PostgreSQL – REPLACE Function
Last Updated :
01 Feb, 2021
In PostgreSQL, the REPLACE function is used to search and replace all occurrences of a string with a new one.
Syntax: REPLACE(source, old_text, new_text );
Let’s analyze the above syntax:
- The source is a string where you want to replace the existing string.
- The old_text is the string that is to be searched and subsequently replaced. The old_text can occur multiple times and each of them gets replaced on the function is executed.
- The new_text is the new text string that is suppose to replace the old text ( old_text ).
Example 1:
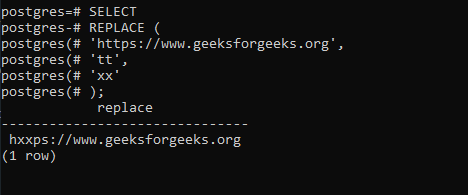
The following statement replaces the substring ‘tt’ with ‘xx’ in a URL:
SELECT
REPLACE (
'https://www.geeksforgeeks.org',
'tt',
'xx'
);
Output:
Example 2:
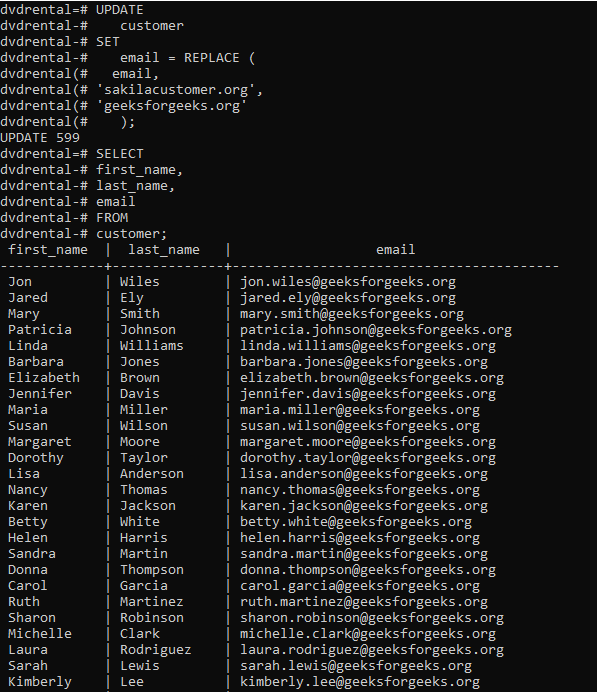
The below statement updates the email column to replace the domain ‘sakilacustomer.org’ with ‘geeksforgeek.org’, in the customer table of the sample database, ie, dvdrental:
UPDATE
customer
SET
email = REPLACE (
email,
'sakilacustomer.org',
'geeksforgeeks.org'
);
To verify it use the below statement:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name,
email
FROM
customer;
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...