long double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return s;
}
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
long double probability = 0.0;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static double find(int N, int sum)
{
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
{
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return s;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
double probability = 0.0;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
System.out.format("%.6f", probability);
}
}
|
Python3
def find(N, sum):
if (sum > 6 * N or sum < N):
return 0
if (N == 1):
if (sum >= 1 and sum <= 6):
return 1.0 / 6
else:
return 0
s = 0
for i in range(1, 7):
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6
return s
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 4
a = 13
b = 17
probability = 0.0
for sum in range(a, b + 1):
probability = probability + find(N, sum)
print(round(probability, 6))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static double find(int N, int sum)
{
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
{
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return s;
}
static void Main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
double probability = 0.0;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
Console.WriteLine(Math.Round(probability,6));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function find(N, sum)
{
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
{
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
let s = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return s;
}
let N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
let probability = 0.0;
for (let sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
document.write(probability.toFixed(6));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O((b-a+1)6n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Dynamic Programming Approach: The above recursive approach needs to be optimized by dealing with the following overlapping subproblems and optimal substructure:
Overlapping Subproblems:
Partial recursion tree for N=4 and sum=15:

Optimal Substructure:
For every state, recur for other 6 states, so the recursive definition of f(N, sum) is:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com dp[N][sum]=\sum_{i=1}^6\frac{dp[N-1][sum-i]}{6}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1d394f059a7bfb962f6b867d230d4747_l3.png)
Top-Down Approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
float dp[105][605];
float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (dp[N][sum])
return dp[N][sum];
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum]
+ find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
}
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static float[][] dp = new float[105][605];
static float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (N < 0 | sum < 0)
return 0;
if (dp[N][sum] > 0)
return dp[N][sum];
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return (float) (1.0 / 6);
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0f;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
System.out.printf("%.6f", probability);
}
}
|
Python3
dp = [[0 for i in range(605)] for j in range(105)];
def find(N, sum):
if (N < 0 | sum < 0):
return 0;
if (dp[N][sum] > 0):
return dp[N][sum];
if (sum > 6 * N or sum < N):
return 0;
if (N == 1):
if (sum >= 1 and sum <= 6):
return (float)(1.0 / 6);
else:
return 0;
for i in range(1,7):
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 4; a = 13; b = 17;
probability = 0.0
f = 0;
for sum in range(a,b+1):
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
print("%.6f"% probability);
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static float[,] dp = new float[105, 605];
static float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (N < 0 | sum < 0)
return 0;
if (dp[N, sum] > 0)
return dp[N, sum];
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return (float) (1.0 / 6);
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N, sum] = dp[N, sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N, sum];
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0f;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
Console.Write("{0:F6}", probability);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var dp = Array(105).fill().map(()=>Array(605).fill(0.0));
function find(N, sum)
{
if (N < 0 | sum < 0)
return 0;
if (dp[N][sum] > 0)
return dp[N][sum];
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
{
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return (1.0 / 6);
else
return 0;
}
for(var i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum] +
find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
}
var N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
var probability = 0.0;
for(sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
document.write(probability.toFixed(6));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(n*sum)
Auxiliary Space: O(n*sum)
Bottom-Up Approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
float dp[105][605];
float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1][i] = 1.0 / 6;
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= 6; k++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j]
+ dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N][sum];
return probability;
}
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static float [][]dp = new float[105][605];
static float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0f;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1][i] = (float) (1.0 / 6);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= 6 && k <= j; k++)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j]
+ dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N][sum];
return probability;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
System.out.printf("%.6f",probability);
}
}
|
Python3
dp = [[0 for i in range(605)] for j in range(105)]
def find(N, a, b) :
probability = 0.0
for i in range(1, 7) :
dp[1][i] = 1.0 / 6
for i in range(2, N + 1) :
for j in range(i, (6*i) + 1) :
for k in range(1, 7) :
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] + dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6
for Sum in range(a, b + 1) :
probability = probability + dp[N][Sum]
return probability
N, a, b = 4, 13, 17
probability = find(N, a, b)
print('%.6f'%probability)
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static float [,]dp = new float[105, 605];
static float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0f;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1, i] = (float) (1.0 / 6);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= 6 && k <= j; k++)
{
dp[i, j] = dp[i, j]
+ dp[i - 1, j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N, sum];
return probability;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
Console.Write("{0:F6}",probability);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let dp = new Array(105);
for(var i = 0; i < dp.length; i++)
{
dp[i] = new Array(2);
}
for(var i = 0; i < dp.length; i++)
{
for(var j = 0; j < dp.length; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
function find(N, a, b)
{
let probability = 0.0;
for(let i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1][i] = (1.0 / 6);
for(let i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
for(let j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++)
{
for(let k = 1; k <= 6 && k <= j; k++)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] +
dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
for(let sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N][sum];
return probability;
}
let N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
let probability = find(N, a, b);
document.write(probability);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N * sum)
Auxiliary Space: O(N * sum)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...