Post Order Traversal of Binary Tree in O(N) using O(1) space
Last Updated :
25 Oct, 2021
Prerequisites:- Morris Inorder Traversal, Tree Traversals (Inorder, Preorder and Postorder)
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to print the elements in post order using O(N) time complexity and constant space.
Input: 1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
/ \
8 9
Output: 8 9 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
Input: 5
/ \
7 3
/ \ / \
4 11 13 9
/ \
8 4
Output: 8 4 4 11 7 13 9 3 5
Method 1: Using Morris Inorder Traversal
- Create a dummy node and make the root as it’s left child.
- Initialize current with dummy node.
- While current is not NULL
- If the current does not have a left child traverse the right child, current = current->right
- Otherwise,
- Find the rightmost child in the left subtree.
- If rightmost child’s right child is NULL
- Make current as the right child of the rightmost node.
- Traverse the left child, current = current->left
- Otherwise,
- Set the rightmost child’s right pointer to NULL.
- From current’s left child, traverse along with the right children until the rightmost child and reverse the pointers.
- Traverse back from rightmost child to current’s left child node by reversing the pointers and printing the elements.
- Traverse the right child, current = current->right
Below is the diagram showing the rightmost child in the left subtree, pointing to its inorder successor.

Below is the diagram which highlights the path 1->2->5->9 and the way the nodes are processed and printed as per the above algorithm.

Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class node
{
public:
int data;
node *left, *right;
};
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* temp = new node();
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void postOrderConstSpace(node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
node* current = newNode(-1);
node* pre = NULL;
node* prev = NULL;
node* succ = NULL;
node* temp = NULL;
current->left = root;
while (current)
{
if (current->left == NULL)
{
current = current->right;
}
else
{
pre = current->left;
while (pre->right &&
pre->right != current)
pre = pre->right;
if (pre->right == NULL)
{
pre->right = current;
current = current->left;
}
else
{
pre->right = NULL;
succ = current;
current = current->left;
prev = NULL;
while (current != NULL)
{
temp = current->right;
current->right = prev;
prev = current;
current = temp;
}
while (prev != NULL)
{
cout << prev->data << " ";
temp = prev->right;
prev->right = current;
current = prev;
prev = temp;
}
current = succ;
current = current->right;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
node* root = NULL;
root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->left->right->left = newNode(8);
root->left->right->right = newNode(9);
postOrderConstSpace(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class TreeNode {
public int data;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
public String toString()
{
return data + " ";
}
}
public class PostOrder {
TreeNode root;
void postOrderConstantspace(TreeNode
root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
TreeNode current
= new TreeNode(-1),
pre = null;
TreeNode prev = null,
succ = null,
temp = null;
current.left = root;
while (current != null) {
if (current.left == null) {
current = current.right;
}
else {
pre = current.left;
while (pre.right != null
&& pre.right != current)
pre = pre.right;
if (pre.right == null) {
pre.right = current;
current = current.left;
}
else {
pre.right = null;
succ = current;
current = current.left;
prev = null;
while (current != null) {
temp = current.right;
current.right = prev;
prev = current;
current = temp;
}
while (prev != null) {
System.out.print(prev);
temp = prev.right;
prev.right = current;
current = prev;
prev = temp;
}
current = succ;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PostOrder tree = new PostOrder();
tree.root = new TreeNode(1);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(2);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(3);
tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right
= new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right.left
= new TreeNode(6);
tree.root.right.right
= new TreeNode(7);
tree.root.left.right.left
= new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.left.right.right
= new TreeNode(9);
tree.postOrderConstantspace(
tree.root);
}
}
|
Python3
class node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def newNode(data):
