Print reverse of a Linked List without actually reversing
Last Updated :
06 Feb, 2023
Given a linked list, print reverse of it using a recursive function. For example, if the given linked list is 1->2->3->4, then output should be 4->3->2->1.
Note that the question is only about printing the reverse. To reverse the list itself see this
Difficulty Level: Rookie
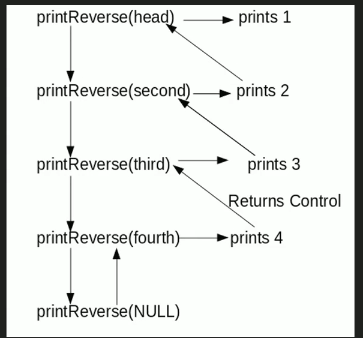
Algorithm
printReverse(head)
1. call print reverse for head->next
2. print head->data
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void printReverse(Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
printReverse(head->next);
cout << head->data << " ";
}
void push(Node** head_ref, char new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printReverse(head);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void printReverse(struct Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
printReverse(head->next);
printf("%d ", head->data);
}
void push(struct Node** head_ref, char new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printReverse(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {data = d; next = null; }
}
void printReverse(Node head)
{
if (head == null) return;
printReverse(head.next);
System.out.print(head.data+" ");
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def printrev(self, temp):
if temp:
self.printrev(temp.next)
print(temp.data, end = ' ')
else:
return
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(4)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
llist.printrev(llist.head)
|
C#
using System;
public class LinkedList
{
Node head;
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d; next = null;
}
}
void printReverse(Node head)
{
if (head == null) return;
printReverse(head.next);
Console.Write(head.data + " ");
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
function printReverse( head) {
if (head == null)
return;
printReverse(head.next);
document.write(head.data + " ");
}
function push(new_data) {
new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
push(4);
push(3);
push(2);
push(1);
printReverse(head);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n) for stack space since using recursion
Another approach:
We can also perform the same action using a stack using iterative method.
Algorithm:
Store the values of the linked list in a stack.
Keep removing the elements from the stack and print them.
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void printReverse(Node* head)
{
stack<int> st;
Node *curr = head;
while(curr!=NULL)
{
st.push(curr->data);
curr = curr->next;
}
while(st.empty()==false)
{
cout << st.top()<<" -> ";
st.pop();
}
}
void printList(Node *head)
{
Node *curr = head;
while(curr!=NULL)
{
cout << curr->data << " -> ";
curr = curr->next;
}
cout<<"\n";
}
void push(Node** head_ref, char new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printList(head);
printReverse(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {data = d; next = null; }
}
void printReverse(Node head)
{
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>();
Node curr = head;
while(curr!=null)
{
st.push(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
while(st.isEmpty()==false)
{
System.out.print(st.peek() + " -> ");
st.pop();
}
}
void printList(Node head)
{
Node curr = head;
while(curr!=null)
{
System.out.print(curr.data + " -> ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printList(llist.head);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def printrev(self, curr):
stack = []
while curr:
stack.append(curr)
curr = curr.next
while len(stack):
print(stack.pop().data,"->" , end = ' ')
print()
def printlist(self,curr):
while curr:
print(curr.data,"->" , end = ' ')
curr = curr.next
print()
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(4)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
llist.printlist(llist.head)
llist.printrev(llist.head)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
void printReverse(Node head)
{
Stack st = new Stack();
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
st.Push(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
while (st.Count != 0) {
Console.Write(st.Peek() + " -> ");
st.Pop();
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
void printList(Node head)
{
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " -> ");
curr = curr.next;
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printList(llist.head);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
function printReverse( head) {
var st = new Stack();
var curr = this.head;
while(curr != null)
{
st.push(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
while(st.idEmpty())
{
document.write(head.data + " -> ");
st.pop();
}
}
void printList( head)
{
var curr = this.head;
while(curr!=null)
{
document.write(curr.data + " -> ");
curr = curr.next;
}
document.write("\n");
}
function push(new_data) {
new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
push(4);
push(3);
push(2);
push(1);
printList(head);
printReverse(head);
</script>
|
Output
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 ->
4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 ->
Time Complexity: O(N)
As we are traversing the linked list only once.
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
The extra space is used in storing the elements in the stack.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...