A priority queue is a type of queue that arranges elements based on their priority values. Elements with higher priority values are typically retrieved before elements with lower priority values.
In a priority queue, each element has a priority value associated with it. When you add an element to the queue, it is inserted in a position based on its priority value. For example, if you add an element with a high priority value to a priority queue, it may be inserted near the front of the queue, while an element with a low priority value may be inserted near the back.
There are several ways to implement a priority queue, including using an array, linked list, heap, or binary search tree. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice will depend on the specific needs of your application.
Priority queues are often used in real-time systems, where the order in which elements are processed can have significant consequences. They are also used in algorithms to improve their efficiencies, such as Dijkstra’s algorithm for finding the shortest path in a graph and the A* search algorithm for pathfinding.
Properties of Priority Queue
So, a priority Queue is an extension of the queue with the following properties.
- Every item has a priority associated with it.
- An element with high priority is dequeued before an element with low priority.
- If two elements have the same priority, they are served according to their order in the queue.
In the below priority queue, an element with a maximum ASCII value will have the highest priority. The elements with higher priority are served first.
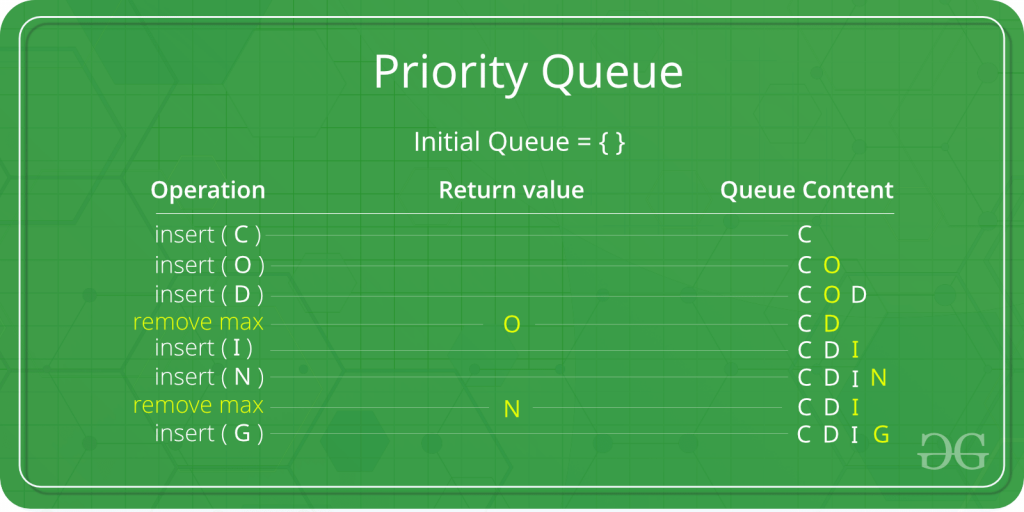
How is Priority assigned to the elements in a Priority Queue?
In a priority queue, generally, the value of an element is considered for assigning the priority.
For example, the element with the highest value is assigned the highest priority and the element with the lowest value is assigned the lowest priority. The reverse case can also be used i.e., the element with the lowest value can be assigned the highest priority. Also, the priority can be assigned according to our needs.
Operations of a Priority Queue:
A typical priority queue supports the following operations:
1) Insertion in a Priority Queue
When a new element is inserted in a priority queue, it moves to the empty slot from top to bottom and left to right. However, if the element is not in the correct place then it will be compared with the parent node. If the element is not in the correct order, the elements are swapped. The swapping process continues until all the elements are placed in the correct position.
2) Deletion in a Priority Queue
As you know that in a max heap, the maximum element is the root node. And it will remove the element which has maximum priority first. Thus, you remove the root node from the queue. This removal creates an empty slot, which will be further filled with new insertion. Then, it compares the newly inserted element with all the elements inside the queue to maintain the heap invariant.
3) Peek in a Priority Queue
This operation helps to return the maximum element from Max Heap or the minimum element from Min Heap without deleting the node from the priority queue.
