Pointers are one of the core components of the C programming language. A pointer can be used to store the memory address of other variables, functions, or even other pointers. The use of pointers allows low-level memory access, dynamic memory allocation, and many other functionality in C.
In this article, we will discuss C pointers in detail, their types, uses, advantages, and disadvantages with examples.
What is a Pointer in C?
A pointer is defined as a derived data type that can store the address of other C variables or a memory location. We can access and manipulate the data stored in that memory location using pointers.
As the pointers in C store the memory addresses, their size is independent of the type of data they are pointing to. This size of pointers in C only depends on the system architecture.
Syntax of C Pointers
The syntax of pointers is similar to the variable declaration in C, but we use the ( * ) dereferencing operator in the pointer declaration.
datatype * ptr;
where
- ptr is the name of the pointer.
- datatype is the type of data it is pointing to.
The above syntax is used to define a pointer to a variable. We can also define pointers to functions, structures, etc.
How to Use Pointers?
The use of pointers in C can be divided into three steps:
- Pointer Declaration
- Pointer Initialization
- Pointer Dereferencing
1. Pointer Declaration
In pointer declaration, we only declare the pointer but do not initialize it. To declare a pointer, we use the ( * ) dereference operator before its name.
Example
int *ptr;
The pointer declared here will point to some random memory address as it is not initialized. Such pointers are called wild pointers.
2. Pointer Initialization
Pointer initialization is the process where we assign some initial value to the pointer variable. We generally use the ( & ) addressof operator to get the memory address of a variable and then store it in the pointer variable.
Example
int var = 10;
int * ptr;
ptr = &var;
We can also declare and initialize the pointer in a single step. This method is called pointer definition as the pointer is declared and initialized at the same time.
Example
int *ptr = &var;
Note: It is recommended that the pointers should always be initialized to some value before starting using it. Otherwise, it may lead to number of errors.
3. Pointer Dereferencing
Dereferencing a pointer is the process of accessing the value stored in the memory address specified in the pointer. We use the same ( * ) dereferencing operator that we used in the pointer declaration.
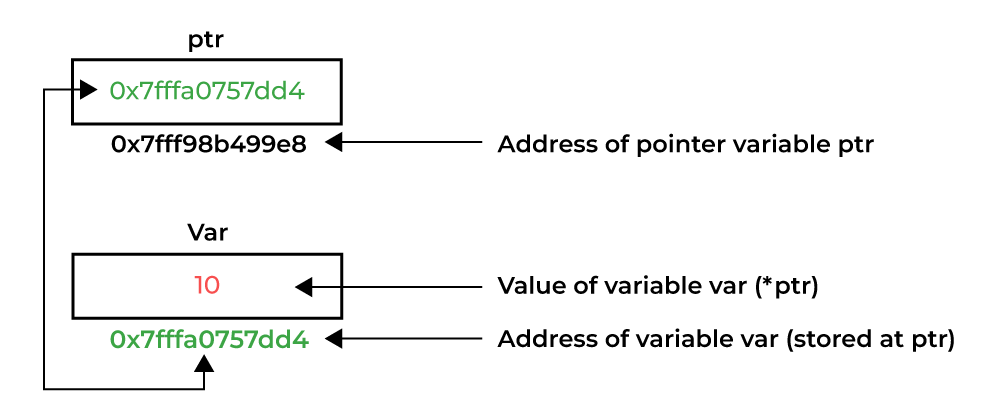
Dereferencing a Pointer in C
C Pointer Example
C
// C program to illustrate Pointers
#include <stdio.h>
void geeks()
{
int var = 10;
// declare pointer variable
int* ptr;
// note that data type of ptr and var must be same
ptr = &var;
// assign the address of a variable to a pointer
printf("Value at ptr = %p \n", ptr);
printf("Value at var = %d \n", var);
printf("Value at *ptr = %d \n", *ptr);
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
geeks();
return 0;
}
Types of Pointers in C
Pointers in C can be classified into many different types based on the parameter on which we are defining their types. If we consider the type of variable stored in the memory location pointed by the pointer, then the pointers can be classified into the following types:
1. Integer Pointers
As the name suggests, these are the pointers that point to the integer values.
Syntax
int *ptr;
These pointers are pronounced as Pointer to Integer.
