PostgreSQL – Variables
Last Updated :
28 Aug, 2020
In PostgreSQL, a variable is a meaningful name for a memory location. A variable holds a value that can be changed through the block or function. A variable is always associated with a particular data type. Before using a variable, you must declare it in the declaration section of the PostgreSQL Block. The following illustrates the syntax of declaring a variable.
Syntax: variable_name data_type [:= expression];
Let’s analyze the above syntax:
- First, specify the name of the variable. It is a good practice to assign a meaningful name to a variable. For example, instead of naming a variable “i“ one should use index or counter.
- Second, associate a specific data type with the variable. The data type can be any valid PostgreSQL data type such as INTEGER, NUMERIC, VARCHAR, and CHAR.
- Third, optionally assign a default value to a variable. If you don’t, the initial value of the variable is initialized to NULL.
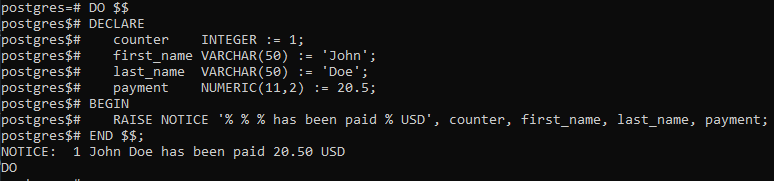
Example 1:
DO $$
DECLARE
counter INTEGER := 1;
first_name VARCHAR(50) := 'John';
last_name VARCHAR(50) := 'Doe';
payment NUMERIC(11,2) := 20.5;
BEGIN
RAISE NOTICE '% % % has been paid % USD', counter, first_name, last_name, payment;
END $$;
Output:
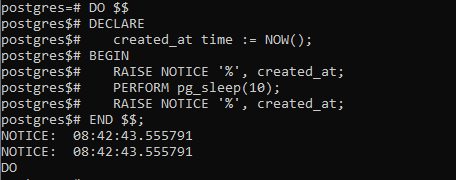
Example 2:
DO $$
DECLARE
created_at time := NOW();
BEGIN
RAISE NOTICE '%', created_at;
PERFORM pg_sleep(10);
RAISE NOTICE '%', created_at;
END $$;
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...