Types of Priority Queue:
1) Ascending Order Priority Queue
As the name suggests, in ascending order priority queue, the element with a lower priority value is given a higher priority in the priority list. For example, if we have the following elements in a priority queue arranged in ascending order like 4,6,8,9,10. Here, 4 is the smallest number, therefore, it will get the highest priority in a priority queue and so when we dequeue from this type of priority queue, 4 will remove from the queue and dequeue returns 4.
2) Descending order Priority Queue
The root node is the maximum element in a max heap, as you may know. It will also remove the element with the highest priority first. As a result, the root node is removed from the queue. This deletion leaves an empty space, which will be filled with fresh insertions in the future. The heap invariant is then maintained by comparing the newly inserted element to all other entries in the queue.
Types of Priority Queues
Difference between Priority Queue and Normal Queue?
There is no priority attached to elements in a queue, the rule of first-in-first-out(FIFO) is implemented whereas, in a priority queue, the elements have a priority. The elements with higher priority are served first.
How to Implement Priority Queue?
Priority queue can be implemented using the following data structures:
- Arrays
- Linked list
- Heap data structure
- Binary search tree
Let’s discuss all these in detail.
1) Implement Priority Queue Using Array:
A simple implementation is to use an array of the following structure.
struct item {
int item;
int priority;
}
- enqueue(): This function is used to insert new data into the queue.
- dequeue(): This function removes the element with the highest priority from the queue.
- peek()/top(): This function is used to get the highest priority element in the queue without removing it from the queue.
|
Arrays
|
enqueue()
|
dequeue()
|
peek()
|
|
Time Complexity
|
O(1)
|
O(n)
|
O(n)
|
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct item {
int value;
int priority;
};
item pr[100000];
int size = -1;
void enqueue(int value, int priority)
{
size++;
pr[size].value = value;
pr[size].priority = priority;
}
int peek()
{
int highestPriority = INT_MIN;
int ind = -1;
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (highestPriority == pr[i].priority && ind > -1
&& pr[ind].value < pr[i].value) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
else if (highestPriority < pr[i].priority) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
}
return ind;
}
void dequeue()
{
int ind = peek();
for (int i = ind; i < size; i++) {
pr[i] = pr[i + 1];
}
size--;
}
int main()
{
enqueue(10, 2);
enqueue(14, 4);
enqueue(16, 4);
enqueue(12, 3);
int ind = peek();
cout << pr[ind].value << endl;
dequeue();
ind = peek();
cout << pr[ind].value << endl;
dequeue();
ind = peek();
cout << pr[ind].value << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class item {
public int value;
public int priority;
};
class GFG {
static item[] pr = new item[100000];
static int size = -1;
static void enqueue(int value, int priority)
{
size++;
pr[size] = new item();
pr[size].value = value;
pr[size].priority = priority;
}
static int peek()
{
int highestPriority = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int ind = -1;
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (highestPriority == pr[i].priority
&& ind > -1
&& pr[ind].value < pr[i].value) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
else if (highestPriority < pr[i].priority) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
}
return ind;
}
static void dequeue()
{
int ind = peek();
for (int i = ind; i < size; i++) {
pr[i] = pr[i + 1];
}
size--;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
enqueue(10, 2);
enqueue(14, 4);
enqueue(16, 4);
enqueue(12, 3);
int ind = peek();