Similarly, a pointer can point to any primitive data type. It can point also point to derived data types such as arrays and user-defined data types such as structures.
2. Array Pointer
Pointers and Array are closely related to each other. Even the array name is the pointer to its first element. They are also known as Pointer to Arrays. We can create a pointer to an array using the given syntax.
Syntax
char *ptr = &array_name;
Pointer to Arrays exhibits some interesting properties which we discussed later in this article.
3. Structure Pointer
The pointer pointing to the structure type is called Structure Pointer or Pointer to Structure. It can be declared in the same way as we declare the other primitive data types.
Syntax
struct struct_name *ptr;
In C, structure pointers are used in data structures such as linked lists, trees, etc.
4. Function Pointers
Function pointers point to the functions. They are different from the rest of the pointers in the sense that instead of pointing to the data, they point to the code. Let’s consider a function prototype – int func (int, char), the function pointer for this function will be
Syntax
int (*ptr)(int, char);
Note: The syntax of the function pointers changes according to the function prototype.
5. Double Pointers
In C language, we can define a pointer that stores the memory address of another pointer. Such pointers are called double-pointers or pointers-to-pointer. Instead of pointing to a data value, they point to another pointer.
Syntax
datatype ** pointer_name;
Dereferencing Double Pointer
*pointer_name; // get the address stored in the inner level pointer
**pointer_name; // get the value pointed by inner level pointer
Note: In C, we can create multi-level pointers with any number of levels such as – ***ptr3, ****ptr4, ******ptr5 and so on.
6. NULL Pointer
The Null Pointers are those pointers that do not point to any memory location. They can be created by assigning a NULL value to the pointer. A pointer of any type can be assigned the NULL value.
Syntax
data_type *pointer_name = NULL;
or
pointer_name = NULL
It is said to be good practice to assign NULL to the pointers currently not in use.
7. Void Pointer
The Void pointers in C are the pointers of type void. It means that they do not have any associated data type. They are also called generic pointers as they can point to any type and can be typecasted to any type.
Syntax
void * pointer_name;
One of the main properties of void pointers is that they cannot be dereferenced.
8. Wild Pointers
The Wild Pointers are pointers that have not been initialized with something yet. These types of C-pointers can cause problems in our programs and can eventually cause them to crash. If values is updated using wild pointers, they could cause data abort or data corruption.
Example
int *ptr;
char *str;
9. Constant Pointers
In constant pointers, the memory address stored inside the pointer is constant and cannot be modified once it is defined. It will always point to the same memory address.
Syntax
data_type * const pointer_name;
10. Pointer to Constant
The pointers pointing to a constant value that cannot be modified are called pointers to a constant. Here we can only access the data pointed by the pointer, but cannot modify it. Although, we can change the address stored in the pointer to constant.
Syntax
const data_type * pointer_name;
Other Types of Pointers in C:
There are also the following types of pointers available to use in C apart from those specified above:
- Far pointer: A far pointer is typically 32-bit that can access memory outside the current segment.
- Dangling pointer: A pointer pointing to a memory location that has been deleted (or freed) is called a dangling pointer.
- Huge pointer: A huge pointer is 32-bit long containing segment address and offset address.
- Complex pointer: Pointers with multiple levels of indirection.
- Near pointer: Near pointer is used to store 16-bit addresses means within the current segment on a 16-bit machine.
- Normalized pointer: It is a 32-bit pointer, which has as much of its value in the segment register as possible.
- File Pointer: The pointer to a FILE data type is called a stream pointer or a file pointer.
Size of Pointers in C
The size of the pointers in C is equal for every pointer type. The size of the pointer does not depend on the type it is pointing to. It only depends on the operating system and CPU architecture. The size of pointers in C is
- 8 bytes for a 64-bit System
- 4 bytes for a 32-bit System
The reason for the same size is that the pointers store the memory addresses, no matter what type they are. As the space required to store the addresses of the different memory locations is the same, the memory required by one pointer type will be equal to the memory required by other pointer types.
How to find the size of pointers in C?
We can find the size of pointers using the sizeof operator as shown in the following program:
Example: C Program to find the size of different pointer types.
