Largest number with maximum trailing nines which is less than N and greater than N-D
Last Updated :
11 Oct, 2022
Given two numbers N and D. The task is to find out the largest number smaller than or equal to N which contains the maximum number of trailing nines and the difference between N and the number should not be greater than D.
Examples:
Input: N = 1029, D = 102
Output: 999
1029 has 1 trailing nine while 999 has three
trailing nine. Also 1029-999 = 30(which is less than 102).
Input: N = 10281, D = 1
Output: 10281
A naive approach will be to iterate from N till N-D and find the number with the largest number of trailing nines.
An efficient approach can be found by some key observations. One key observation for this problem is that the largest number smaller than N ending with at least say(K) nines is
[n – (n MOD 10^k) – 1]
Traverse all possible values of k starting from total no of digits of N to 1, and check whether d > n%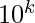 . If no such value is obtained, the final answer will be N itself. Otherwise, check for the answer using the above observation.
. If no such value is obtained, the final answer will be N itself. Otherwise, check for the answer using the above observation.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
ll dig(ll a)
{
ll count = 0;
while (a > 0) {
a /= 10;
count++;
}
return count;
}
void required_number(ll num, ll n, ll d)
{
ll i, j, power, a, flag = 0;
for (i = num; i >= 1; i--) {
power = pow(10, i);
a = n % power;
if (d > a) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
ll t = 0;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++) {
t += 9 * pow(10, j);
}
if (n % power == t)
cout << n;
else {
cout << n - (n % power) - 1;
}
}
else
cout << n;
}
int main()
{
ll n = 1029, d = 102;
ll num = dig(n);
required_number(num, n, d);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static long dig(long a)
{
long count = 0;
while (a > 0)
{
a /= 10;
count++;
}
return count;
}
static void required_number(long num, long n, long d)
{
long i, j, power=1, a, flag = 0;
for (i = num; i >= 1; i--)
{
power = (long)Math.pow(10, i);
a = n % power;
if (d > a)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag>0)
{
long t = 0;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
t += 9 * Math.pow(10, j);
}
if (n % power == t)
System.out.print( n);
else {
System.out.print( n - (n % power) - 1);
}
}
else
System.out.print(n);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
long n = 1029, d = 102;
long num = dig(n);
required_number(num, n, d);
}
}
|
Python3
def dig(a):
count = 0;
while (a > 0):
a /= 10
count+=1
return count
def required_number(num, n, d):
flag = 0
power=0
a=0
for i in range(num,0,-1):
power = pow(10, i)
a = n % power
if (d > a):
flag = 1
break
if(flag):
t=0
for j in range(0,i):
t += 9 * pow(10, j)
if(n % power ==t):
print(n,end="")
else:
print((n - (n % power) - 1),end="")
else:
print(n,end="")
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 1029
d = 102
num = dig(n)
required_number(num, n, d)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static long dig(long a)
{
long count = 0;
while (a > 0)
{
a /= 10;
count++;
}
return count;
}
static void required_number(long num,
long n,
long d)
{
long i, j, power = 1, a, flag = 0;
for (i = num; i >= 1; i--)
{
power = (long)Math.Pow(10, i);
a = n % power;
if (d > a)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag > 0)
{
long t = 0;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
t += (long)(9 * Math.Pow(10, j));
}
if (n % power == t)
Console.Write( n);
else
{
Console.Write(n - (n % power) - 1);
}
}
else
Console.Write(n);
}
public static void Main()
{
long n = 1029, d = 102;
long num = dig(n);
required_number(num, n, d);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function dig($a)
{
$count = 0;
while ($a > 0)
{
$a = (int)($a / 10);
$count++;
}
return $count;
}
function required_number($num, $n, $d)
{
$flag = 0;
for ($i = $num; $i >= 1; $i--)
{
$power = pow(10, $i);
$a = $n % $power;
if ($d > $a)
{
$flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if ($flag)
{
$t = 0;
for ($j = 0; $j < $i; $j++)
{
$t += 9 * pow(10, $j);
}
if ($n % $power == $t)
echo $n;
else
{
echo ($n - ($n % $power) - 1);
}
}
else
echo $n;
}
$n = 1029;
$d = 102;
$num = dig($n);
required_number($num, $n, $d);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function dig(a)
{
var count = 0;
while (a > 0)
{
a /= 10;
count++;
}
return count;
}
function required_number(num , n , d)
{
var i, j, power=1, a, flag = 0;
for (i = num; i >= 1; i--)
{
power = Math.pow(10, i);
a = n % power;
if (d > a)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag>0)
{
var t = 0;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
t += 9 * Math.pow(10, j);
}
if (n % power == t)
document.write( n);
else {
document.write( n - (n % power) - 1);
}
}
else
document.write(n);
}
var n = 1029, d = 102;
var num = dig(n);
required_number(num, n, d);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(logn)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Another Approach: The approach is to reduce n by variable num that is 9 99 999 and so on and divide it by temp which is 1 10 100 1000 and so on. If at any point n is less than num we break and return the ans. For each iteration we calculate a value x as (n-num)/temp then if (x*temp)+ num is greater than equal to (n-d) this will be our ans with most number of nines as basically we are reducing n by a factor and adding num (the most number of 9s possible) as it is of the form 9 99 999 and so on.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxPossible9s(int n, int d)
{
int temp = 1;
int ans = 1;
int num = 0;
while (true) {
if (n < num) {
break;
}
else {
int x = (n - num) / temp;
if (x * temp + num >= (n - d)) {
ans = x * temp + num;
}
temp *= 10;
num = num * 10 + 9;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n = 1029;
int d = 102;
cout << maxPossible9s(n, d) << endl;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int maxPossible9s(int n, int d)
{
int temp = 1;
int ans = 1;
int num = 0;
while (true) {
if (n < num) {
break;
}
else
{
int x = (n - num) / temp;
if (x * temp + num >= (n - d)) {
ans = x * temp + num;
}
temp *= 10;
num = num * 10 + 9;
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 1029;
int d = 102;
System.out.println(maxPossible9s(n, d));
}
}
|
Python3
def maxPossible9s(n, d):
temp = 1
ans = 1
num = 0
while (True):
if (n < num):
break
else:
x = (n - num) // temp
if (x * temp + num >= (n - d)):
ans = x * temp + num
temp *= 10
num = num * 10 + 9
return ans
n = 1029
d = 102
print(maxPossible9s(n, d))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int maxPossible9s(int n, int d)
{
int temp = 1;
int ans = 1;
int num = 0;
while (true) {
if (n < num) {
break;
}
else
{
int x = (n - num) / temp;
if (x * temp + num >= (n - d)) {
ans = x * temp + num;
}
temp *= 10;
num = num * 10 + 9;
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 1029;
int d = 102;
Console.Write(maxPossible9s(n, d));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function maxPossible9s(n, d)
{
let temp = 1;
let ans = 1;
let num = 0;
while (true) {
if (n < num) {
break;
}
else {
let x = Math.floor((n - num) / temp);
if (x * temp + num >= (n - d)) {
ans = x * temp + num;
}
temp *= 10;
num = num * 10 + 9;
}
}
return ans;
}
let n = 1029;
let d = 102;
document.write(maxPossible9s(n, d),"</br>");
</script>
|
Output:
999
Time Complexity: O(logn)
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as no extra space is used
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...