System.out.println(pr[ind].value);
dequeue();
ind = peek();
System.out.println(pr[ind].value);
dequeue();
ind = peek();
System.out.println(pr[ind].value);
}
}
|
Python3
import sys
class item :
value = 0
priority = 0
class GFG :
pr = [None] * (100000)
size = -1
@staticmethod
def enqueue( value, priority) :
GFG.size += 1
GFG.pr[GFG.size] = item()
GFG.pr[GFG.size].value = value
GFG.pr[GFG.size].priority = priority
@staticmethod
def peek() :
highestPriority = -sys.maxsize
ind = -1
i = 0
while (i <= GFG.size) :
if (highestPriority == GFG.pr[i].priority and ind > -1 and GFG.pr[ind].value < GFG.pr[i].value) :
highestPriority = GFG.pr[i].priority
ind = i
elif(highestPriority < GFG.pr[i].priority) :
highestPriority = GFG.pr[i].priority
ind = i
i += 1
return ind
@staticmethod
def dequeue() :
ind = GFG.peek()
i = ind
while (i < GFG.size) :
GFG.pr[i] = GFG.pr[i + 1]
i += 1
GFG.size -= 1
@staticmethod
def main( args) :
GFG.enqueue(10, 2)
GFG.enqueue(14, 4)
GFG.enqueue(16, 4)
GFG.enqueue(12, 3)
ind = GFG.peek()
print(GFG.pr[ind].value)
GFG.dequeue()
ind = GFG.peek()
print(GFG.pr[ind].value)
GFG.dequeue()
ind = GFG.peek()
print(GFG.pr[ind].value)
if __name__=="__main__":
GFG.main([])
|
C#
using System;
public class item {
public int value;
public int priority;
};
public class GFG
{
static item[] pr = new item[100000];
static int size = -1;
static void enqueue(int value, int priority)
{
size++;
pr[size] = new item();
pr[size].value = value;
pr[size].priority = priority;
}
static int peek()
{
int highestPriority = int.MinValue;
int ind = -1;
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (highestPriority == pr[i].priority && ind > -1
&& pr[ind].value < pr[i].value) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
else if (highestPriority < pr[i].priority) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
}
return ind;
}
static void dequeue()
{
int ind = peek();
for (int i = ind; i < size; i++) {
pr[i] = pr[i + 1];
}
size--;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
enqueue(10, 2);
enqueue(14, 4);
enqueue(16, 4);
enqueue(12, 3);
int ind = peek();
Console.WriteLine(pr[ind].value);
dequeue();
ind = peek();
Console.WriteLine(pr[ind].value);
dequeue();
ind = peek();
Console.WriteLine(pr[ind].value);
}
}
|
Javascript
class item {
constructor()
{
this.value;
this.priority;
}
};
let pr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
pr.push(new item());
let size = -1;
function enqueue(value, priority)
{
size++;
pr[size] = new item();
pr[size].value = value;
pr[size].priority = priority;
}
function peek()
{
let highestPriority = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
let ind = -1;
for (var i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (highestPriority == pr[i].priority && ind > -1
&& pr[ind].value < pr[i].value) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
else if (highestPriority < pr[i].priority) {
highestPriority = pr[i].priority;
ind = i;
}
}
return ind;
}
function dequeue()
{
let ind = peek();
for (var i = ind; i < size; i++) {
pr[i] = pr[i + 1];
}
size--;
}
enqueue(10, 2);
enqueue(14, 4);
enqueue(16, 4);
enqueue(12, 3);
let ind = peek();
console.log(pr[ind].value);
dequeue();
ind = peek();
console.log(pr[ind].value);
dequeue();
ind = peek();
console.log(pr[ind].value);
|
Note: Read this article for more details.
2) Implement Priority Queue Using Linked List:
In a LinkedList implementation, the entries are sorted in descending order based on their priority. The highest priority element is always added to the front of the priority queue, which is formed using linked lists. The functions like push(), pop(), and peek() are used to implement a priority queue using a linked list and are explained as follows:
- push(): This function is used to insert new data into the queue.
- pop(): This function removes the element with the highest priority from the queue.