C
// C Program to find the size of different pointers types
#include <stdio.h>
// dummy structure
struct str {
};
// dummy function
void func(int a, int b){};
int main()
{
// dummy variables definitions
int a = 10;
char c = 'G';
struct str x;
// pointer definitions of different types
int* ptr_int = &a;
char* ptr_char = &c;
struct str* ptr_str = &x;
void (*ptr_func)(int, int) = &func;
void* ptr_vn = NULL;
// printing sizes
printf("Size of Integer Pointer \t:\t%d bytes\n",
sizeof(ptr_int));
printf("Size of Character Pointer\t:\t%d bytes\n",
sizeof(ptr_char));
printf("Size of Structure Pointer\t:\t%d bytes\n",
sizeof(ptr_str));
printf("Size of Function Pointer\t:\t%d bytes\n",
sizeof(ptr_func));
printf("Size of NULL Void Pointer\t:\t%d bytes",
sizeof(ptr_vn));
return 0;
}
As we can see, no matter what the type of pointer it is, the size of each and every pointer is the same.
Now, one may wonder that if the size of all the pointers is the same, then why do we need to declare the pointer type in the declaration? The type declaration is needed in the pointer for dereferencing and pointer arithmetic purposes.
C Pointer Arithmetic
The Pointer Arithmetic refers to the legal or valid arithmetic operations that can be performed on a pointer. It is slightly different from the ones that we generally use for mathematical calculations as only a limited set of operations can be performed on pointers. These operations include:
- Increment in a Pointer
- Decrement in a Pointer
- Addition of integer to a pointer
- Subtraction of integer to a pointer
- Subtracting two pointers of the same type
- Comparison of pointers of the same type.
- Assignment of pointers of the same type.
C
// C program to illustrate Pointer Arithmetic
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Declare an array
int v[3] = { 10, 100, 200 };
// Declare pointer variable
int* ptr;
// Assign the address of v[0] to ptr
ptr = v;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// print value at address which is stored in ptr
printf("Value of *ptr = %d\n", *ptr);
// print value of ptr
printf("Value of ptr = %p\n\n", ptr);
// Increment pointer ptr by 1
ptr++;
}
return 0;
}
C Pointers and Arrays
In C programming language, pointers and arrays are closely related. An array name acts like a pointer constant. The value of this pointer constant is the address of the first element. For example, if we have an array named val then val and &val[0] can be used interchangeably.
If we assign this value to a non-constant pointer of the same type, then we can access the elements of the array using this pointer.
Example 1: Accessing Array Elements using Pointer with Array Subscript
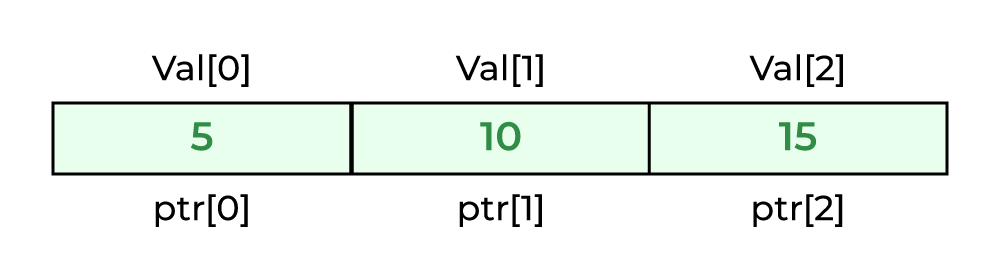
C
// C Program to access array elements using pointer
#include <stdio.h>
void geeks()
{
// Declare an array
int val[3] = { 5, 10, 15 };
// Declare pointer variable
int* ptr;
// Assign address of val[0] to ptr.
// We can use ptr=&val[0];(both are same)
ptr = val;
printf("Elements of the array are: ");
printf("%d, %d, %d", ptr[0], ptr[1], ptr[2]);
return;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
geeks();
return 0;
}
Not only that, as the array elements are stored continuously, we can pointer arithmetic operations such as increment, decrement, addition, and subtraction of integers on pointer to move between array elements.