temp = node(data)
return temp
def postOrderConstSpace(root):
if (root == None):
return
current = newNode(-1)
pre = None
prev = None
succ = None
temp = None
current.left = root
while (current):
if (current.left == None):
current = current.right
else:
pre = current.left
while (pre.right and
pre.right != current):
pre = pre.right
if (pre.right == None):
pre.right = current
current = current.left
else:
pre.right = None
succ = current
current = current.left
prev = None
while (current != None):
temp = current.right
current.right = prev
prev = current
current = temp
while (prev != None):
print(prev.data, end = ' ')
temp = prev.right
prev.right = current
current = prev
prev = temp
current = succ
current = current.right
if __name__=='__main__':
root = None
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
root.right.left = newNode(6)
root.right.right = newNode(7)
root.left.right.left = newNode(8)
root.left.right.right = newNode(9)
postOrderConstSpace(root)
|
C#
using System;
public class TreeNode
{
public int data;
public TreeNode left, right;
public TreeNode(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class PostOrder{
public TreeNode root;
void postOrderConstantspace(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
TreeNode current = new TreeNode(-1), pre = null;
TreeNode prev = null,
succ = null,
temp = null;
current.left = root;
while (current != null)
{
if (current.left == null)
{
current = current.right;
}
else
{
pre = current.left;
while (pre.right != null &&
pre.right != current)
pre = pre.right;
if (pre.right == null)
{
pre.right = current;
current = current.left;
}
else
{
pre.right = null;
succ = current;
current = current.left;
prev = null;
while (current != null)
{
temp = current.right;
current.right = prev;
prev = current;
current = temp;
}
while (prev != null)
{
Console.Write(prev.data + " ");
temp = prev.right;
prev.right = current;
current = prev;
prev = temp;
}
current = succ;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
}
static public void Main ()
{
PostOrder tree = new PostOrder();
tree.root = new TreeNode(1);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(2);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(3);
tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
tree.root.right.right = new TreeNode(7);
tree.root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.left.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
tree.postOrderConstantspace(tree.root);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class TreeNode
{
constructor(item)
{
this.data = item;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
var root;
function postOrderConstantspace(root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
var current = new TreeNode(-1), pre = null;
var prev = null,
succ = null,
temp = null;
current.left = root;
while (current != null)
{
if (current.left == null)
{
current = current.right;
}
else
{
pre = current.left;
while (pre.right != null &&
pre.right != current)
pre = pre.right;
if (pre.right == null)
{
pre.right = current;
current = current.left;
}
else
{
pre.right = null;
succ = current;
current = current.left;
prev = null;
while (current != null)
{
temp = current.right;
current.right = prev;
prev = current;
current = temp;
}
while (prev != null)
{
document.write(prev.data + " ");
temp = prev.right;
prev.right = current;
current = prev;
prev = temp;
}
current = succ;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
}
var tree = new TreeNode();
tree.root = new TreeNode(1);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(2);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(3);
tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
tree.root.right.right = new TreeNode(7);
tree.root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.left.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
postOrderConstantspace(tree.root);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method 2: In method 1, we traverse a path, reverse references, print nodes as we restore the references by reversing them again. In method 2, instead of reversing paths and restoring the structure, we traverse to the parent node from the current node using the current node’s left subtree. This could be faster depending on the tree structure, for example in a right-skewed tree.
The following algorithm and diagrams provide the details of the approach.

Below is the conceptual diagram showing how the left and right child references are used to traverse back and forth.