- peek() / top(): This function is used to get the highest priority element in the queue without removing it from the queue.
|
Linked List
|
push()
|
pop()
|
peek()
|
|
Time Complexity
|
O(n)
|
O(1)
|
O(1)
|
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int data;
int priority;
struct node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int d, int p)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = d;
temp->priority = p;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
int peek(Node** head) { return (*head)->data; }
void pop(Node** head)
{
Node* temp = *head;
(*head) = (*head)->next;
free(temp);
}
void push(Node** head, int d, int p)
{
Node* start = (*head);
Node* temp = newNode(d, p);
if ((*head)->priority < p) {
temp->next = *head;
(*head) = temp;
}
else {
while (start->next != NULL
&& start->next->priority > p) {
start = start->next;
}
temp->next = start->next;
start->next = temp;
}
}
int isEmpty(Node** head) { return (*head) == NULL; }
int main()
{
Node* pq = newNode(4, 1);
push(&pq, 5, 2);
push(&pq, 6, 3);
push(&pq, 7, 0);
while (!isEmpty(&pq)) {
cout << " " << peek(&pq);
pop(&pq);
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.* ;
class Solution
{
static class Node {
int data;
int priority;
Node next;
}
static Node node = new Node();
static Node newNode(int d, int p)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = d;
temp.priority = p;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
static int peek(Node head)
{
return (head).data;
}
static Node pop(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
(head) = (head).next;
return head;
}
static Node push(Node head, int d, int p)
{
Node start = (head);
Node temp = newNode(d, p);
if ((head).priority < p) {
temp.next = head;
(head) = temp;
}
else {
while (start.next != null &&
start.next.priority > p) {
start = start.next;
}
temp.next = start.next;
start.next = temp;
}
return head;
}
static int isEmpty(Node head)
{
return ((head) == null)?1:0;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node pq = newNode(4, 1);
pq =push(pq, 5, 2);
pq =push(pq, 6, 3);
pq =push(pq, 7, 0);
while (isEmpty(pq)==0) {
System.out.printf("%d ", peek(pq));
pq=pop(pq);
}
}
}
|
Python
class PriorityQueueNode:
def _init_(self, value, pr):
self.data = value
self.priority = pr
self.next = None
class PriorityQueue:
def _init_(self):
self.front = None
def isEmpty(self):
return True if self.front == None else False
def push(self, value, priority):
if self.isEmpty() == True:
self.front = PriorityQueueNode(value,
priority)
return 1
else:
if self.front.priority < priority:
newNode = PriorityQueueNode(value,
priority)
newNode.next = self.front
self.front = newNode
return 1
else:
temp = self.front
while temp.next:
if priority >= temp.next.priority:
break
temp = temp.next
newNode = PriorityQueueNode(value,
priority)
newNode.next = temp.next
temp.next = newNode
return 1
def pop(self):
if self.isEmpty() == True:
return
else:
self.front = self.front.next
return 1
def peek(self):
if self.isEmpty() == True:
return
else:
return self.front.data
def traverse(self):
if self.isEmpty() == True:
return "Queue is Empty!"
else:
temp = self.front
while temp:
print(temp.data, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
if _name_ == "_main_":
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.push(4, 1)
pq.push(5, 2)
pq.push(6, 3)
pq.push(7, 0)
pq.traverse()
pq.pop()
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public int priority;
public Node next;
}
public static Node node = new Node();
public static Node newNode(int d, int p)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = d;
temp.priority = p;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
public static int peek(Node head)
{
return (head).data;
}
public static Node pop(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
(head) = (head).next;
return head;
}
public static Node push(Node head,
int d, int p)
{
Node start = (head);
Node temp = newNode(d, p);
if ((head).priority < p)
{
temp.next = head;
(head) = temp;
}
else
{
while (start.next != null &&
start.next.priority > p)
{
start = start.next;
}
temp.next = start.next;
start.next = temp;
}
return head;
}
public static int isEmpty(Node head)
{
return ((head) == null) ? 1 : 0;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node pq = newNode(4, 1);
pq = push(pq, 5, 2);
pq = push(pq, 6, 3);
pq = push(pq, 7, 0);
while (isEmpty(pq) == 0)
{
Console.Write("{0:D} ", peek(pq));
pq = pop(pq);
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.priority = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
var node = new Node();
function newNode(d, p) {
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = d;
temp.priority = p;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
function peek(head) {
return head.data;
}
function pop(head) {
var temp = head;
head = head.next;
return head;
}
function push(head, d, p) {
var start = head;
var temp = newNode(d, p);
if (head.priority < p) {
temp.next = head;
head = temp;
}
else {
while (start.next != null && start.next.priority > p) {
start = start.next;
}
temp.next = start.next;
start.next = temp;
}
return head;
}
function isEmpty(head) {
return head == null ? 1 : 0;
}
var pq = newNode(4, 1);
pq = push(pq, 5, 2);
pq = push(pq, 6, 3);
pq = push(pq, 7, 0);
while (isEmpty(pq) == 0) {
console.log(peek(pq)," ");
pq = pop(pq);
}
|
Refer to this article for more details.