Example 2: Accessing Array Elements using Pointer Arithmetic
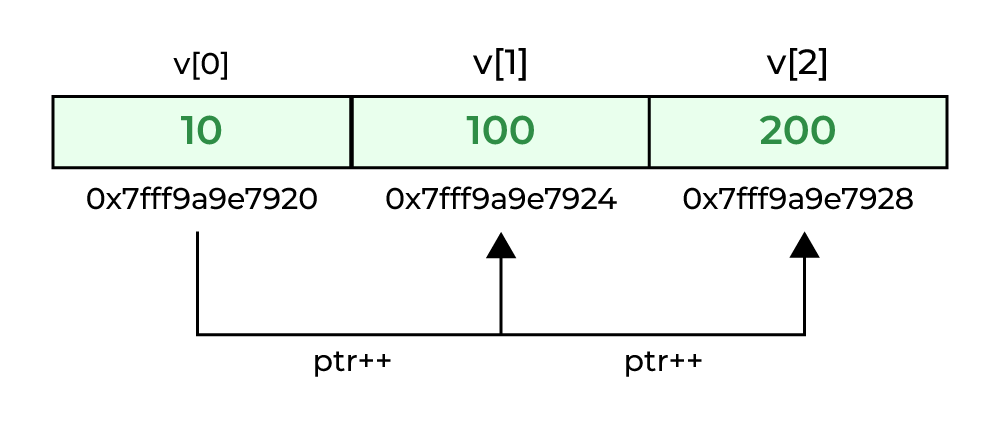
C
// C Program to access array elements using pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// defining array
int arr[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// defining the pointer to array
int* ptr_arr = arr;
// traversing array using pointer arithmetic
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", *ptr_arr++);
}
return 0;
}
This concept is not limited to the one-dimensional array, we can refer to a multidimensional array element as well using pointers.
To know more about pointers to an array, refer to this article – Pointer to an Array
Uses of Pointers in C
The C pointer is a very powerful tool that is widely used in C programming to perform various useful operations. It is used to achieve the following functionalities in C:
- Pass Arguments by Reference
- Accessing Array Elements
- Return Multiple Values from Function
- Dynamic Memory Allocation
- Implementing Data Structures
- In System-Level Programming where memory addresses are useful.
- In locating the exact value at some memory location.
- To avoid compiler confusion for the same variable name.
- To use in Control Tables.
Advantages of Pointers
Following are the major advantages of pointers in C:
- Pointers are used for dynamic memory allocation and deallocation.
- An Array or a structure can be accessed efficiently with pointers
- Pointers are useful for accessing memory locations.
- Pointers are used to form complex data structures such as linked lists, graphs, trees, etc.
- Pointers reduce the length of the program and its execution time as well.
Disadvantages of Pointers
Pointers are vulnerable to errors and have following disadvantages:
- Memory corruption can occur if an incorrect value is provided to pointers.
- Pointers are a little bit complex to understand.
- Pointers are majorly responsible for memory leaks in C.
- Pointers are comparatively slower than variables in C.
- Uninitialized pointers might cause a segmentation fault.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pointers in C are very capable tools and provide C language with its distinguishing features, such as low-level memory access, referencing, etc. But as powerful as they are, they should be used with responsibility as they are one of the most vulnerable parts of the language.
FAQs on Pointers in C
Q1. Define pointers.
Answer:
Pointers are the variables that can store the memory address of another variable.
Q2. What is the difference between a constant pointer and a pointer to a constant?
Answer:
A constant pointer points to the fixed memory location, i.e. we cannot change the memory address stored inside the constant pointer.
On the other hand, the pointer to a constant point to the memory with a constant value.
Q3. What is pointer to pointer?
Answer:
A pointer to a pointer (also known as a double pointer) stores the address of another pointer.
Q4. Does pointer size depends on its type?
Answer:
No, the pointer size does not depend upon its type. It only depends on the operating system and CPU architecture.
Q5. What are the differences between an array and a pointer?
Answer:
The following table list the differences between an array and a pointer:
Pointer
| Array
|
|---|
| A pointer is a derived data type that can store the address of other variables. | An array is a homogeneous collection of items of any type such as int, char, etc. |
| Pointers are allocated at run time. | Arrays are allocated at runtime. |
| The pointer is a single variable. | An array is a collection of variables of the same type. |
| Dynamic in Nature | Static in Nature. |
Q6. Why do we need to specify the type in the pointer declaration?
Answer:
Type specification in pointer declaration helps the compiler in dereferencing and pointer arithmetic operations.
Quizzes:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...