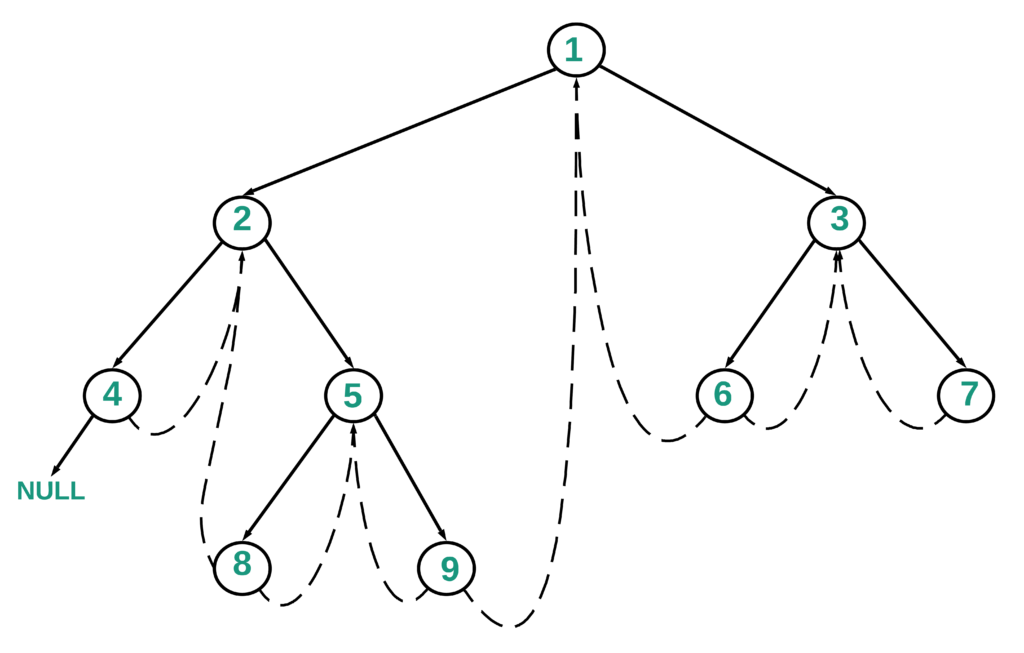
Below is the diagram which highlights the path 1->2->5->9 and the way the nodes are processed and printed as per the above algorithm.

Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
int data;
TreeNode(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->left = nullptr;
this->right = nullptr;
}
};
TreeNode* root;
static void postOrderConstantspace(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
TreeNode* current = nullptr;
TreeNode* prevNode = nullptr;
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
TreeNode* ptr = nullptr;
TreeNode* netChild = nullptr;
TreeNode* prevPtr = nullptr;
current = root;
while (current != nullptr)
{
if (current->left == nullptr)
{
current->left = prevNode;
prevNode = current;
current = current->right;
}
else
{
pre = current->left;
while (pre->right != nullptr &&
pre->right != current)
pre = pre->right;
if (pre->right == nullptr)
{
pre->right = current;
current = current->left;
}
else
{
pre->right = nullptr;
cout << pre->data << " ";
ptr = pre;
netChild = pre;
prevPtr = pre;
while (ptr != nullptr)
{
if (ptr->right == netChild)
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr->left = nullptr;
}
if (ptr == current->left)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr->left;
}
prevNode = current;
current = current->right;
}
}
}
cout << prevNode->data << " ";
ptr = prevNode;
netChild = prevNode;
prevPtr = prevNode;
while (ptr != nullptr)
{
if (ptr->right == netChild)
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr->left = nullptr;
}
if (ptr == root)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr->left;
}
}
int main()
{
root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(5);
root->right->left = new TreeNode(6);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(7);
root->left->right->left = new TreeNode(8);
root->left->right->right = new TreeNode(9);
postOrderConstantspace(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class TreeNode {
public int data;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
public String toString()
{
return data + " ";
}
}
public class PostOrder {
TreeNode root;
void postOrderConstantspace(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
TreeNode current = null;
TreeNode prevNode = null;
TreeNode pre = null;
TreeNode ptr = null;
TreeNode netChild = null;
TreeNode prevPtr = null;
current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (current.left == null) {
current.left = prevNode;
prevNode = current;
current = current.right;
}
else {
pre = current.left;
while (pre.right != null
&& pre.right != current)
pre = pre.right;
if (pre.right == null) {
pre.right = current;
current = current.left;
}
else {
pre.right = null;
System.out.print(pre);
ptr = pre;
netChild = pre;
prevPtr = pre;
while (ptr != null) {
if (ptr.right == netChild) {
System.out.print(ptr);
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr.left = null;
}
if (ptr == current.left)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr.left;
}
prevNode = current;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
System.out.print(prevNode);
ptr = prevNode;
netChild = prevNode;
prevPtr = prevNode;
while (ptr != null) {
if (ptr.right == netChild) {
System.out.print(ptr);
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr.left = null;
}
if (ptr == root)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr.left;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PostOrder tree = new PostOrder();
tree.root = new TreeNode(1);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(2);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(3);
tree.root.left.left
= new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right
= new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right.left
= new TreeNode(6);
tree.root.right.right
= new TreeNode(7);
tree.root.left.right.left
= new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.left.right.right
= new TreeNode(9);
tree.postOrderConstantspace(
tree.root);
}
}
|
Python3
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def postOrderConstantspace(root):
if root == None:
return
current = None
prevNode = None
pre = None
ptr = None
netChild = None
prevPtr = None
current = root
while current != None:
if current.left == None:
current.left = prevNode
prevNode = current
current = current.right
else:
pre = current.left
while pre.right != None and pre.right != current:
