Pointers vs Array in C++
Last Updated :
07 Aug, 2023
Arrays and pointers are two derived data types in C++ that have a lot in common. In some cases, we can even use pointers in place of arrays. But even though they are so closely related, they are still different entities.
In this article, we will study how the arrays and pointers are different from each other in C++.
What is an Array?
An array is the collection of multiple items of the same type stored in contiguous memory locations. While declaring Arrays, the size should be mentioned and their indexing starts from 0 in C++.
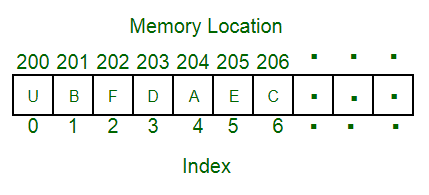
The position of each element can be calculated by adding an offset to the base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array.
Syntax
datatype var_name[size_of_array] = {elements};
Example
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, j;
int a[5];
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
a[i] = i + 1;
}
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
cout << a[j] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|
What are Pointers?
A pointer is the symbolic representation of addresses. It stores the address of variables or memory location. Pointers enable programmers to create and manipulate dynamic data structures. Variables can be of type int, array, char, function, or any other pointer.
Syntax
datatype *var_name;
Example:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 20;
int* ptr;
ptr = &a;
cout << a << " " << ptr <<
" " << *ptr;
return 0;
}
|
Output
20 0x7ffe2ae2d4ec 20
Arrays vs Pointers
The following table list the points that distinguish the arrays and pointers from each other:
|
S. No.
|
Array
|
Pointer
|
|
1.
|
Arrays are declared as type var_name[size]; |
Pointers are declared as type * var_name; |
|
2.
|
Collection of elements of similar data type. |
Store the address of another variable. |
|
3.
|
The array can be initialized at the time of definition. |
Pointers cannot be initialized at definition. |
|
4.
|
The size of the array decides the number of elements it can store. |
The pointer can store the address of only one variable. |
|
5.
|
Arrays are allocated at compile time. |
Pointers are allocated at run-time. |
|
6.
|
Memory allocation is contiguous. |
Memory allocation is random. |
|
7.
|
Arrays are static in nature i.e. they cannot be resized according to the user requirements. |
Pointers are dynamic in nature i.e. memory allocated can be resized later. |
|
8.
|
An array of pointers can be created. |
A pointer to an array can be created. |
Related Articles
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...