Print Head node of every node in Binary Tree
Last Updated :
11 Apr, 2023
Given the root of the Binary Tree. Print the parent node of each node in the given Binary Tree.
Examples :
Input: Binary Tree = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, NULL, NULL, NULL, 6}
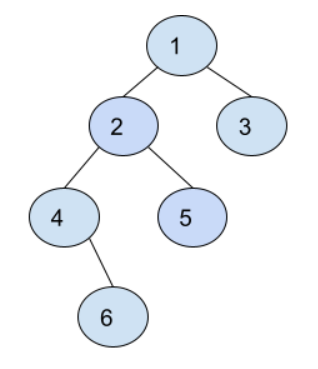
Example 1
Output :
- The Head Node of 6 is 4
- The Head Nodeof 5 is 2
- The Head Node of 4 is 2
- The Head Node of 3 is 1
- The Head Node of 2 is 1
Explanation: Clearly By Observing Image we are finding parent node for each and every Node.
Input: Binary Tree ={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
Output:
- The Head Node of 10 is 5
- The Head Nodeof 9 is 4
- The Head Node of 8 is 4
- The Head Node of 7 is 3
- The Head Node of 6 is 3
- The Head Node of 5 is 2
- The Head Nodeof 4 is 2
- The Head Node of 3 is 1
- The Head Node of 2 is 1
Approach: This can be solved with the following idea:
Using map data structure, and using child node as a key and it’s parent node as a value for that particular value. Traversing in Level order in binary tree using queue.
Steps involved in the implementation of code:
- Create an unordered map function with parameters of type Node* as ParentNodes.
- Push root into the queue q.
- while the queue is not empty iterate throughout the queue and assign root to its left and right as :
- ParentNodes[root->left] = root
- ParentNodes[root->right] = root
- Parallelly push the left and right nodes of the root into the queue for further iteration.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void Print_Head_Nodes(
Node* root, unordered_map<Node*, Node*>& ParentNodes)
{
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* k = q.front();
q.pop();
if (k->left) {
ParentNodes[k->left] = k;
q.push(k->left);
}
if (k->right) {
ParentNodes[k->right] = k;
q.push(k->right);
}
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left->right = newNode(6);
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> ParentNodes;
Print_Head_Nodes(root, ParentNodes);
for (auto i : ParentNodes) {
cout << "The Head Node of " << i.first->data
<< " is " << i.second->data << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
static void
Print_Head_Nodes(Node root,
HashMap<Node, Node> ParentNodes)
{
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node k = q.peek();
q.remove();
if (k.left != null) {
ParentNodes.put(k.left, k);
q.add(k.left);
}
if (k.right != null) {
ParentNodes.put(k.right, k);
q.add(k.right);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left.right = new Node(6);
HashMap<Node, Node> ParentNodes = new HashMap<>();
Print_Head_Nodes(root, ParentNodes);
for (Map.Entry<Node, Node> i :
ParentNodes.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("The Head Node of "
+ i.getKey().data + " is "
+ i.getValue().data);
}
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def newNode(data):
temp = Node(data)
return temp
def Print_Head_Nodes(root, ParentNodes):
q = []
q.append(root)
while q:
k = q.pop(0)
if k.left:
ParentNodes[k.left] = k
q.append(k.left)
if k.right:
ParentNodes[k.right] = k
q.append(k.right)
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
root.left.left.right = newNode(6)
ParentNodes = {}
Print_Head_Nodes(root, ParentNodes)
for i in ParentNodes:
print("The Head Node of ", i.data,
" is ", ParentNodes[i].data)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class GFG {
public static void
Print_Head_Nodes(Node root,
Dictionary<Node, Node> ParentNodes)
{
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
while (q.Count > 0) {
Node k = q.Dequeue();
if (k.left != null) {
ParentNodes[k.left] = k;
q.Enqueue(k.left);
}
if (k.right != null) {
ParentNodes[k.right] = k;
q.Enqueue(k.right);
}
}
}
public static void Main()
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left.right = new Node(6);
Dictionary<Node, Node> ParentNodes
= new Dictionary<Node, Node>();
Print_Head_Nodes(root, ParentNodes);
for (int i = ParentNodes.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
KeyValuePair<Node, Node> pair
= new List<KeyValuePair<Node, Node> >(
ParentNodes)[i];
Console.WriteLine("The Head Node of {0} is {1}",
pair.Key.data,
pair.Value.data);
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function Print_Head_Nodes(root, ParentNodes) {
let q = [];
q.push(root);
while (q.length > 0) {
let k = q.shift();
if (k.left) {
ParentNodes.set(k.left, k);
q.push(k.left);
}
if (k.right) {
ParentNodes.set(k.right, k);
q.push(k.right);
}
}
}
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left.right = new Node(6);
let ParentNodes = new Map();
Print_Head_Nodes(root, ParentNodes);
let entries = Array.from(ParentNodes.entries());
for (let i = entries.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let [key, value] = entries[i];
console.log(`The Head Node of ${key.data} is ${value.data}`);
}
|
Output
The Head Node of 6 is 4
The Head Node of 5 is 2
The Head Node of 4 is 2
The Head Node of 3 is 1
The Head Node of 2 is 1
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...