pre = pre.right
if pre.right == None:
pre.right = current
current = current.left
else:
pre.right = None
print(pre.data, end = " ")
ptr = pre
netChild = pre
prevPtr = pre
while ptr != None:
if ptr.right == netChild:
print(ptr.data, end = " ")
netChild = ptr
prevPtr.left = None
if ptr == current.left:
break
prevPtr = ptr
ptr = ptr.left
prevNode = current
current = current.right
print(prevNode.data, end = " ")
ptr = prevNode
netChild = prevNode
prevPtr = prevNode
while ptr != None:
if ptr.right == netChild:
print(ptr.data, end = " ")
netChild = ptr
prevPtr.left = None
if (ptr == root):
break
prevPtr = ptr
ptr = ptr.left
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
root.right.left = TreeNode(6)
root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
root.left.right.left = TreeNode(8)
root.left.right.right = TreeNode(9)
postOrderConstantspace(root)
|
C#
using System;
class TreeNode{
public int data;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
public string toString()
{
return data + " ";
}
}
class PostOrder{
TreeNode root;
void postOrderConstantspace(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
TreeNode current = null;
TreeNode prevNode = null;
TreeNode pre = null;
TreeNode ptr = null;
TreeNode netChild = null;
TreeNode prevPtr = null;
current = root;
while (current != null)
{
if (current.left == null)
{
current.left = prevNode;
prevNode = current;
current = current.right;
}
else
{
pre = current.left;
while (pre.right != null &&
pre.right != current)
pre = pre.right;
if (pre.right == null)
{
pre.right = current;
current = current.left;
}
else
{
pre.right = null;
Console.Write(pre.data + " ");
ptr = pre;
netChild = pre;
prevPtr = pre;
while (ptr != null)
{
if (ptr.right == netChild)
{
Console.Write(ptr.data + " ");
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr.left = null;
}
if (ptr == current.left)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr.left;
}
prevNode = current;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
Console.Write(prevNode.data + " ");
ptr = prevNode;
netChild = prevNode;
prevPtr = prevNode;
while (ptr != null)
{
if (ptr.right == netChild)
{
Console.Write(ptr.data + " ");
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr.left = null;
}
if (ptr == root)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr.left;
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
PostOrder tree = new PostOrder();
tree.root = new TreeNode(1);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(2);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(3);
tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
tree.root.right.right = new TreeNode(7);
tree.root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.left.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
tree.postOrderConstantspace(tree.root);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class TreeNode
{
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
let root;
function postOrderConstantspace(root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
let current = null;
let prevNode = null;
let pre = null;
let ptr = null;
let netChild = null;
let prevPtr = null;
current = root;
while (current != null)
{
if (current.left == null)
{
current.left = prevNode;
prevNode = current;
current = current.right;
}
else
{
pre = current.left;
while (pre.right != null &&
pre.right != current)
pre = pre.right;
if (pre.right == null)
{
pre.right = current;
current = current.left;
}
else
{
pre.right = null;
document.write(pre.data + " ");
ptr = pre;
netChild = pre;
prevPtr = pre;
while (ptr != null)
{
if (ptr.right == netChild)
{
document.write(ptr.data + " ");
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr.left = null;
}
if (ptr == current.left)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr.left;
}
prevNode = current;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
document.write(prevNode.data + " ");
ptr = prevNode;
netChild = prevNode;
prevPtr = prevNode;
while (ptr != null)
{
if (ptr.right == netChild)
{
document.write(ptr.data + " ");
netChild = ptr;
prevPtr.left = null;
}
if (ptr == root)
break;
prevPtr = ptr;
ptr = ptr.left;
}
}
root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(7);
root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(8);
root.left.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
postOrderConstantspace(root);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...