Note: We can also use Linked List, time complexity of all operations with linked list remains same as array. The advantage with linked list is deleteHighestPriority() can be more efficient as we don’t have to move items.
3) Implement Priority Queue Using Heaps:
Binary Heap is generally preferred for priority queue implementation because heaps provide better performance compared to arrays or LinkedList. Considering the properties of a heap, The entry with the largest key is on the top and can be removed immediately. It will, however, take time O(log n) to restore the heap property for the remaining keys. However if another entry is to be inserted immediately, then some of this time may be combined with the O(log n) time needed to insert the new entry. Thus the representation of a priority queue as a heap proves advantageous for large n, since it is represented efficiently in contiguous storage and is guaranteed to require only logarithmic time for both insertions and deletions. Operations on Binary Heap are as follows:
- insert(p): Inserts a new element with priority p.
- extractMax(): Extracts an element with maximum priority.
- remove(i): Removes an element pointed by an iterator i.
- getMax(): Returns an element with maximum priority.
- changePriority(i, p): Changes the priority of an element pointed by i to p.
|
Binary Heap
|
insert()
|
remove()
|
peek()
|
|
Time Complexity
|
O(log n)
|
O(log n)
|
O(1)
|
Refer to this article for code implementation.
4) Implement Priority Queue Using Binary Search Tree:
A Self-Balancing Binary Search Tree like AVL Tree, Red-Black Tree, etc. can also be used to implement a priority queue. Operations like peek(), insert() and delete() can be performed using BST.
| Binary Search Tree |
peek() |
insert() |
delete() |
| Time Complexity |
O(1) |
O(log n) |
O(log n) |
Applications of Priority Queue:
Advantages of Priority Queue:
- It helps to access the elements in a faster way. This is because elements in a priority queue are ordered by priority, one can easily retrieve the highest priority element without having to search through the entire queue.
- The ordering of elements in a Priority Queue is done dynamically. Elements in a priority queue can have their priority values updated, which allows the queue to dynamically reorder itself as priorities change.
- Efficient algorithms can be implemented. Priority queues are used in many algorithms to improve their efficiency, such as Dijkstra’s algorithm for finding the shortest path in a graph and the A* search algorithm for pathfinding.
- Included in real-time systems. This is because priority queues allow you to quickly retrieve the highest priority element, they are often used in real-time systems where time is of the essence.
Disadvantages of Priority Queue:
- High complexity. Priority queues are more complex than simple data structures like arrays and linked lists, and may be more difficult to implement and maintain.
- High consumption of memory. Storing the priority value for each element in a priority queue can take up additional memory, which may be a concern in systems with limited resources.
- It is not always the most efficient data structure. In some cases, other data structures like heaps or binary search trees may be more efficient for certain operations, such as finding the minimum or maximum element in the queue.
- At times it is less predictable:. This is because the order of elements in a priority queue is determined by their priority values, the order in which elements are retrieved may be less predictable than with other data structures like stacks or queues, which follow a first-in, first-out (FIFO) or last-in, first-out (LIFO) order.
See also:
- Applications of Priority Queue
- Priority Queue in C++
- Priority Queue in Java
- Priority Queue in Python
- Priority Queue in JavaScript
- Recent articles on Priority Queue!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...